Name this view:
Apical 2 chamber
Recurrent fevers and this on PLAX:
Mitral valve Endocarditis
Prominent Finding(s) seen in this RUQ clip:
Ascites and Pleural Effusion with Jellyfish sign
Whats this sign called:
D Sign
Cause of Dyspnea in patient with these findings: (See both clips):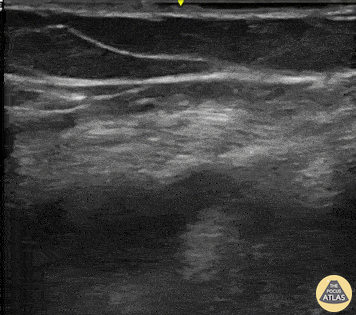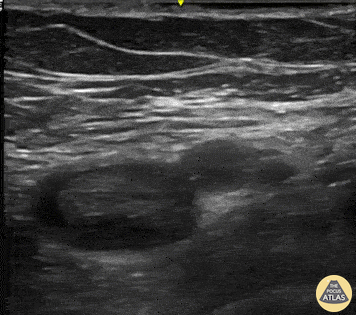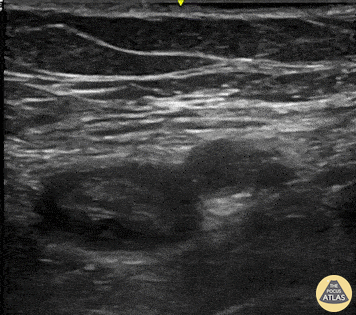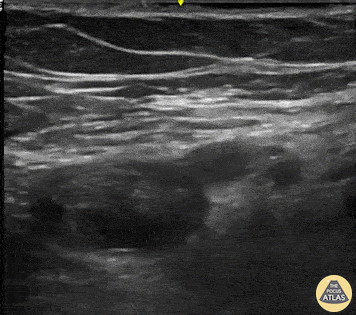

Acute PE
