What are the clinical and exam/diagnostic hallmarks of Atrial Fibrillation?
Clinical: Palpitations, tachycardia, SOB, dizziness, fatigue
Diagnostic: “Irregularly irregular rhythm”, absent P waves
Which structure normally initiates the cardiac electrical impulse and determines the intrinsic heart rate?
A. Atrioventricular node
B. Bundle of His
C. Sinoatrial node
D. Purkinje fibers
C. Sinoatrial node
An EKG shows distinct P waves before every QRS complex with regular R–R intervals. Which rhythm is most consistent with this tracing?
A. Atrial fibrillation
B. Normal sinus rhythm
C. Atrial flutter
D. Multifocal atrial tachycardia
B. Normal sinus rhythm
Why would Holter monitoring be preferred over a standard 12-lead EKG in a patient like Claire?
Holter monitoring is preferred because it continuously records heart rhythm over hours to days, allowing detection of intermittent arrhythmias that may be missed during the brief snapshot of a standard 12-lead EKG.
Diltiazem lowers ventricular rate in AF primarily by:
A. Blocking L-type Ca²⁺ channels in AV nodal tissue
B. Blocking factor Xa
C. Increasing sodium influx in atrial tissue
D. Blocking potassium channels to prolong repolarization
A. Blocking L-type Ca²⁺ channels in AV nodal tissue
In Atrial Fibrillation, which two structures are ectopic foci typically found in?
Left atrium and Pulmonary Veins
Which property of the AV node is most responsible for allowing adequate ventricular filling during the cardiac cycle?
A. Faster conduction velocity than the SA node
B. Slower conduction velocity than the SA node
C. Direct conduction to the Purkinje fibers
D. Ability to generate impulses faster than the SA node
B. Slower conduction velocity than the SA node
Which EKG feature best describes the ventricular rhythm in atrial fibrillation?
A. Regular with fixed R–R intervals
B. Regular with intermittent pauses
C. Irregularly irregular R–R intervals
D. Progressive PR interval prolongation
C. Irregularly irregular R–R intervals
What is the primary purpose of the CHA₂DS₂-VASc score?
A. To diagnose atrial fibrillation
B. To estimate bleeding risk from anticoagulation
C. To estimate annual stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation
D. To decide which rate-control medication to use
C. To estimate annual stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation
Why would digoxin be a poor standalone choice for an avid cyclist like Claire?
A. Causes QT prolongation
B. Ineffective during sympathetic activation
C. Causes hypertension
D. Contraindicated in AFib
B. Ineffective during sympathetic activation
A 50 y/o patient with atrial fibrillation develops shortness of breath and fatigue. Which pathophysiologic mechanism best explains these symptoms?
A. Increased ventricular filling due to loss of atrial kick
B. Compression of pulmonary circuit
C. Rapid right-sided ventricular contraction
D. Impaired ventricular filling due to ineffective atrial contraction
E. Ineffective atrial contraction due to dilation of heart chamber
D. Impaired ventricular filling due to ineffective atrial contraction
A patient has normal P waves preceding each QRS complex, consistent R-R intervals, and a heart rate of 72 bpm. Which additional finding is REQUIRED to define normal sinus rhythm?
A. Wide QRS complexes (>120 ms)
B. Absence of atrial depolarization
C. PR interval between 120–200 ms
D. Ventricular rate greater than atrial rate
C. PR interval between 120–200 ms
Shown below is an EKG rhythm strip. Compared to normal sinus rhythm, which finding visible on this tracing most directly indicates loss of coordinated atrial depolarization?
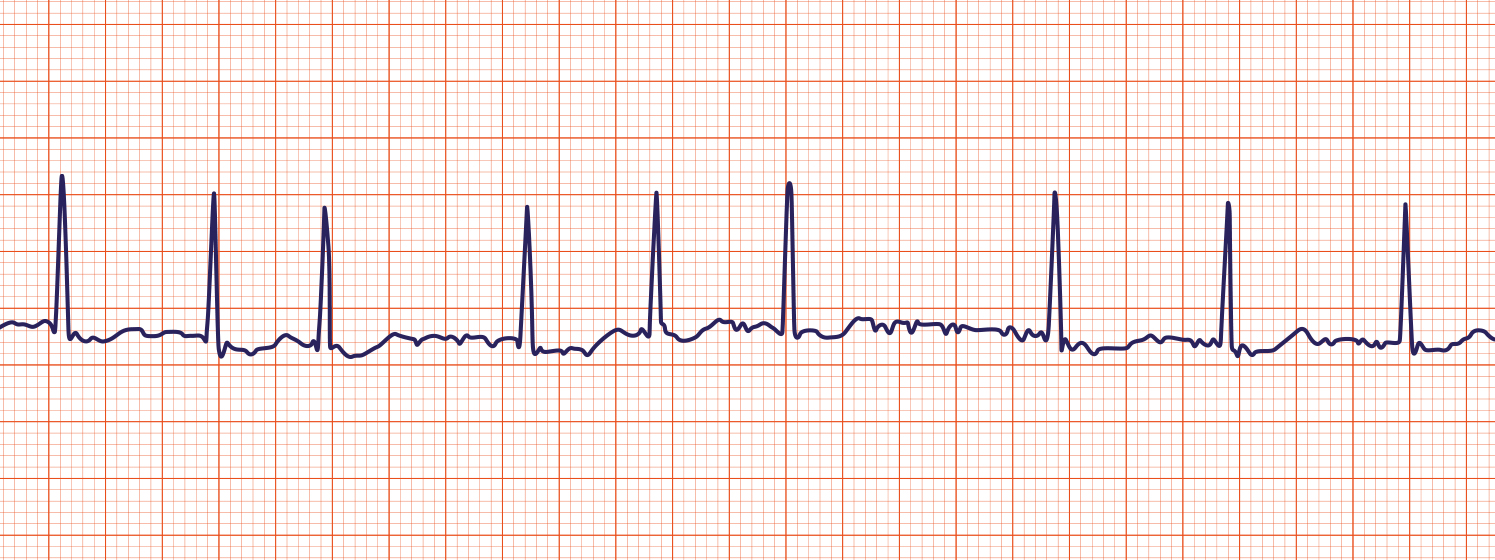
A. Narrow QRS complexes
B. Absence of discrete P waves before each QRS complex
C. Presence of T waves following each QRS complex
D. Ventricular depolarization occurring at a slower rate than atrial activity
B. Absence of discrete P waves before each QRS complex
Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation is most commonly performed by creating lesions at which anatomical location?
