A patient is ordered 250mg PO. Available is 125mg/5mL. Calculate the dose mLs.
What is 10 mL?
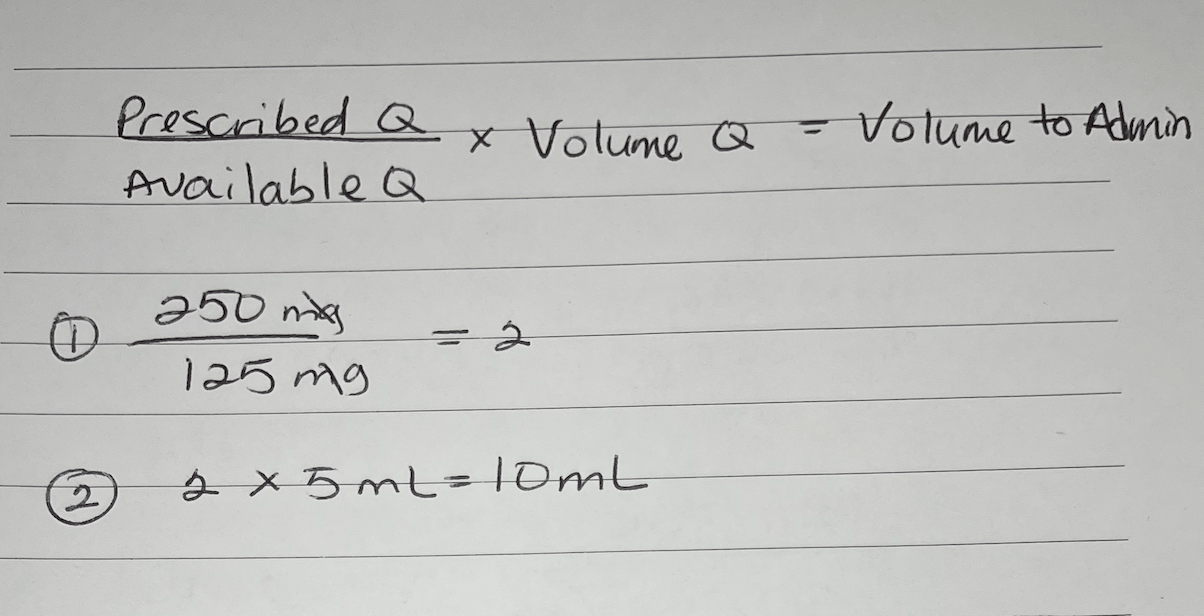
This is the normal lab value range for Potassium.
What is 3.5 to 5.3 mEq/L?
A pH below 7.35 is classified as this.
What is acidosis?
Priority assessment for a patient with a sodium level of 120 mEq/L.
What is neurological status?
First intervention for a patient with respiratory alkalosis due to anxiety.
What is slow, deep breathing?
Convert 44 lbs to kg.
What is 20 kg?
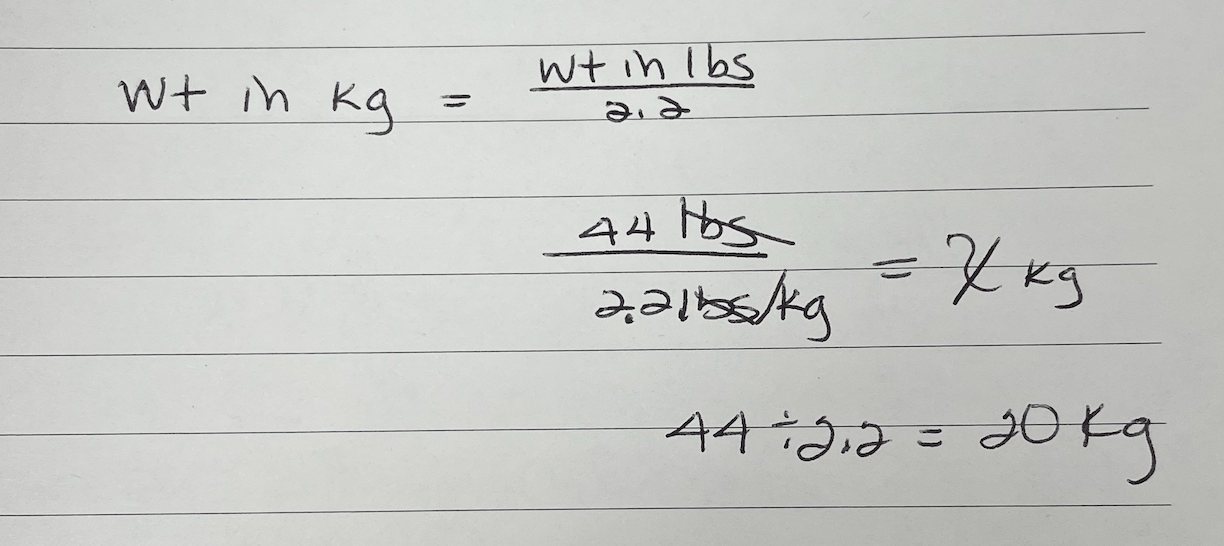
Trousseau’s and Chvostek’s signs indicate a deficit in this ion.