Name this view and level: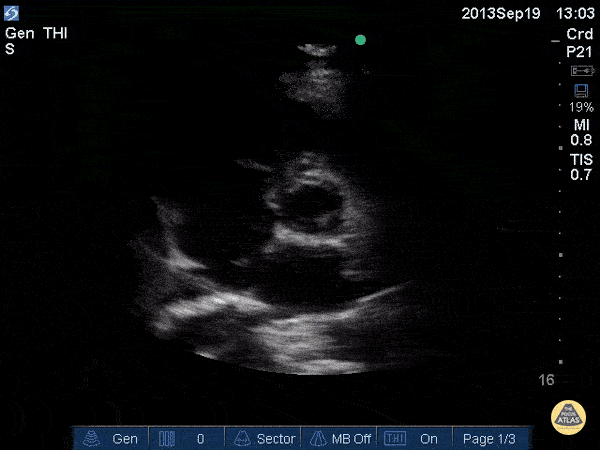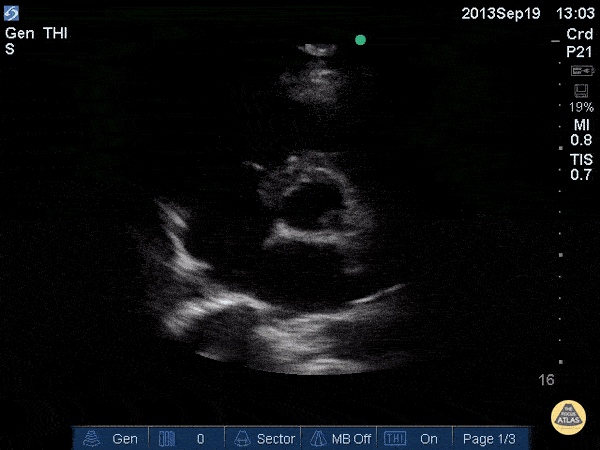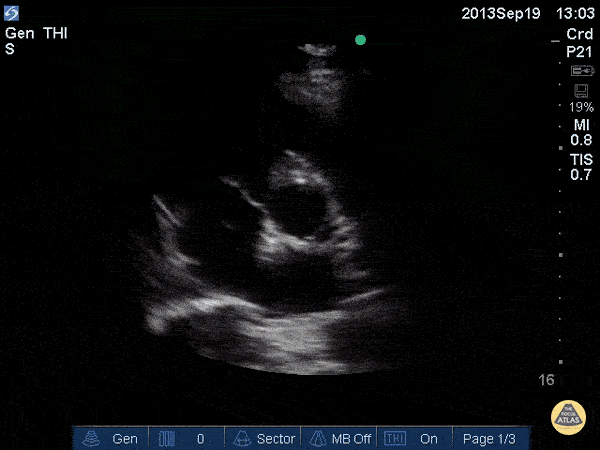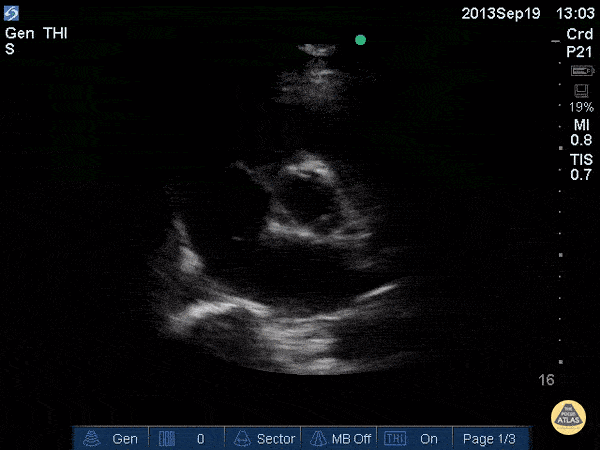
Parasternal Short (SAX) Aortic valve
Hypotension and the following PLAX and PSSX view:
Cardiac tamponade
Cause of hematuria in this patient:
Bladder cancer
What "mammalian" sign is shown here:
Bat-wing sign
Cause of Dyspnea in a patient with these findings:
