Water "sticks" to other water molecules because of this property of water.
What is cohesion?
This stage of the water cycle happens as a result of the Sun's energy.
What is evaporation?
 This macromolecule is made up of simple sugars and provides quick energy for the body.
This macromolecule is made up of simple sugars and provides quick energy for the body.
What is a carbohydrate?
This theory states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and all cells come from preexisting cells
What is the cell theory?
 DNA has this well-known shape made up of two strands twisted around each other.
DNA has this well-known shape made up of two strands twisted around each other.
What is a double helix?
Ice floats on top of water because of this property of water.
What is expansion upon freezing?
Plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through this process.
What is photosynthesis?
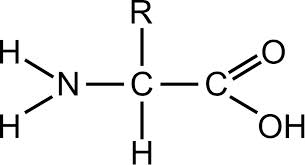 Amino acids are the monomers that make up this type of macromolecule. Two functions of this macromolecule are digestive enzymes and transportation of molecules across the cell membrane.
Amino acids are the monomers that make up this type of macromolecule. Two functions of this macromolecule are digestive enzymes and transportation of molecules across the cell membrane.
What is a protein?
These simple cells do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
What are prokaryotic cells?
A DNA nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a nitrogen base, and this type of five-sided sugar.
What is deoxyribose?
Water is ______ because it has a negative oxygen side and a positive hydrogen side.
What is polar?
Consumers and decomposers release carbon by this process.
What is cell respiration?
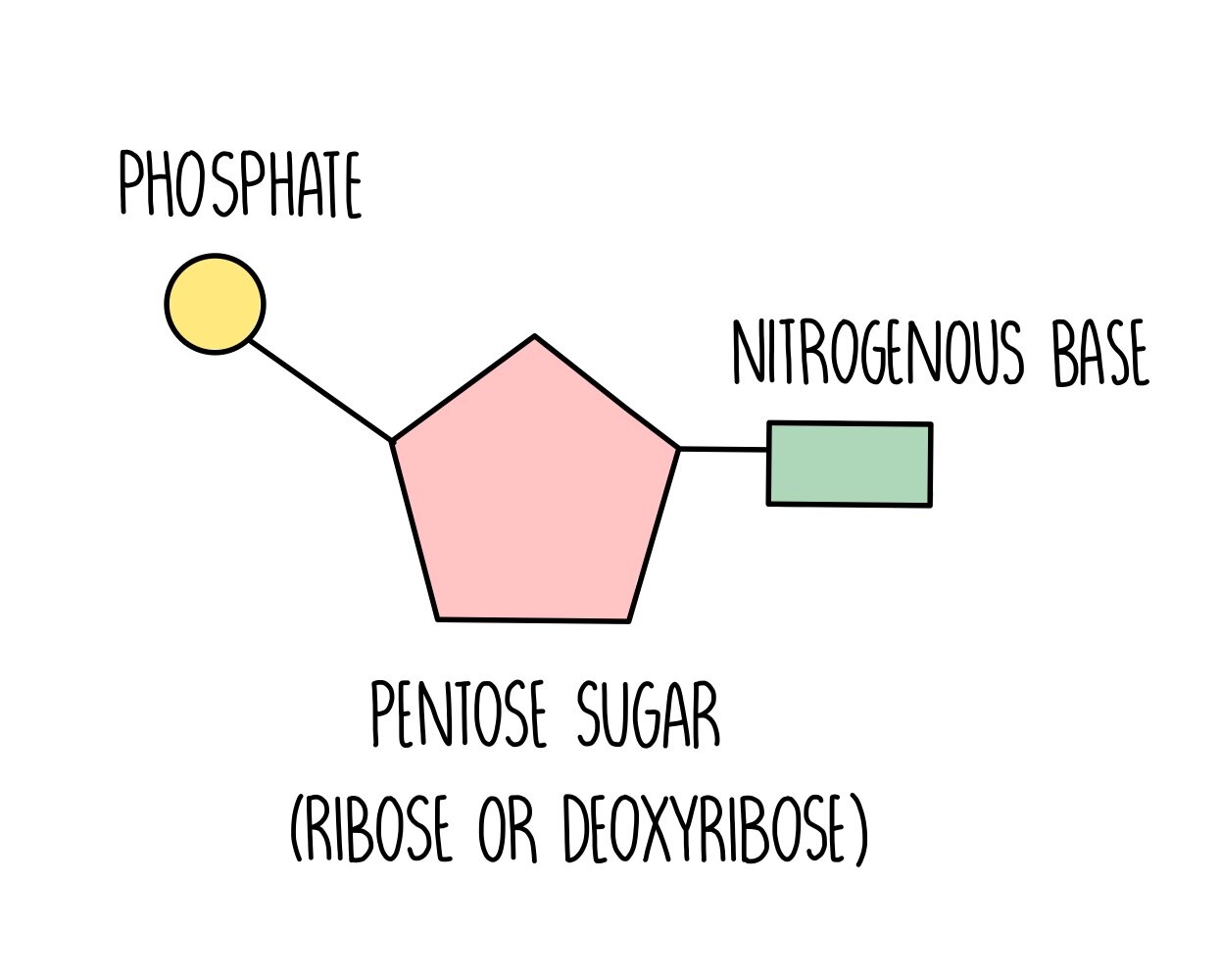 This macromolecule stores genetic information in all living organisms.
This macromolecule stores genetic information in all living organisms.
What is a nucleic acid?
This organelle acts as the cell’s “powerhouse” by producing energy in the form of ATP. These are found in both plant and animal cells.
What is the mitochondrion?
 These four nitrogen bases make up the “rungs” of the DNA ladder. (Do your best to pronounce these.)
These four nitrogen bases make up the “rungs” of the DNA ladder. (Do your best to pronounce these.)
What are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine?
Less dense things, like a paperclip or a flower petal, may rest on the surface of the water because of this property of water.
What is surface tension/cohesion?
Living things cannot use the nitrogen gas in our atmosphere because of their strong _____ _______.
What is a chemical bond OR triple bond?
This macromolecule has two main functions: long-term energy storage and being part of the cell membrane.
What is a lipid?
This organelle, found in plant but not animal cells, converts sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
What is the chloroplast?
During DNA replication, this enzyme is responsible for adding complementary nucleotides to form new DNA strands.
What is DNA polymerase?
Coastal cities (like Jacksonville) experience greater temperature fluctuations compared to inland cities (like Lake City) because of this property of water.
What is high specific heat capacity OR temperature moderation?
In the nitrogen cycle, this process carried out by specialized bacteria converts ammonium (NH₄⁺) into nitrates (NO₃⁻), which plants can then absorb and use.
What is nitrification?
Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering this energy barrier.
What is activation energy?
This network of folded membranes helps modify and transport proteins made by ribosomes. These are found in both plant and animal cells.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
If one DNA strand has the sequence A–T–G–C–A, the complementary strand will read like this:
(Remember: Apples fall from Trees; Cars go in Garages.)
What is T–A–C–G–T?