If the site bleeds, or this is not created when you perform an intradermal injection, you administered the medication too deeply.
What is a bleb?
Route of administration, like subcutaneous, impacts this - the movement of medication molecules into the blood from the site of the administration.
What is absorption?
Technique used to administer intramuscular injections that reduces the likelihood of medications seeping out of the muscle into the subcutaneous tissue.
What is Z-track?
Like most drugs, oral medications are typically metabolized primarily by this organ.
What is the liver?
In order to avoid dosing yourself with your patient's topical medication, make sure to don these prior to administration.
What are gloves?
5 - 15 degrees
What is the angle of administration?
Clear to Cloudy.
What is the correct order to draw up insulins into a single syringe?
Following these six rights is necessary to ensure the safety of a patient receiving IM medications.
1. The right medication
2. The right dose
3. The right patient
4. The right route
5. The right time
6. The right documentation
Oral opioid pain medications commonly cause N/V. These are ______, predictable and often unavoidable impacts of a therapeutic drug dose.
What are side effects?
This is the federal agency that enforces laws which ensure that all medications - topical or otherwise- undergo vigorous testing before they are sold to the public.
What is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)?
The gauge range for needle selection.
What is 25-27 gauge?
Gauge and length range for subcutaneous injections.
What is 25 gauge, 3/8-5/8 inch.
Acceptable: insulin may have smaller needles approx 3/16
Describe the process of withdrawing medications from two vials into a single syringe.
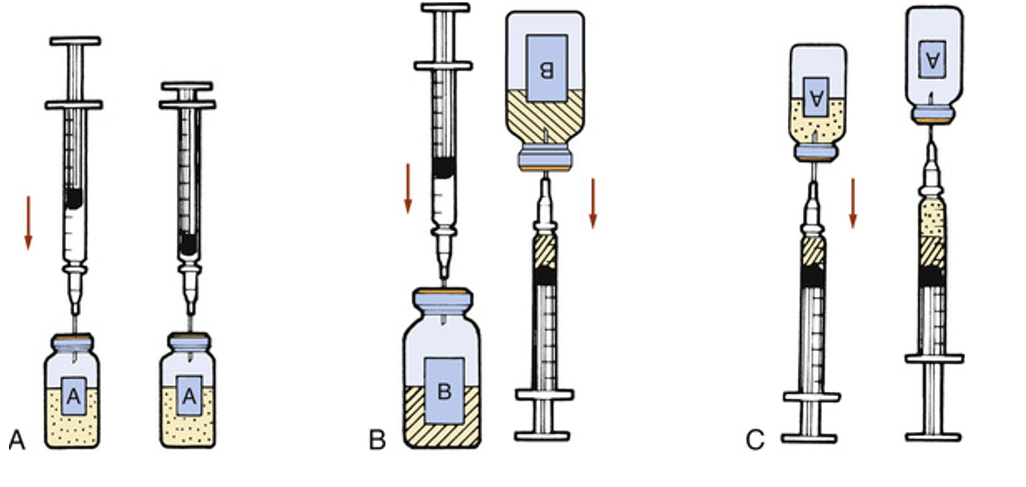
True or False: A patient with an NG Tube to suction cannot have a sublingual dose of Ativan.
What is False?
Sublingual medications passively diffuse into the capillary system. They do not enter the stomach and are not absorbed through GI mucosa.
List the 5 routes of medication administration we learned about (including topical) from fastest to slowest absorption rates.
What are topical, oral, intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular?
This is a common location for intradermal injections and the one typically used for PPD placement.
What is the forearm?
This is the technique used and the two acceptable angles for subcutaneous injection.
What is "pinch and stick" and 45 or 90 degrees?
To administer to the deltoid, find this anatomical landmark and inject 2-3 widths below.
What is the acromion process?
Before administering a medication to your patient's G-tube you must do this to ensure patency.
What is flush with 30mL of tap water or sterile water for critically ill or immunocompromised patients?
The anatomical area of the eye into which you place eye drops.
What is the conjunctival sac?
The nurse is preparing to administer a PPD to a patient being discharged to a LTC facility. This - a required component of complete orders - is missing.
ORDER: written 1650, 10/03/2024
Administer tubersol 0.1mL one time. 0800 10/04/2024.
eSigned: Jack O'Lantern, NP
What is route?
When injecting lovenox (low molecular weight heparin), do this with the air bubble in the prefilled syringe.
What is do not expel it - inject it into the tissue?
The preferred site for all adult injections over 2mL.
What is the ventrogluteal muscle?
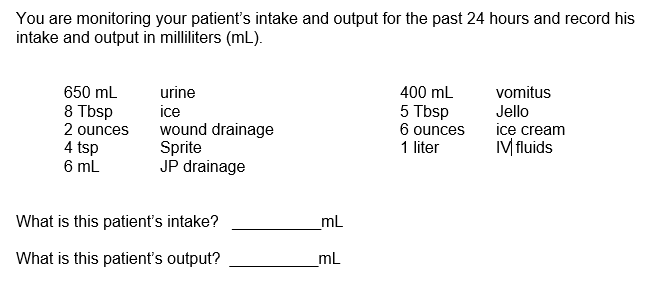
What is....
INTAKE: 1, 335mL
OUTPUT: 1,116mL
The direction to pull the ear when administering otic drops to an adult.
What is up and back?