Which part of the pleura is attached above by a suprapleural membrane?
What is cervical pleura
A monoclonal antibody given to high-risk infants and young children as immunoprophylaxis
What is Palivizumab?
Bacteria in artificial aquatic environments: watercooling towers, shower heads, sink faucets, and hot tubs
What is Legionella pneumophila?
Comment on the penetration
What is over penetration?
For patients with a penicillin allergy, this antibiotic is used to treat sepsis or endocarditis caused by MRSA.
What is vancomycin?
Tongue-like projection of the upper lobe at the cardiac notch
What is the lingula?
This term describes the slow, minor genetic changes in the Influenza virus that contribute to seasonal epidemics.
What is antigenic drift?
Red currant jelly sputum is characteristic of which type of pneumonia?
What is Klebsiella pneumonia?
Which chest x-ray view is this?
Posterior-Anterior (PA)
Vancomycin resistance is due to the modification of this terminal dipeptide in peptidoglycan, preventing effective binding.
What is D-Ala-D-Lac?
This anatomical landmark is obliterated on imaging due to the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity, often seen in cases of pleural effusion or hydrothorax.
What is the costophrenic angle (or Costo-diaphragmatic recess)?
This bacteria causing pneumonia has major virulence factor of polysaccharide capsule that helps prevent phagocytosis.
What is Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Which stage of lobar pneumonia is this?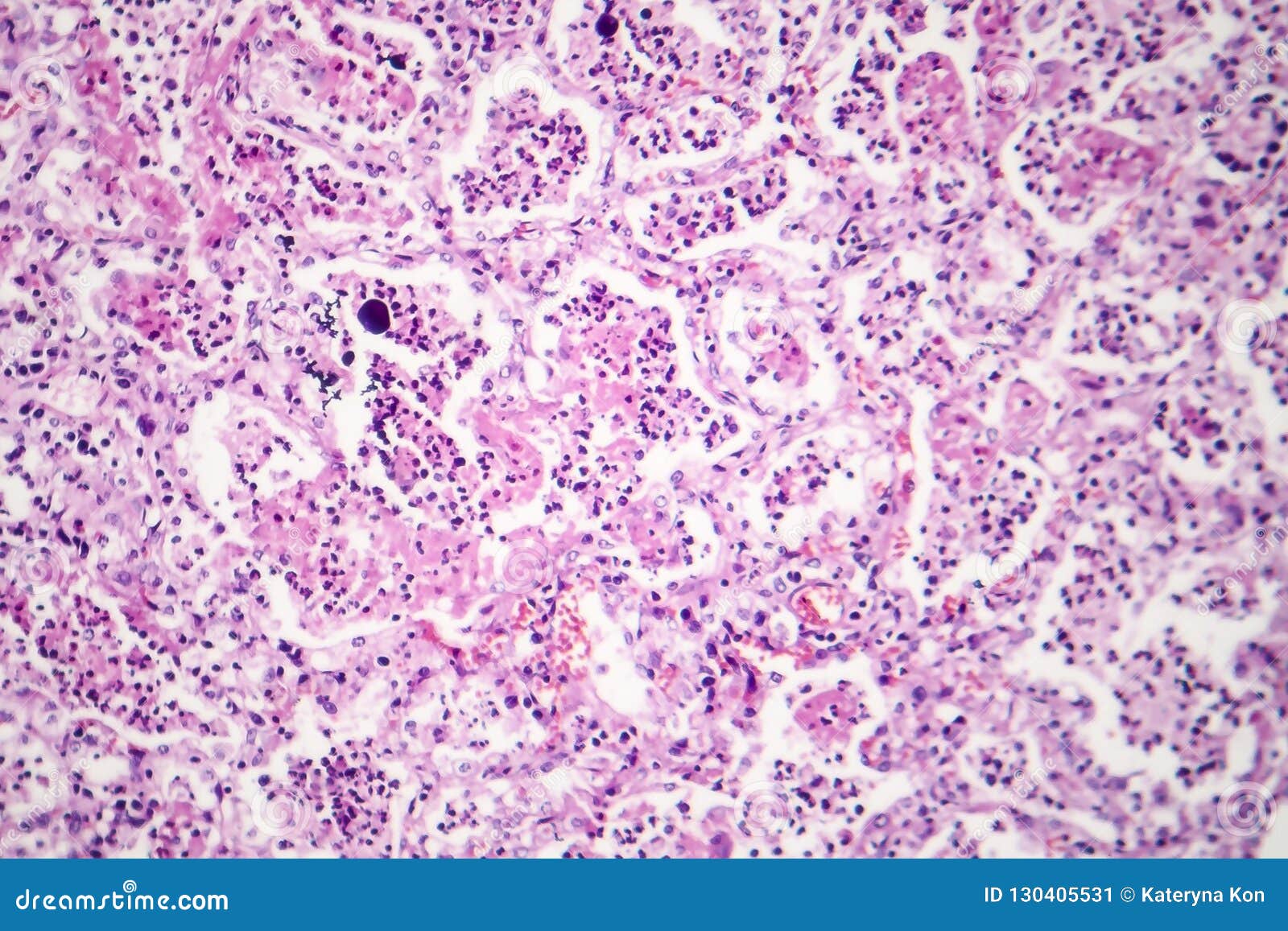
What is Red hepatization?
Comment on opacity and silhouette
nonhomogeneous opacity in right middle & lower zones with preserved cardiac border (-ve silhouette)
This syndrome, caused by rapid intravenous infusion of vancomycin, leads to flushing, rash, and in severe cases, hypotension and dizziness.
What is Red Man Syndrome?
Which fissure follows the medial border of the scapula when the arm is abducted?
What is oblique fissure?
This condition is characterized by bilateral interstitial pneumonia and is a common opportunistic infection in patients with HIV/AIDS
What is Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia?
A patient with AIDS presenting with pneumonia symptoms and a CD4 count below 40, along with loss of vision, is likely suffering from this viral infection.
What is Cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonia?
This radiological sign, visible on a chest X-ray, indicates the presence of air-filled bronchi surrounded by fluid or consolidated lung tissue, often associated with pneumonia.
What is an air bronchogram?
These proteins, carried on plasmids, protect DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV from fluoroquinolone binding, reducing the antibiotic's efficacy.
What are Qnr proteins?
The nerve passing between the grooves for the left common carotid and left subclavian.
What is the left phrenic nerve?
This vaccine for Pneumococcal Pneumonia, including PCV13, involves linking polysaccharides to a protein carrier, enabling a T-cell dependent immune response and promoting long-lasting immunity.
What is Conjugate vaccine?
This microscopic organism is a common cause of pneumonia
What is Aspergillosis?
Comment on the rotation, inspiration, penetration, and finally the pathology
centralized, good inspiration, optimal penetration: normal chest x-ray
These two fluoroquinolones are most commonly used to treat systemic Pseudomonas infections due to their substantial antibacterial activity.
What are ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin?