Whoa, Oh, Oh,
Whoa, Oh, Oh
This pea-sized gland located beneath the hypothalamus in the small, saddle-like depression of the sphenoid bone is known as the master gland.
What is the pituitary gland?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 51 p. 1733
Prednisone (hydrocortisone) can promote the retention of sodium. When sodium is retained, so is ________, because they go everywhere together!
Hint: this can lead to swelling......
What is water?
Sodium + Water = Best Friends Forever! They go everywhere together!
ATI 9th ed. PN Pharm, Ch. 35 p. 307
What are thyroid-hormone producing cells?
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 303
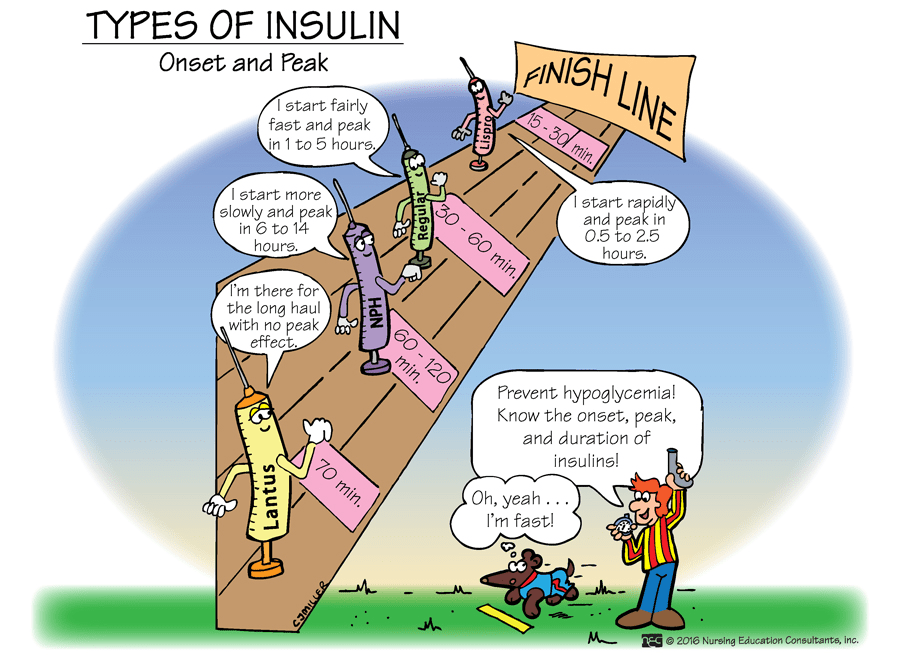
When studying insulins, nurses need to know the _______, ________, and __________.
What are onset, peak, and duration?
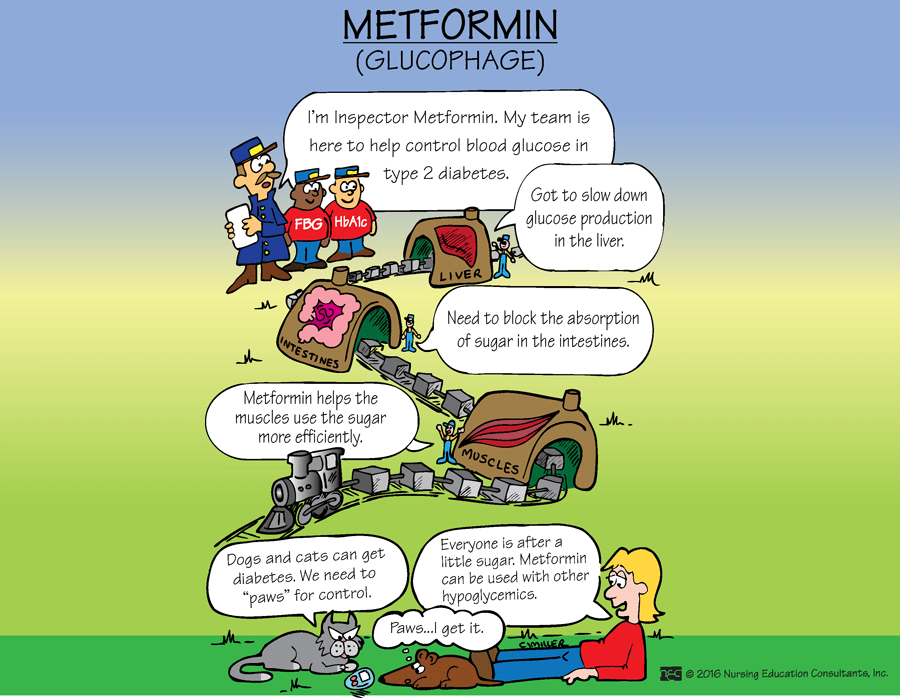
This class of oral antidiabetic agents increases sensitivity to the insulin already being produced by the patient. *A member of this class is metformin (glucophage).