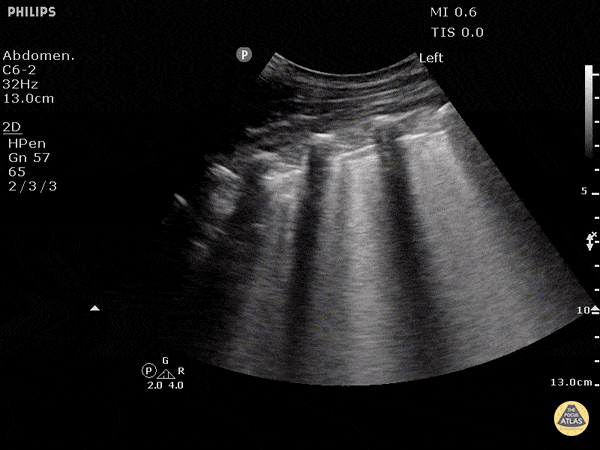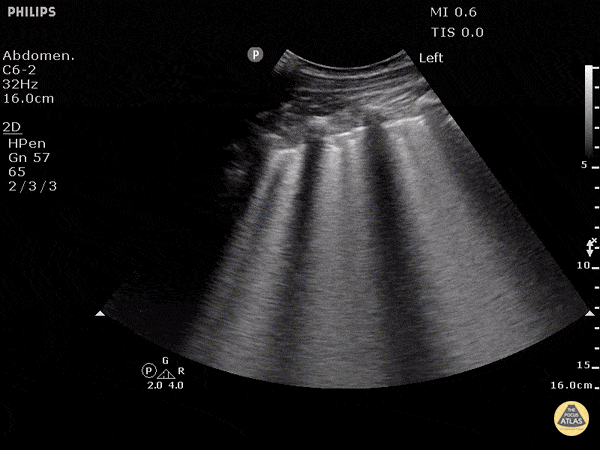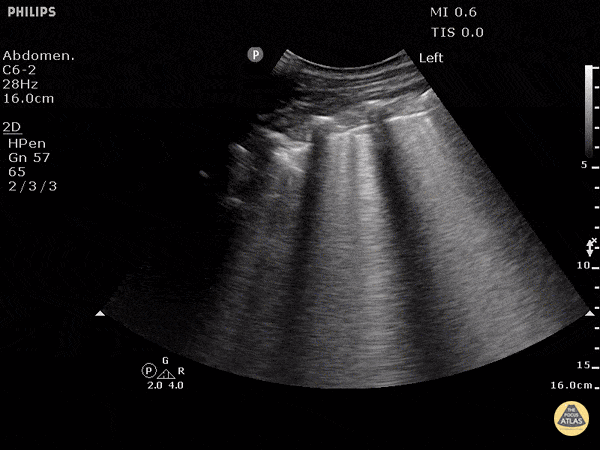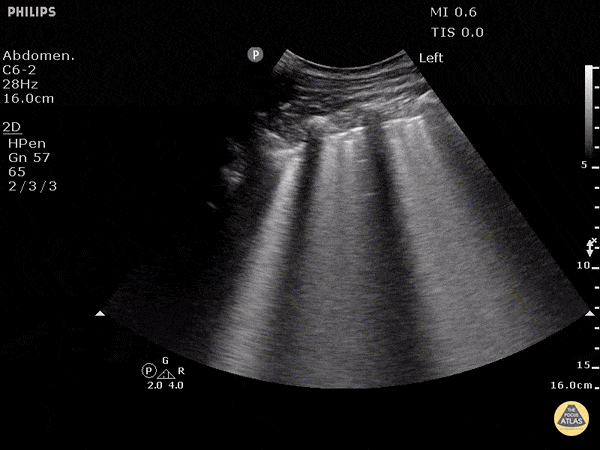
CHF exacerbation
Based on this image, most likely type of cardiomyopathy: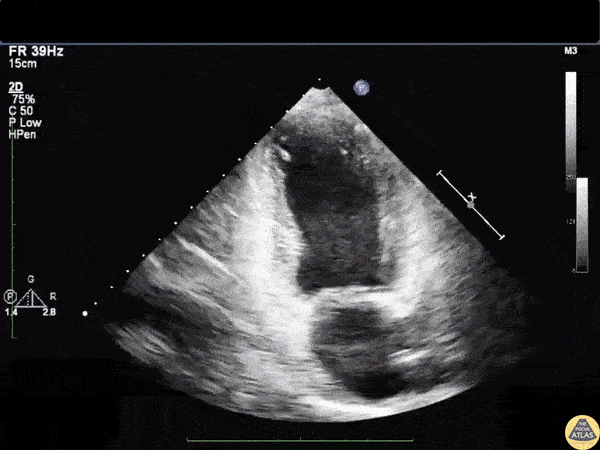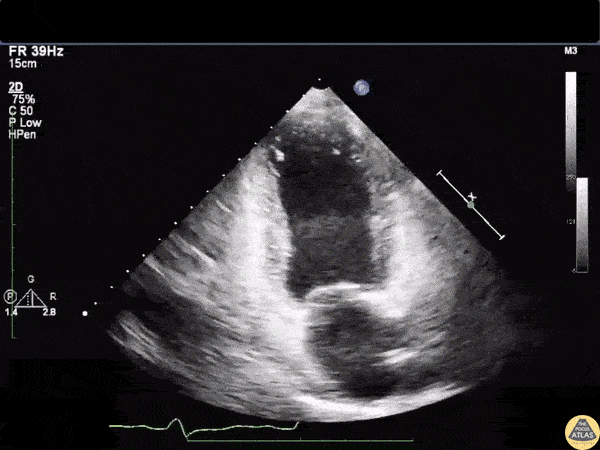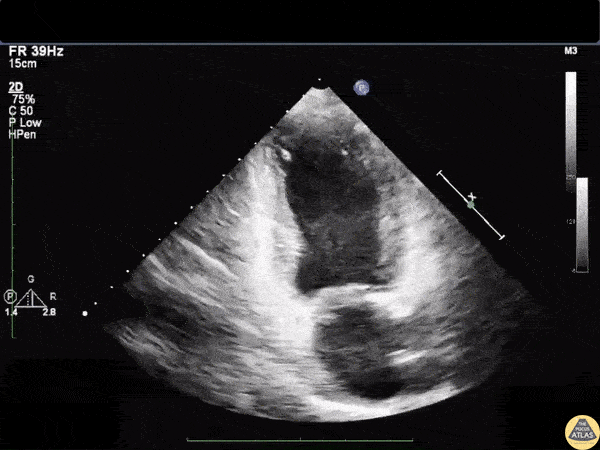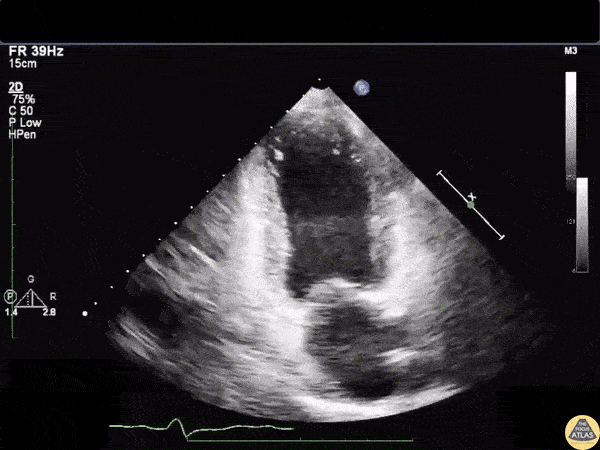
Stress/takotsubo
Chest pain and this image on PLAX: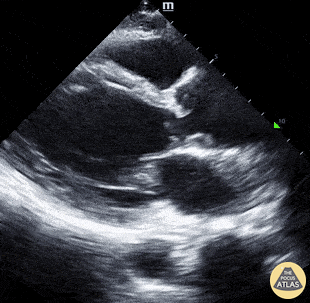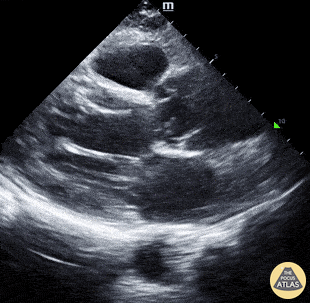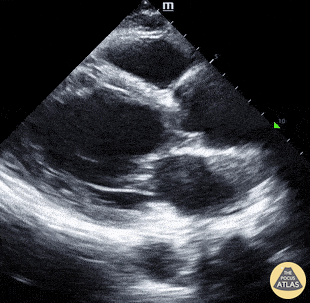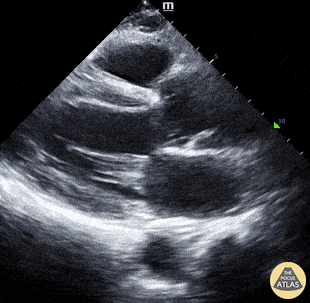