A. Atrioventricular node
B. Right atrial appendage
C. Pulmonary vein ostia
D. Interventricular septum
C. Pulmonary vein ostia
The main reason apixaban is prescribed in atrial fibrillation patients is to prevent this complication.
A. Ventricular tachycardia
B. Heart failure
C. Embolic stroke
D. Myocardial infarction
C. Embolic stroke
Which of the following mechanisms most directly explains a high-risk complication in atrial fibrillation?
A. Mitral Stenosis: Fibrosis of the mitral valve due to structural remodeling
B. Ventricular Tachycardia: Rapid depolarization originating from ectopic foci in the vetricles
C. Thromboembolism Stroke: Blood clotting in the left atrium due to ineffective atrial contraction, propagating to the brain
D. Coronary Artery Disease: Compression of coronary arteries from atrial enlargement
E. Congestive Heart Failure: Embolization of plaque from the coronary arteries
C. Thromboembolism Stroke: Blood clotting in the left atrium due to ineffective atrial contraction
A long-distance endurance athlete has a resting heart rate of 52 bpm but otherwise normal EKG findings. Which mechanism best explains this resting bradycardia according to normal cardiac physiology?
A. Decreased intrinsic firing rate of the SA node
B. Increased parasympathetic (vagal) tone on the SA node
C. Increased AV nodal conduction velocity
D. Failure of sympathetic innervation of the ventricles
B. Increased parasympathetic (vagal) tone on the SA node
Shown below is an EKG rhythm strip. The irregular baseline oscillations seen between QRS complexes represent what type of atrial electrical activity?
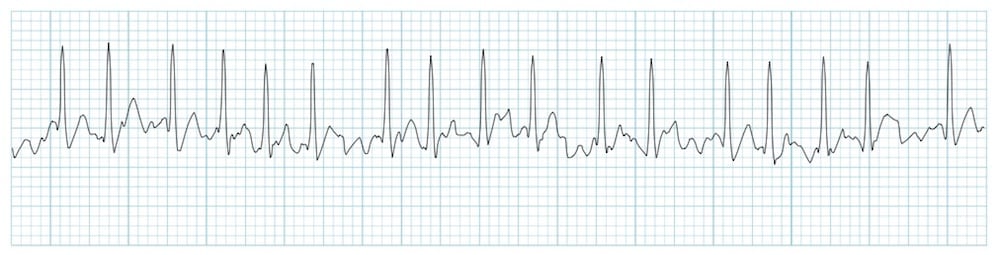
A. Organized atrial depolarization producing P waves
B. Ventricular repolarization during the T wave
C. Chaotic fibrillatory atrial electrical activity
D. AV nodal escape rhythm
C. Chaotic fibrillatory atrial electrical activity
In the workup of atrial fibrillation, which imaging study is used to evaluate overall cardiac structure and function?
A. TEE
B. TTE
C. Holter monitor
D. Cardiac MRI
B. TTE
Which effect is NOT a direct result of diltiazem’s mechanism of action?
A. Negative dromotropic effect
B. Negative chronotropic effect
C. Restoration of coordinated atrial contraction
D. Slowing conduction through the AV node
C. Restoration of coordinated atrial contraction
You’re a first-year medical student treating a patient with chronic history of atrial fibrillation. Their EKG is described as “irregularly irregular.” Which of the following best directly explains the underlying mechanism behind AFib’s “irregularly irregular” rhythm?
A. Irregular R-R intervals
B. Irregular circuits within the right atria rapidly firing
C. Chaotic atrial depolarization with variable AV nodal conduction to the ventricles
D. Chaotic ventricular depolarization resulting in irregular R-R intervals
E. Ineffective atrial contraction resulting in out of sync ventricular contraction
C. Chaotic atrial depolarization with variable AV nodal conduction to the ventricles
In atrial fibrillation, ventricular rate becomes irregular despite an intact conduction system. Which component normally prevents the ventricles from depolarizing at the same rate as chaotic atrial impulses?
A. SA node automaticity
B. Bachmann’s bundle
C. AV node refractory properties
D. Purkinje fiber synchronization
C. AV node refractory properties
A patient undergoes EKG monitoring for intermittent palpitations. The tracing shows narrow QRS complexes and atrial electrical activity between QRS complexes. There are no normal sinus P waves, and atrial activity is present throughout the baseline. However, the atrial activity appears uniform and repetitive, producing a consistent pattern rather than chaotic oscillations.
Which of the following EKG findings most strongly supports atrial flutter rather than atrial fibrillation?
A. Regular, repeating atrial electrical activity
B. Narrow QRS complexes
C. Absence of discrete P waves
D. Presence of atrial activity between QRS complexes
A. Regular, repeating atrial electrical activity
Direct current cardioversion terminates atrial fibrillation by delivering a shock that is synchronized to which wave?
R Wave
Name the class and a key contraindication of Flecainide:
Class: 1C Antiarrhythmic
Contraindications: Ischemia, Prior Myocardial Infarction, Active Coronary Artery Disease