What structure is responsible for controlling the amount of light that enters the eye? Name the two muscles which are involved
The iris.
The circular muscle (inner)
The radial muscle (outer)
Study tip: Know the mechanism of this!
Which branch of the autonomic nervous system has long preganglionic neurons and short postganglionic neurons that are located near effector organs?
The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
Explain the power stroke in cross-bridge cycling. (use the terms actin, myosin, ADP, phosphate group)
The myosin heads are bound to both actin filaments and ADP and a phosphate group. The phosphate group is released, causing power stroke, which pushes the actin to the middle of sarcomere and myosin head in (contraction).
What structure attaches muscle to bone?
Tendon
What does the Amsler grid test for? Explain. (LAB)
Retinal function - specifically that of the macula, the depression near the center of the retina. Patient covers each eye and looks for distortions in the grid.
Name the portion of the brain that is responsible for overall activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
The hypothalamus.
Action potential travels down the T-tubules. What occurs? Include the name of the two receptors involved, and what happens regarding the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
DHP (dihydropyridine) receptors are activated after receiving an action potential. The DHP receptors then activate the ryanodine receptors, which sit on top of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The ryanodine receptor channels are opened, allowing calcium ions to exit the sarcoplasmic reticulum and flow into the muscle cell. This calcium is needed for crossbridge cycling.
Where does the exchange between blood and interstitial fluid occur?
At the capillaries.
What causes astigmatism? Name the main structures involved and explain.
Irregularities on the surface of the cornea or lens cause erratic bending of light waves.
What is the function of the Rinne test? How does it work? Explain. (LAB)
This test differentiates between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Tester uses a tuning fork and places it in different locations. Patient indicates how well they can hear the sound.
BONUS (100 points)... explain the differences between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
What does calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum bind to, allowing cross bridge cycling to occur. Explain.
Calcium binds to troponin proteins, which are located on the actin filaments. The tropomyosin is moved, exposing the myosin-binding sites on the actin.
What is the importance of AV node delay?
To allow the atria to finish contracting.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!! (Get double points for answering this question)
Draw the neural pathway for vision on a whiteboard. Use different colors for info from the right and left visual fields. Label key structures (optic chasm, optic nerve, optic tract, etc.)
Study Tip: know how to draw this quickly on scratch paper in case you get this question on the exam! Know what occurs at the optic chiasm.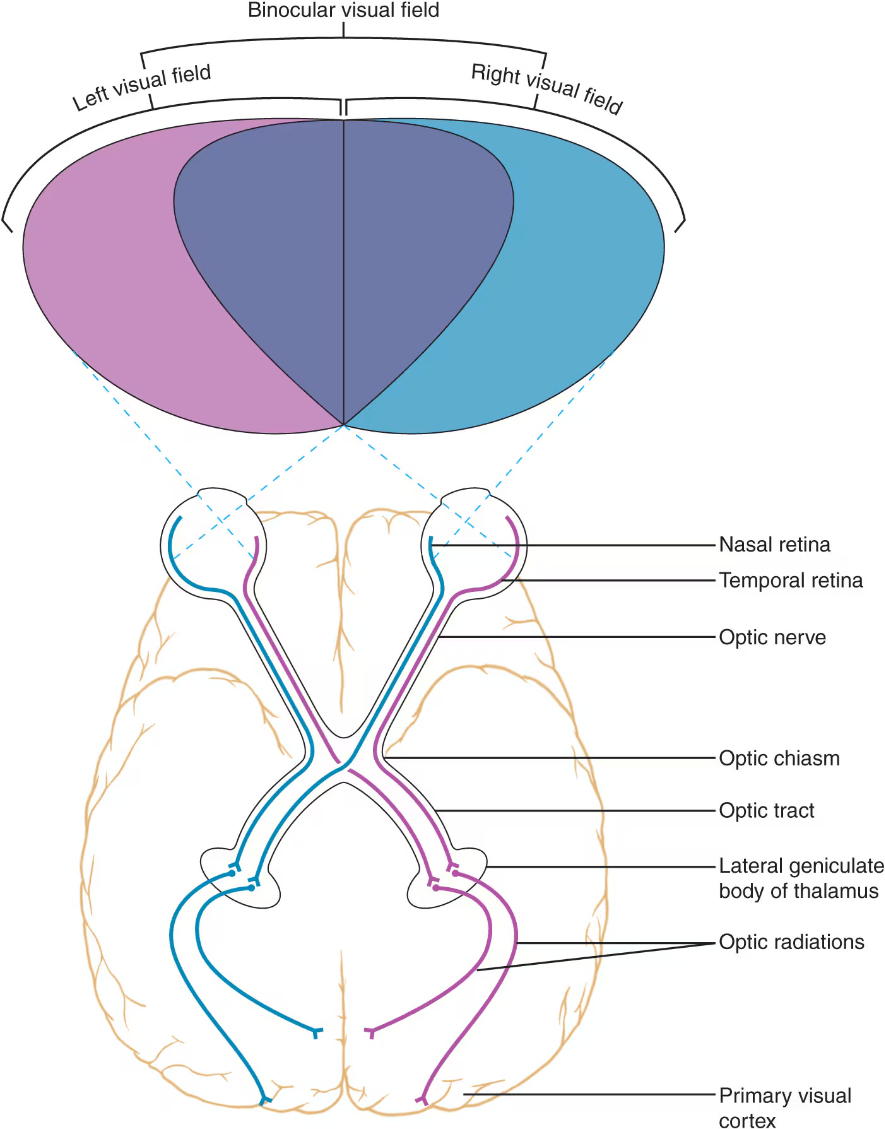
What structure releases neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft in the autonomic nervous system?