What is calcium?
This organ regulates pH by excreting or retaining bicarbonate.
What is the kidneys?
Best action for a client with a potassium level of 6.2 mEq/L.
What is place on the cardiac monitor?
Manifestation often seen in metabolic acidosis (Kussmaul's).
What is deep, rapid respirations?
Ordered: 0.1g. Available: 50mg tablets. Calculate dose in tablets.
What is 2 tablets?
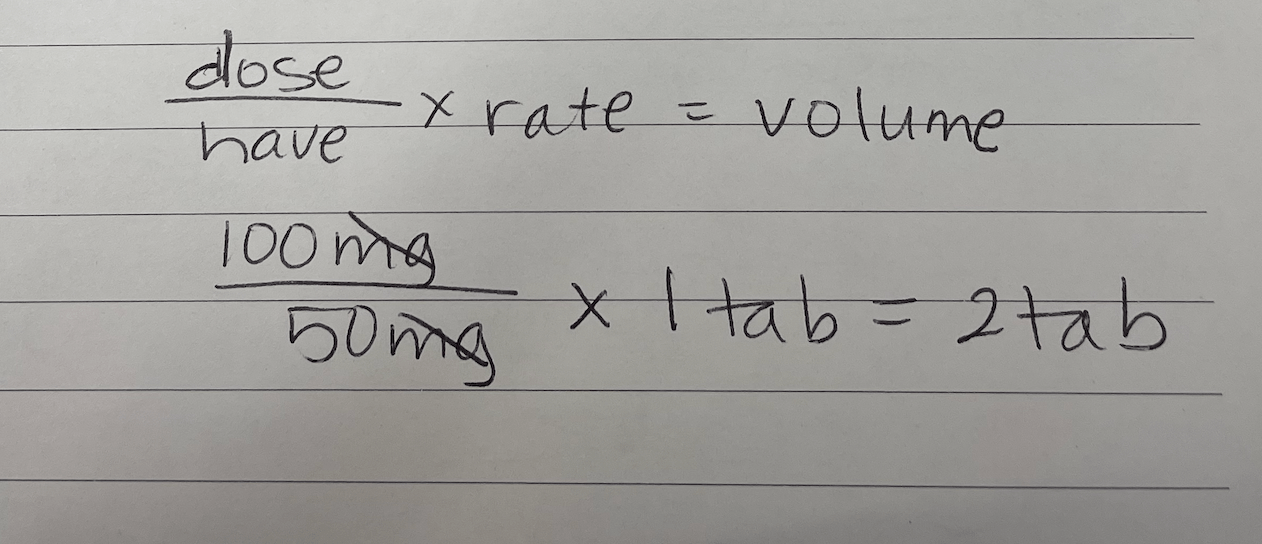
A major intracellular cation responsible for cardiac function.
What is potassium (K+)?
ABG results: pH 7.32, PaCO2 50, HCO3 24. State the condition.
What is Respiratory Acidosis?
Manifestation of Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD) in the elderly.
What is the confusion?
Nursing action for metabolic alkalosis caused by vomiting.
What is administer IV fluids/replace electrolytes?
Ordered: 4 mg/kg. Patient weight: 60 kg. Available: 40 mg/mL. Calculate dose in mL.
What is 6 mL?
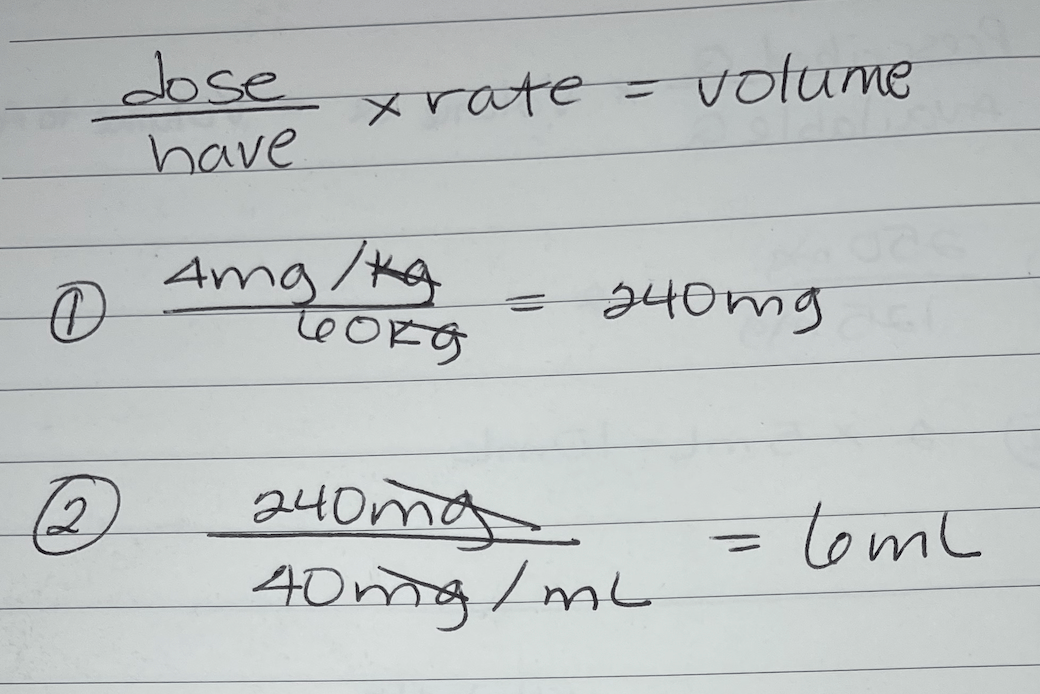
This condition is characterized by a serum sodium above 145 mEq/L.