What are biguanides?
ATI PN Pharm Ch. 34 p. 293
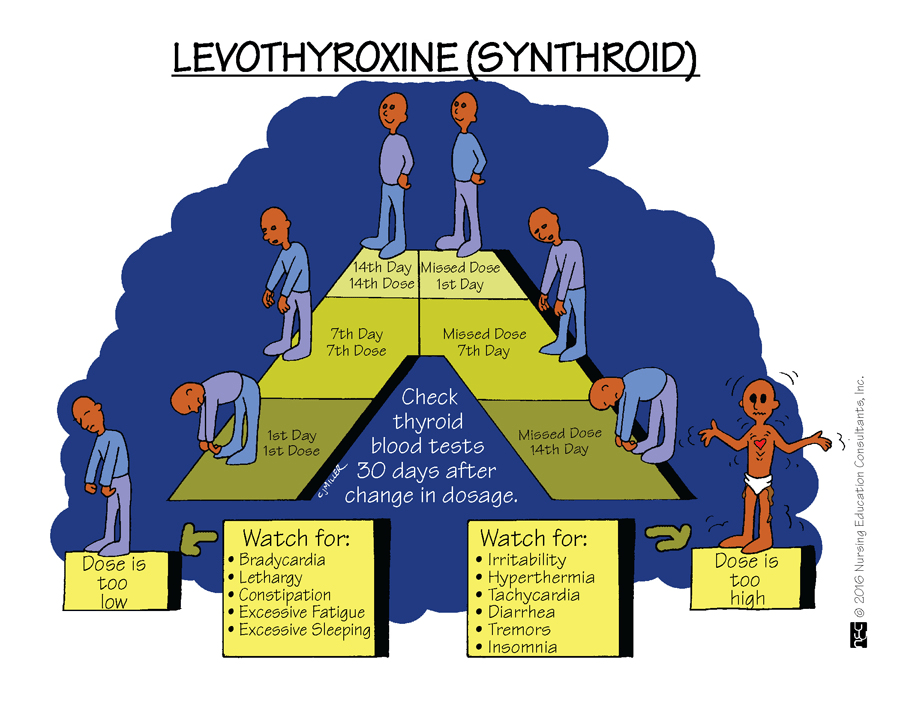
Chronic underproduction of T3 & T4 , can result in a hypothyroid state. Levothyroxine (Synthroid) is the drug given to supplement and restore the thyroid levels. What is the optimal time the patient should take this medication?
What is 30-60 min before breakfast?
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 302
This butterfly shaped gland lies anterior to the trachea; the (L) and (R) sides are connected by an isthmus; and, it is a highly vascular gland, receiving 80-120 mL of blood/ minute.
What is the thyroid gland?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 51 p. 1733
If the patient is retaining sodium and water, list three nursing interventions to perform:
1.
2.
3.
(Answers may vary)
1. Daily weights
2. I & O
3. Monitor Potassium levels
4. Monitor Vital Signs: BP specifically (retained sodium and water can lead to elevated BP)
5. Monitor breath sounds (for fluid overload)
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 307
The nurse recognizes this symbol to mean ________.
What is radioactive or radioactive material?
Special handling and precautions are required when this symbol is posted. If you are not specially trained, you should leave the area and not handle the materials.