Aortic dissection
Cause of abdominal distention in this patient:
Ascites
What is the sign shown in this lung scan:
Lung Point
Patient with severe chest pain, Scan of the right neck, what is the Dx:
Aortic dissection extending to the carotid
Name the view and the prominent finding: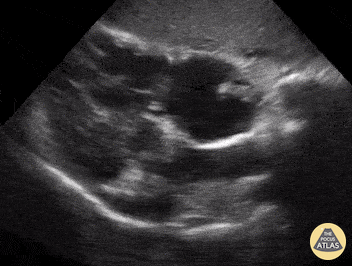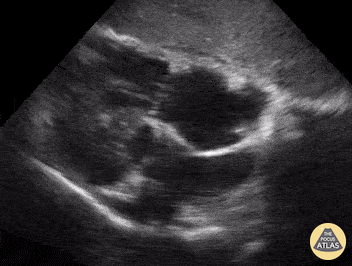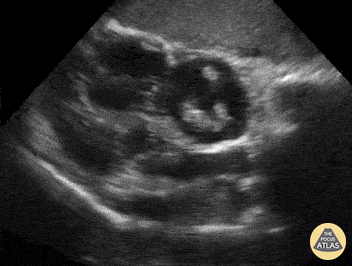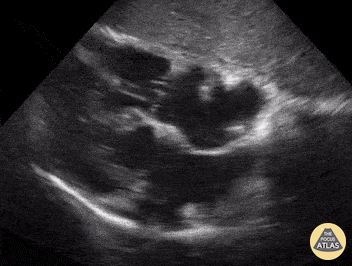
