State 10 rights of medications
1) Right Patient
2) Right Medication
3) Right Dose
4) Right Route
5) Right Time/Frequency
6) Right Patient Education
7) Right Documentation
8) Right to Refuse
9) Right Assessment
10) Right Evaluation
Normal Vital Signs
Blood Pressure 120/80 mmHg
Heart Rate 60-100 bpm
Respiratory Rate 12-20 breaths/minute
Oxygen Saturation 95-100%
Temperature 36-38 degrees C Average 37.0
Pneumonia
Infection that flares up the lungs sacs (alveoli)
Hypotension
Low blood pressure
Q4H
Every 4 hours
What angle do you perform SC injections?
45
Where would you locate the apical pulse?
Fifth intercostal space, left midclavicular line (apex of the heart)

Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is a long-term condition that happens when your heart can’t pump blood well enough to give your body a normal supply. Blood and fluids collect in your lungs and legs over time
Tachycardia
Heart rate of over 100 beats per minute
PRN
As needed
State a common side effect of hydromorphone
Drowsniness
Headache
Shallow breathing
Syncope
Nausea
Give two examples of what you are looking for in the Cognitive Perceptual Pattern section of Gordon's Functional Health Patter Assessment
Level of consciousness
Memory
Rested
Oriented x3 (person/place/time)
How well they can see/hear
Osteoarthritis
Degenerative joint disease. Cartilage within a joint begins to break down.
Edema
Swelling caused by fluid accumulation.
DC
Discontinued
What is Sennosides (Sennokot) used for?
Stool softener
What do you check for in a pain assessment?
Precipitating factor
Quality
Region/radiation
Severity
Timing
Atherosclerosis
Thickening or hardening of arteries caused by build up of plaque in the inner lining of an artery.
Biopsy
A procedure where a small amount of cells/tissue is removed for examination to determine presence or extent of the disease.
CXR
Chest X-ray
Name a site for IM injection and how you would landmark
Ventrogluteal muscle of hip
To locate the muscle, place the palm of a hand over the greater trochanter of the femur, facing the index finger and thumb towards the umbilicus, along the anterior iliac spine. Place the middle finger toward the iliac crest creating a ‘V’ shape. The injection is given in the middle of the ‘V’.

Deltoid muscle of the arm
The deltoid muscle is a rounded triangle shape. To landmark this site, the patient should be sitting comfortably with their arm visible from the shoulder to the top of the elbow. Palpate the acromion (outer edge of the scapula) and trace an imaginary inverted triangle below the shoulder. The injection should be given 3-5cms below the acromion, in the middle of the triangle.
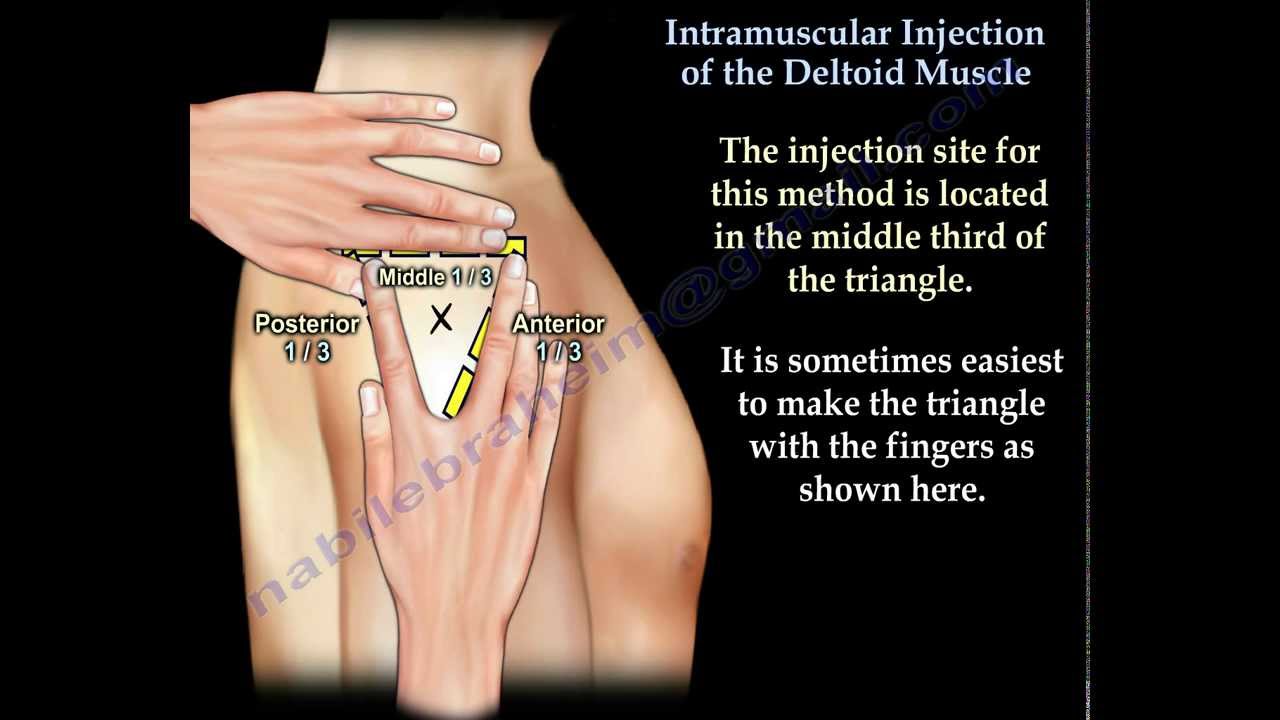
Dorsogluteal
(not recommended due to its proximity to the sciatic nerve and major blood vessels)
Vastus Lateralis of the thigh
Rectus Femoris of the thigh
What do you look for when checking an IV site?
Redness
Discharge
Pain
Swelling
Gastro esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Digestive disorder that happens when gastric acid from your stomach flows back up to your esophagus
Thrombosis
Blood clot in artery or vein
CBC
Complete Blood Count