Meal coverage is often provided by Sliding Scale insulin coverage. The two insulins used for this coverage are ________ and _________, because they are rapid and fast acting, specifically.
What are Humalog (rapid) and Regular (fast) ?
*Remember, it is a good idea to administer the sliding scale coverage to the patient for meals when the meal trays arrive on the floor. This way, the nurse doesn't risk making the patient hypoglycemic.
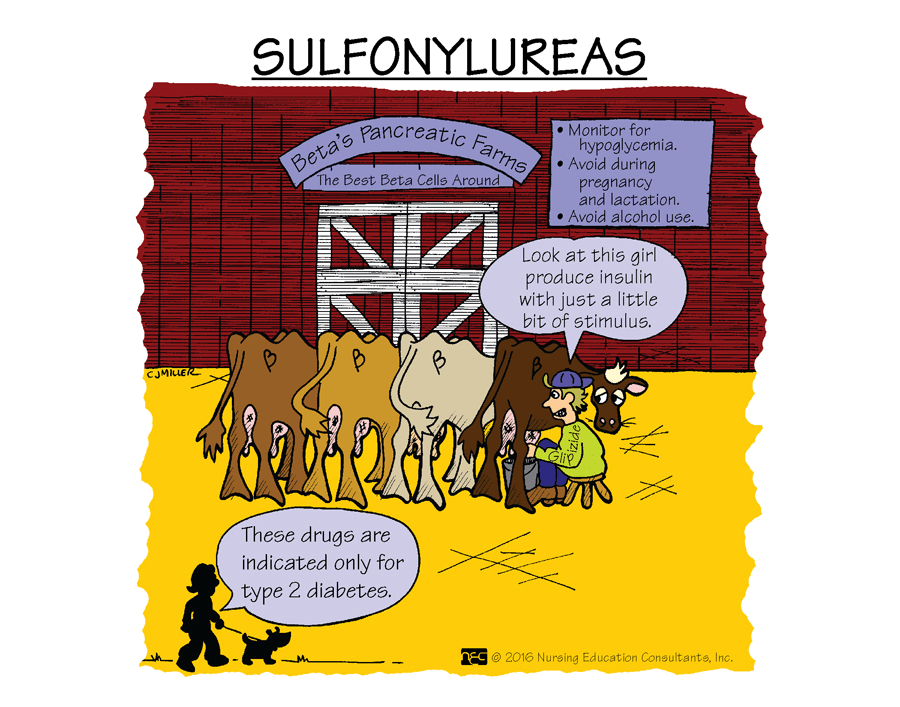
This class of oral antidiabetic agents increases both insulin production AND sensitivity to insulin. *A member of this class of oral antidiabetic agents is Glipizide.
What are sulfonylureas?
Nurses understand that TSH released from the pituitary gland stimulates T3 & T4 to be produced by the thyroid (negative feedback loop). When levels of T3 & T4 aren't high enough, the pituitary gland never gets the signal to stop production of TSH. If the TSH continues to be produced, the thyroid gland can enlarge. This is one of the causes of a __________.
What is a goiter?
Link: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/goiter/symptoms-causes/syc-20351829

1. The thyroid gland secretes two main hormones: T3 & T4 (triiodothyronine & thyroxine, specifically). The release of these hormones is controlled by ______, which is secreted from the pituitary gland.
2. Adequate oral intake of __________ is necessary from the formation of thyroid hormones.
*Hint: it is often added to table salt, to ensure that dietary intake has been met.
