Rigid layer that provides protection for plant cells.
Cell Wall
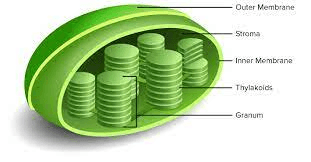 Found only in PLANT cells. Its purpose is photosynthesis.
Found only in PLANT cells. Its purpose is photosynthesis.
Chloroplast.
Complex organelles that convert energy from food into a form that the cell can use.
Mitochondria
This organelle in a cell is semipermeable. It regulates the flow of nutrients
cell membrane
Fluid that fills up the space inside the cell.
Cytoplasm
Protective phospholipid layer ALL cells have
Cell Membrane
This type of cell has a cell wall, a large central vacuole and chloroplasts
plant cell
These cells in plants form structure that carry water
xylem cells
Makes Protein; ALL cells have these
Ribosome
Serves as the cell’s command center, sending directions to the cell to grow, mature, divide, or die. It also houses DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the cell’s hereditary material.
Nucleus
Specialized cells in brain that carry impulses are called
neurons
Disc shaped cells that carry oxygen
blood cells
This is the pigment present in plants
chlorophyll
This is the recycling center of the cell. They digest foreign bacteria that invade the cell, rid the cell of toxic substances, and recycle worn-out cell components.
Lysosomes
How is transfer of nutrient affected if surface area to volume ratio of cells decrease.
Nutrient transfer reduces.
Stores food, water, and waste; extra large in plant cells
Vacuole
This function is performed by all cells to get energy
cellular respiration
Packages molecules processed by the endoplasmic reticulum to be transported out of the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
A tool used to view cells.
Microscope
These compounds are products of photosynthesis
sugar and oxygen
These are the energy molecules in the cell
ATP
This is the first step of cellular respiration where sugar is broken into smaller molecules
glycolysis
What are the two steps of photsynthesis
energy capture to break water molecule
Making sugar using hydrogen from water.
Give the equation of photsynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O