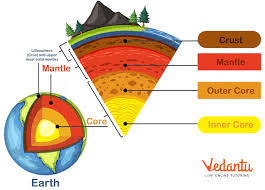
Name the 4 layers of the Earth's Interior
Crust, mantle, inner core, outer core
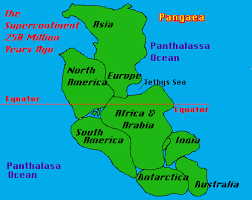
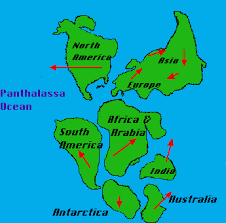
What do we call the single huge continent that scientists think existed long ago?
Pangea
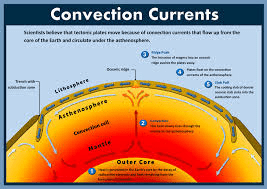
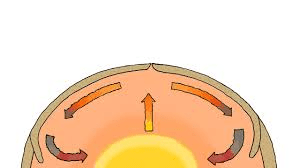
What is the flow of warm rock rising and cool rock sinking inside Earth called?
Convection Currents
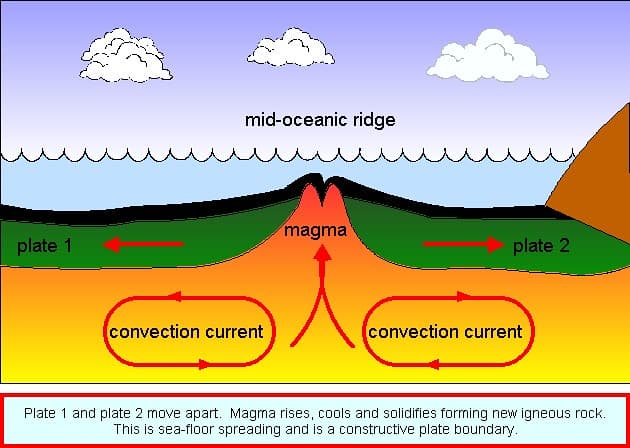
What happens at the mid-ocean ridge where new ocean floor forms?
New rock (lava) comes up and makes new ocean floor
What do we call the edges where two tectonic plates meet?
Plate boundary (or plate edge)
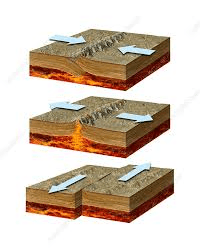
Which layer of Earth is mostly made of liquid iron and nickel and helps create Earth's magnetic field?
Outer Core
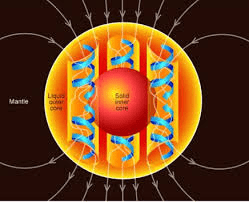
Name one piece of evidence scientists use to show that continents used to fit together.
Matching coastlines (shapes), similar fossils, or similar rocks on different continents
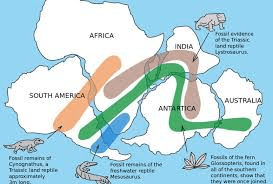
Do convection currents occur in the mantle or the crust?
Mantle
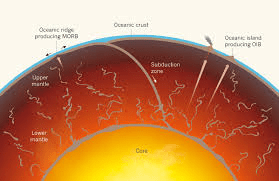
When new rock forms at the mid-ocean ridge, does it move away from or toward the ridge?
It moves away from the ridge

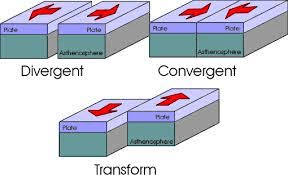
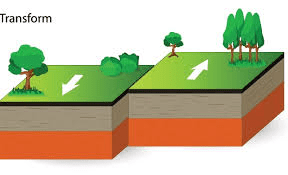
Name the three main types of plate boundaries.
Divergent, convergent, transform
DAILY DOUBLE
The solid rock layer that we live on is called the what?
The crust
If the continents were once joined, what happened to make them move apart?
The plates moved apart over millions of years because of plate motions driven by the mantle
How do convection currents help move tectonic plates?
Warm rock rises and pushes plates; cool rock sinks pulling plates — this movement causes plates to move
How does seafloor spreading help prove that continents move?
It shows new rock forming and pushing old rock away, which helps move continents apart
At which type of boundary do plates slide past each other and can cause earthquakes?
Transform Boundary
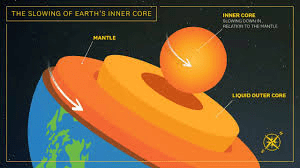
Which layer is the hottest part of Earth?
Inner Core
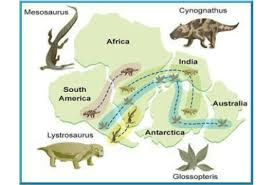
How could fossils help scientists know that continents were once connected?
Same fossils of plants or animals found on continents now far apart suggest they were once joined
DAILY DOUBLE!
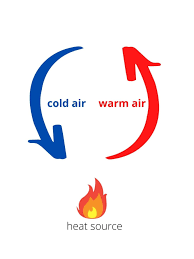
If rock in the mantle heats up, does it become more or less dense? What happens next?
It becomes less dense and rises; then it cools and sinks again
What happens to the oldest ocean crust: does it stay at the ridge or move farther away? Bonus 100 if you can name which layer of the earth it goes back into!
It moves farther away from the ridge and becomes older and or it goes back down the trenches to the mantle
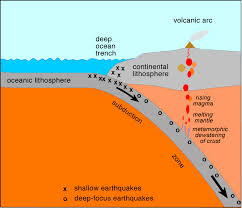
What happens at a convergent boundary when one plate goes under another?
Subduction
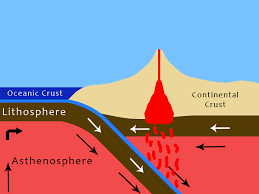
Explain why the mantle is important for moving plates.
The mantle flows slowly and its movement (convection) pushes plates above it. or Something like this or about convection currents is acceptable.
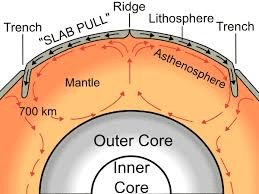
describe one map detail that would help prove Pangea existed.
matching puzzle-like coastlines or matching fossil locations across continents
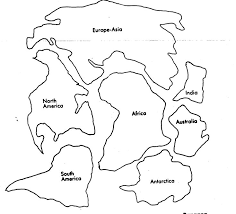
Give a short real-world example of convection currents
Example: boiling soup where warm soup rises from the bottom and cools at the top, similar to mantle rock circulation
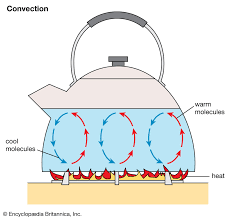
Describe why rocks near a mid-ocean ridge are younger than rocks far away from the ridge.
Because new rock continually forms at the ridge, the youngest rocks are near the ridge and older rocks are farther away
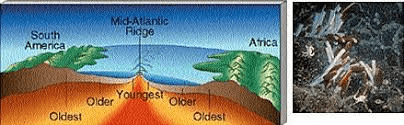
Give a short explanation of what happens at a divergent boundary and name one place on Earth where this happens
At a divergent boundary plates move apart and new crust forms (example: mid-ocean ridge)