1. What is TSH?
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 51 p. 1735
2. What is iodine?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 51 p. 1735
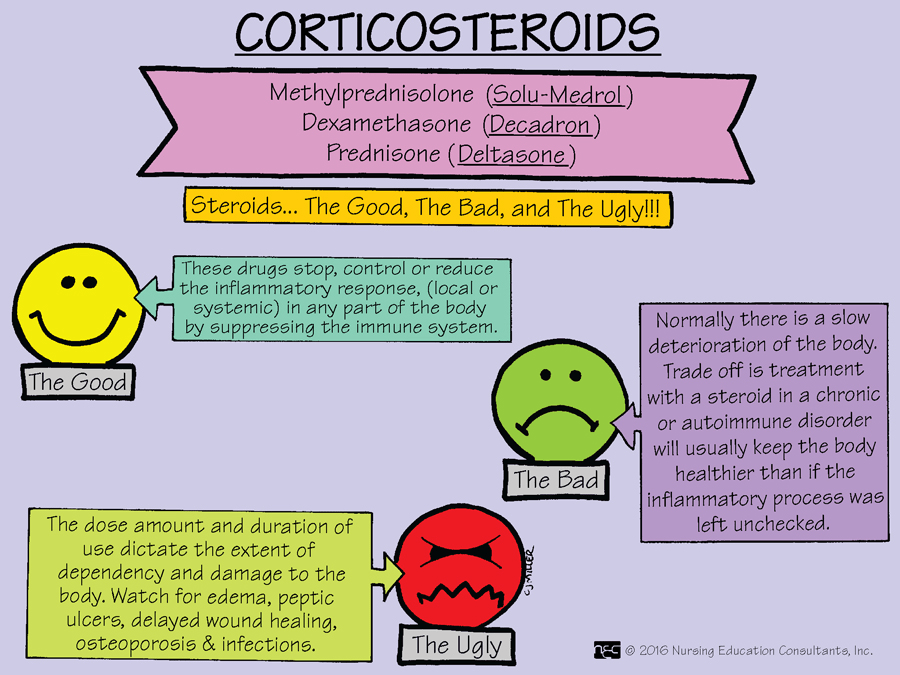
Prednisone (Hydrocortisone) is a glucocorticoid. This class of medications is known for increasing plasma glucose levels. Because of this, patients may need to use _________ during their steroid therapy, to maintain their blood glucose levels within range.
What is insulin?
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 307
List three nursing interventions for a patient on Radioactive Iodine therapy:
1.
2.
3.
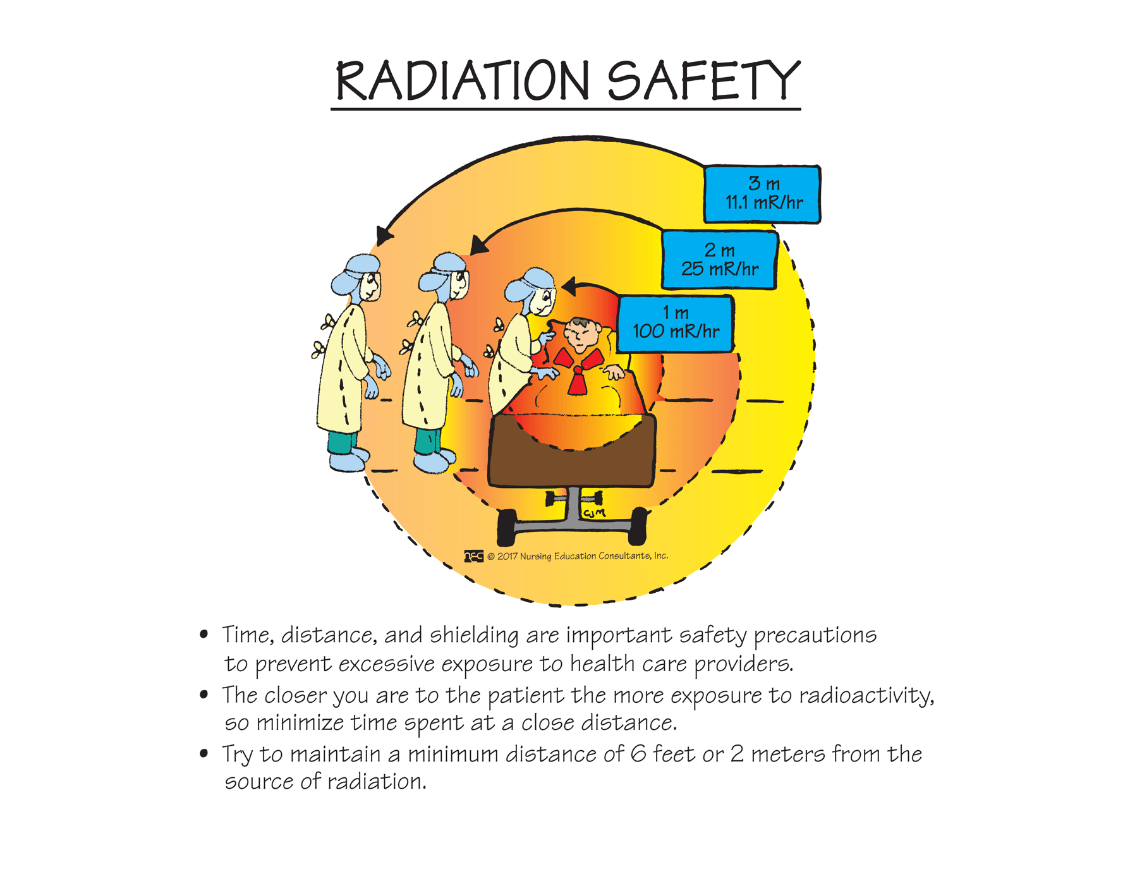
Answers will vary:
1. Maintain a distance of 6 feet from other people.
2. Do NOT prepare food for others or share utensils.
3. Avoid close contact with children (no children sitting on the lap, etc.)
4. Avoid contact with those who are pregnant.
5. Increase fluid intake, usually to 2-3 L/ day.
6. Special disposal of body wastes due to radioactivity.
ATI PN Pharm Ch. 35 p. 304
This long acting insulin is typically given at night, and works over a period of 24 hours.
What is Lantus?
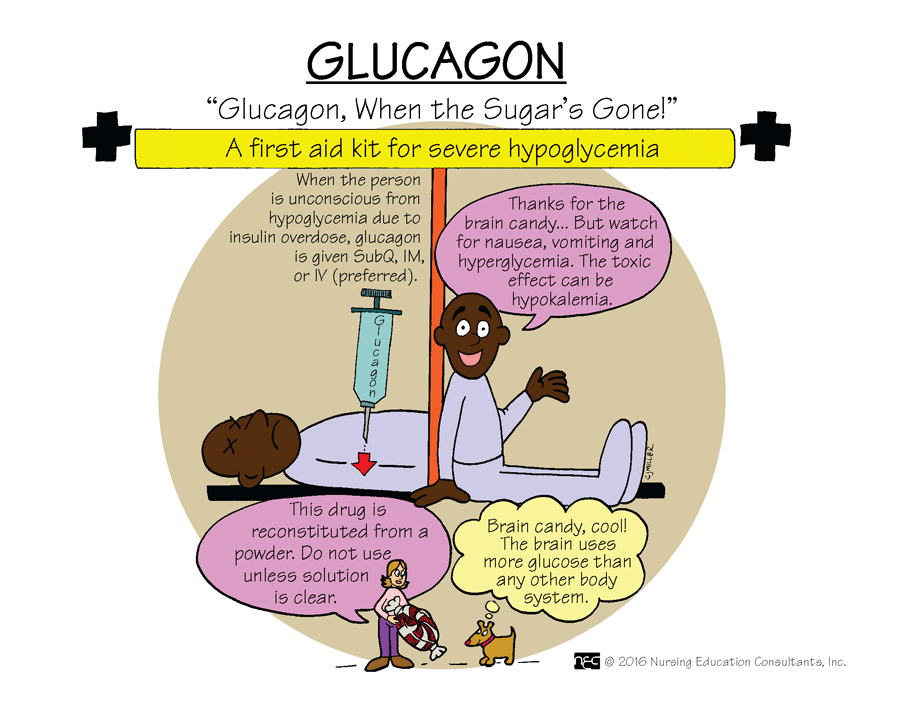
The normal blood glucose range is 70-100 mg/dL. Patients who are close to 70 mg/dL or lower, may present with symptoms of hypoglycemia. If they are unable to take medications by mouth and they have no IV line, this medication may be used to increase their blood glucose. This medication can be given IM.
What is glucagon?
True or False?
Patients who are on thyroid replacement medication are typically on it for life.