Varicosities. This is different than in the somatic nervous system!
DOUBLE JEOPARDY! Get double points for answering the question correctly.
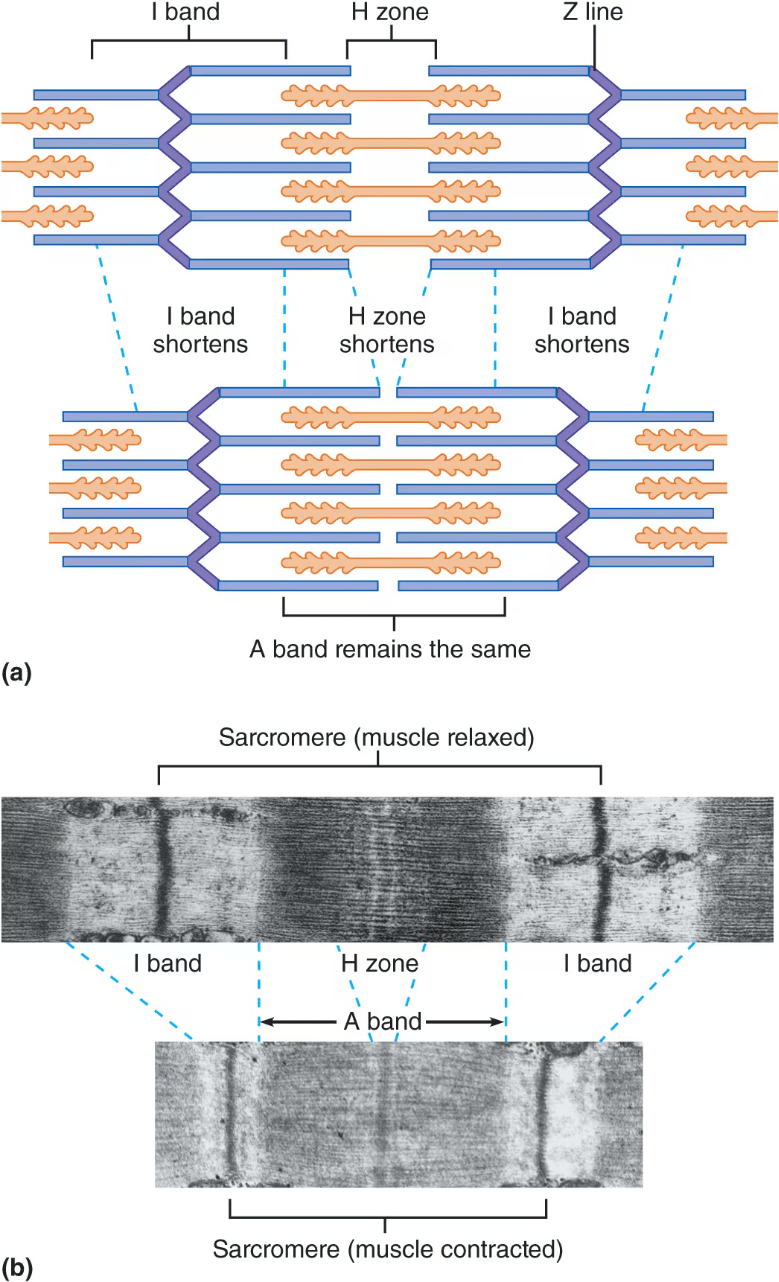
Draw the sarcomere.
Indicate regions that become shorter (or stay the same length) during contraction
For each phase (0-4) of Contractile Cell Action Potential, explain what is happening regarding ion concentrations.