Water is carried up from the roots in this
Xylem
Tissue with thin-walled cells with interconnecting air spaces between them
Aerenchyma tissue
Identify tissue B
Intercalary meristematic tissue
This is an opening in the dermal tissue of a leaf that allows for gas exchange.
Stomata
The most abundant of all pigments; it's why leaves are green except in autumn
Chlorophyll
Xylem fibers are composed of this type of cell
Sclerenchyma
Identify the plant tissue
Fibers ( Sclerenchyma)
At what age do plants stop growing?
They never stop growing
A waxy secretion land plants have developed to aid in the prevention of water loss
Cuticle
Requires Sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water
Photosynthesis
Phloem carries _________ in which direction?
Food , Bi/ All directions
Ground tissue is primarily made of this kind of tissue
Parenchyma
Which meristem is being cut in this onion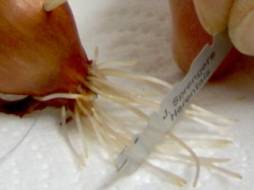
Root apical meristem
Fatty substance in the walls of cork cells
Suberin
The process that involves the loss of water through the plant's leaves
Transpiration
Sugars are transported to these storage organs
Fruits and roots
Plant cell walls (non-woody) contain this important component that is unique to plants
Cellulose
Meristems grow by the process of this
Cell division (mitosis)
Common name given to this tissue
Bark
Occurs to enable plants to make more plants
Reproduction
Identify the Cell types shown
Sieve tubes and Companion cells
Identify the type of plant tissue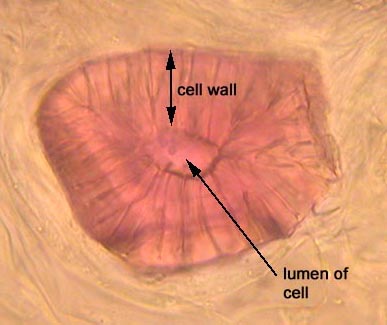
Sclerenchyma (Sclereid)
Which meristematic tissue regenerates plant branches lost by grazers?
Intercalary meristematic tissue
Where is cuticle absent in a plant? (2 regions)
Stomata and Roots
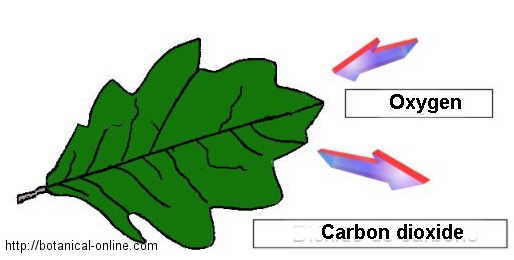
Respiration in Plants