TRUE!
Lifelong replacement is important even after improvement. Do not ever discontinue thyroid replacement medications without talking with the provider.
ATI PN Pharm Ch. 35 p. 302
This organ secretes insulin.
What is the pancreas?
Specifically, the Beta cells, in the Islets of Langerhans, in the pancreas secrete insulin.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 51 p. 1757
List three therapeutic uses for prednisone (hydrocortisone).
1.
2.
3.
Answers will vary:
1. Acute & chronic replacement therapy for adrenocortical insufficiency
2. Anti-inflammatory
3. Allergic reactions
4. To reduce swelling and inflammation in CA patients.
*Can be administered IV, IM, PO
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 306
True or False?
Using Radioactive iodine can suppress the bone marrow function to the point where leukemia develops.
TRUE!
Monitor the CBC for anemia and low WBC count. Leukemias can be induced by Radioactive Iodine therapy.
ATI PN Pharm Ch. 35 p. 303
Of the following laboratory values reported by the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP),which one indicates an urgent need for the nurse to assess the patient?
a. Bedtime glucose of 140 mg/dL
b. Noon blood glucose of 52 mg/dL
c. Fasting blood glucose of 130 mg/dL
d. 2-hr postprandial glucose of 220 mg/dL
C. Noon blood glucose of 52 mg/dL
Rationale:
The nurse should assess the patient with a blood glucose level of 52 mg/dL for symptoms of hypoglycemia and initiate the hypoglycemia protocol. The other values are within an acceptable range or not immediately dangerous for a patient with diabetes.
If the patient takes this medication and is scheduled for a CT contrast with injected dye, the patient should hold off on this medication for the next 48 hours.
___________________
What is metformin (glucophage)?
How would we know that the thyroid replacement therapy is working?
1.
2.
3.
ATI PN Pharm Ch. 35, p. 302
1. Decreased TSH levels. TSH decreases as the negative feedback loop is closed when T4 rises to signal it to turn off.
2. T4 levels in expected range.
3. Symptoms of hypothyroidism are resolved.
When Gland Number One secretes a hormone to stimulate target cells in Gland Number Two to release another hormone, and then Gland Number One stops secreting based on the levels secreted by Gland Number Two, this is known as ____________.
What is a negative feedback loop?
Step 1: Gland A secretes a hormone which stimulates Gland B to secrete a different hormone.
Step 2: Gland B secretes. The blood level of the hormone secreted by Gland B rises.
Step 3: This rise signals Gland A to stop secreting.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 51 p. 1733
If the patient is under stress, the dose of prednisone may need to be ___________ to produce the desired effect. When stopping the dose of prednisone, it needs to be ____________.
What is increased and tapered?
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 307
The two absolute contraindications for Radioactive Iodine therapy (aside from iodine allergy) are:
1.
2.
What are
1. pregnancy
2. lactation
ATI PN Pharm 9th ed. Ch. 35 p. 304
A hospitalized patient who is diabetic received 38 units of NPH insulin at 7:00 AM. At 1:00 PM, the patient has been away from the nursing unit for 2 hours, missing the lunch delivery while awaiting a chest x-ray which has been delayed. What is the best action by the nurse to prevent hypoglycemia?
a. Plan to discontinue the evening dose of insulin.
b. Save the lunch tray for the patient's return.
c. Call the Radiology department, and ask that if the testing needs to be further delayed, that the patient be sent back to eat lunch.
d. Send a glass of orange juice to the patient in the diagnostic testing area.
c. Call the Radiology department, and ask that if the testing needs to be further delayed, that the patient be sent back to eat lunch.
Rationale:
Consistency for mealtimes assists with regulation of blood glucose, so the best option is for the patient to have lunch at the usual time. Waiting to eat until after the procedure is likely to cause hypoglycemia. Holding the insulin dose later will not prevent hypoglycemia from the peak of the NPH dose. A glass of juice may keep the patient from becoming hypoglycemic but will cause a rapid rise in blood glucose because of the rapid absorption of the simple carbohydrate in these items, and who will deliver the juice??