What is hypernatremia?
This process is the body’s attempt to return pH to normal.
What is compensation?
This only IV solution is used to prime tubing for blood transfusions.
What is 0.9% Normal Saline?
Priority nursing care for a patient with metabolic acidosis.
What is monitor for dysrhythmias (hyperkalemia)?
Drip rate for 1000mL over 8 hours with drop factor of 15 gtt/mL. Calculate gtt/min.
What is 31 gtt/min (approx)?
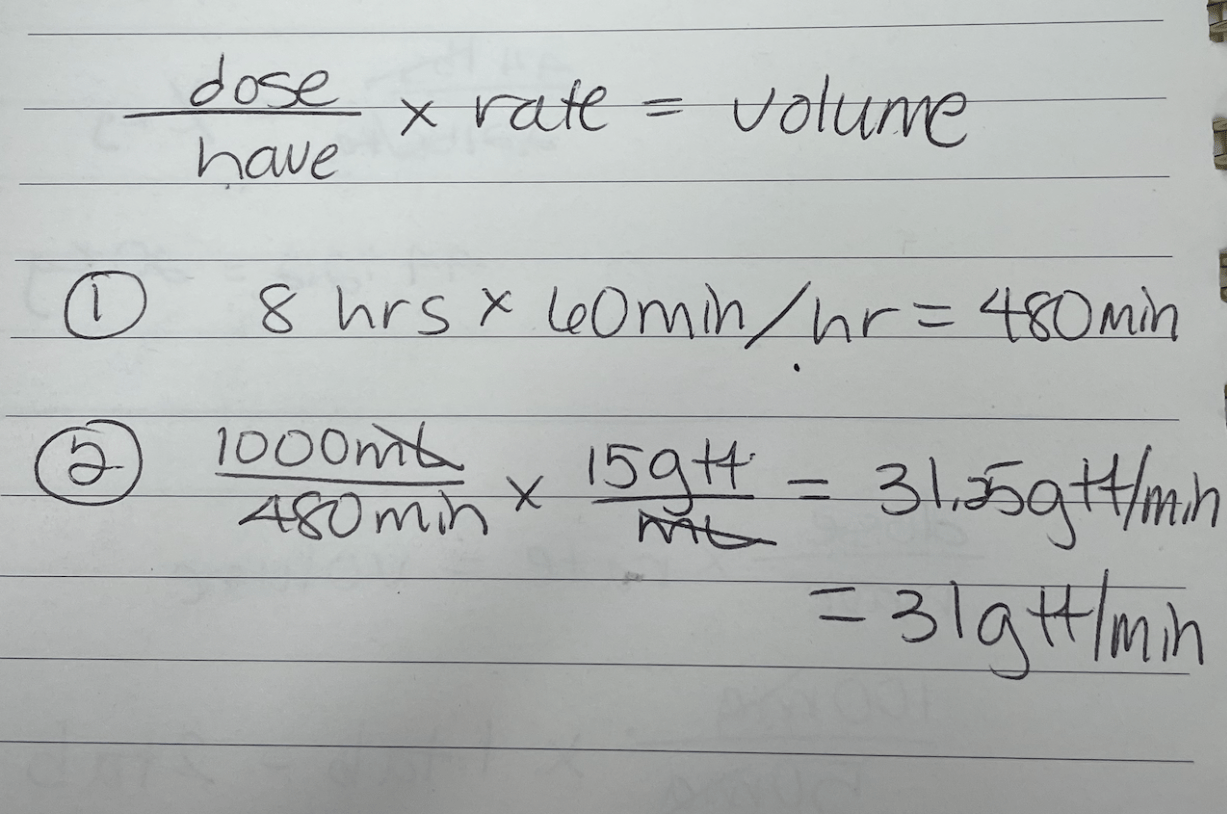
This electrolyte imbalance causes "Moans, Groans, and Stones."
What is hypercalcemia?
Condition caused by prolonged gastric suctioning.
What is Metabolic Alkalosis?
Intervention for a client with fluid volume excess (FVE).
What is restrict fluids/administer diuretics?
Explain why a patient with chronic COPD is at risk for acid-base imbalance.
What is retaining CO2 leading to respiratory acidosis?