This green pigment absorbs light energy required for photosynthesis.
What is chlorophyll?
These structures anchor the plant and absorb water and mineral ions from the soil.
What are the roots?
These tiny holes on the underside of the leaf allow for gas exchange.
What are stomata?
The movement of water from the roots, up the stem, and out of the leaves.
What is transpiration?
These cells have a long projection to increase surface area for water absorption.
What are root hair cells?
In the word equation for photosynthesis, these are the two reactants.
Carbon Dioxide and Water?
This part of the plant holds leaves up to the light and contains transport tubes.
What is the stem?
This transparent, waxy layer sits at the very top of the leaf to reduce water loss.
What is the waxy cuticle?
The process by which dissolved sugars (food) are moved through the plant.
What is translocation?
These two cells surround the stomata and control their opening and closing.
What are guard cells?
Because photosynthesis takes in energy from the surroundings, it is described as this type of reaction.
What is an endothermic reaction?
These are the reproductive organs of the plant, often brightly colored to attract insects.
What are flowers?
Cell organelles found in greater concentration in the cells near the surface of leaves.
What are chloroplasts?
Water moves into the root hair cells from the soil via this process.
What is osmosis?
These dead, hollow cells form a continuous tube to transport water.
What is xylem?
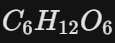 The substance produced during photosynthesis.
The substance produced during photosynthesis.
What is glucose?
A section of the root where cells reproduce asexually so that the roots can grow longer.
What is the root tip?
The single layer of cells at the surface and the underside of the leaf.
Mineral ions move from the soil into the roots against the concentration gradient using this process.
What is active transport?
These living cells transport sugars and have pores in their end walls called sieve plates.
What are phloem cells?
To store the glucose made during photosynthesis, plants convert it into this insoluble substance.
What is starch?
The top of the stem where asexual reproduction leads to growth.
What is the terminal bud?
This layer of the leaf contains air spaces to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse to the cells.
What is the spongy mesophyll?
A deficiency in this specific mineral ion causes chlorosis (yellow leaves) because the plant cannot make chlorophyll.
What is Magnesium?
Phloem sieve tubes lack a nucleus, so they rely on these attached cells to provide energy for transport.
What are companion cells?