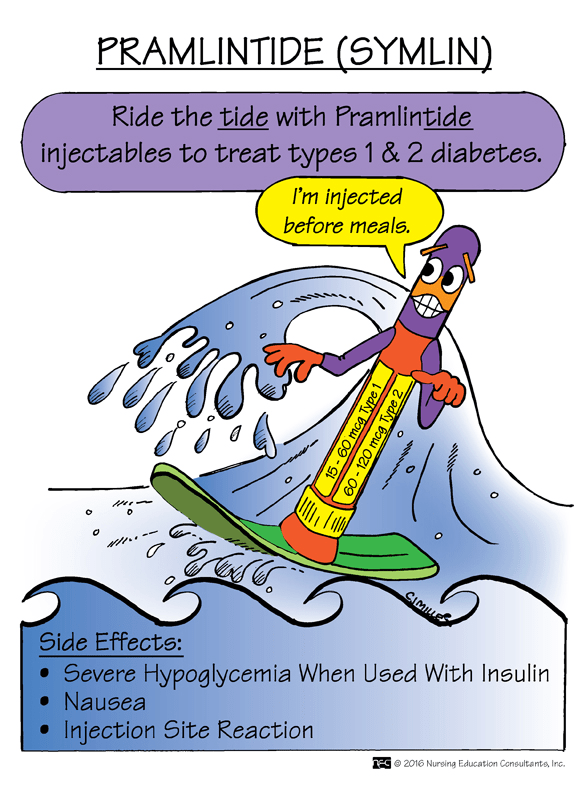
These medications bind to the GLP-1 receptor reducing appetite, stimulating insulin release, and preventing glucagon release. What is this class of medication?
What are semaglutides?
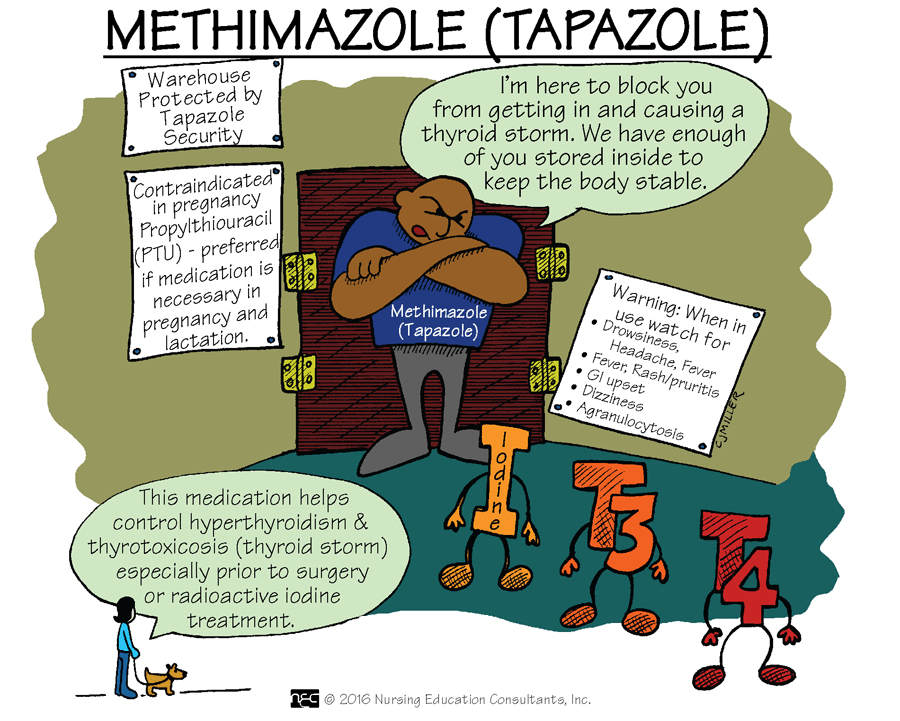
The two medications used to block the synthesis of thyroid hormones in an overactive thyroid are:
_________ and __________. They work to produce a euthyroid state before surgery.
Methimazole and PTU
ATI PN Pharm Ch. 35 p. 302
1st line is Methimazole