The subatomic particle is responsible for electricity?
What is the electron?
"Every object retains its state of rest or state of uniform straight line motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force"
What is Newton's First Law?
The scientific units for weight.
What is a Newton?
An objects tendency to stay in motion or at rest
What is inertia
300, 000, 000 m/s in a vacuum
What is the speed of light?
What is Gravity/Friction/Tension?
The boson responsible for beta decay
What is the W boson
The findings from this experiment supported Einstein's first postulate and addressed a misconception of Huygen's model of light.
What is the Michelson-Morley experiment.
 What does the negative portion of this Velocity/Time graph show?
What does the negative portion of this Velocity/Time graph show?
The object is traveling West/Left/Negative direction and speeding up.
When the vertical velocity an object has when reaching the peak of it trajectory while in free-fall.
What is zero?
The force that counters the electric force in the nucleus of an atom.
What is the Strong Nuclear Force?
The total energy of a satellite with mass = 500 orbiting at an altitude of 1200km above Earth?
What is -1.32 x 10^10 J
The phenomena responsible for the observed pattern
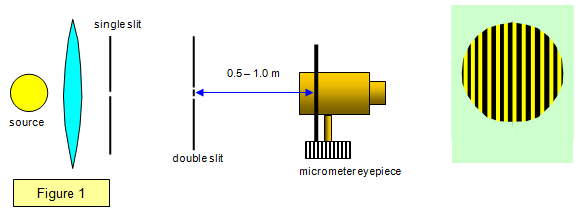
What is diffraction and interference.
This determines if the frequency of a wave emitted will appear to be higher or lower to an observer compared to the original frequency.
What is the Doppler Effect?
The scientist responsible for providing the planetary model of the atom.
Who is Rutherford?
The intensity of light after it passes through the polariser.

What is 50%.
The chronological order of the models of the atom following Dalton.
What is Thomson's Plum-pudding, Rutherford's Planetary, Bohr's and Electron Cloud?
The range achieved by a ball launched with a velocity of 10 m/s at an angle of 30 degrees above the horizontal. The ball starts and finishes at the same height.
What is s = 8.83 m
The names of the primary methods of energy production at positions A, B and D.
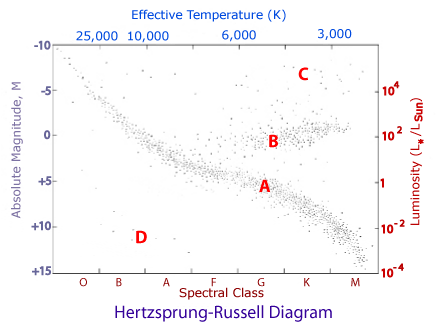
What is p-p chain, Triple alpha and nothing.
The threshold frequency of a material that has a work function of 10eV.
What is 2.5 x 10^15 Hz
The temperature of a star emitting a peak frequency of 5.45 x 10^14 Hz.
What is 5265 K