Subcostal 4 chamber, clot in transit
Fevers and this image: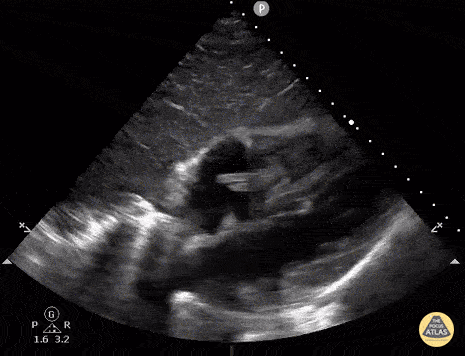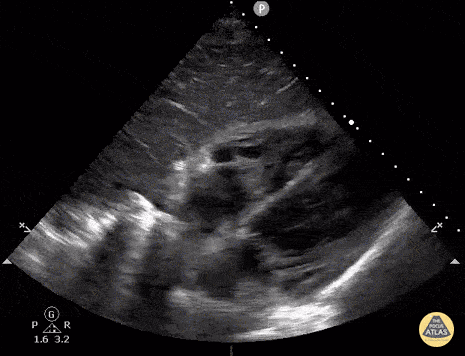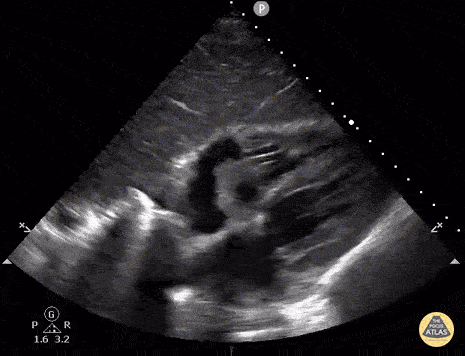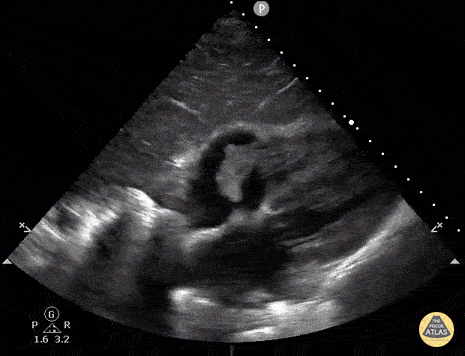
Tricuspid valve endocarditis
What disease does this patient have:

Polycystic kidney disease
Renal Sign shown here:
Bear paw sign/Bear claw sign (severe Hydro)
Cause of dyspnea ina patient with this lung scan: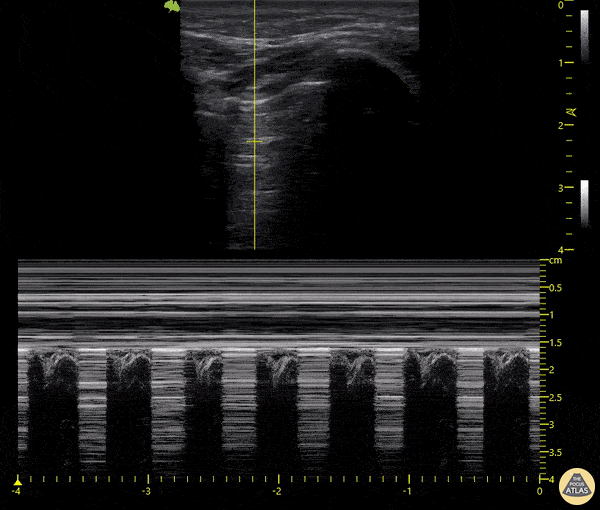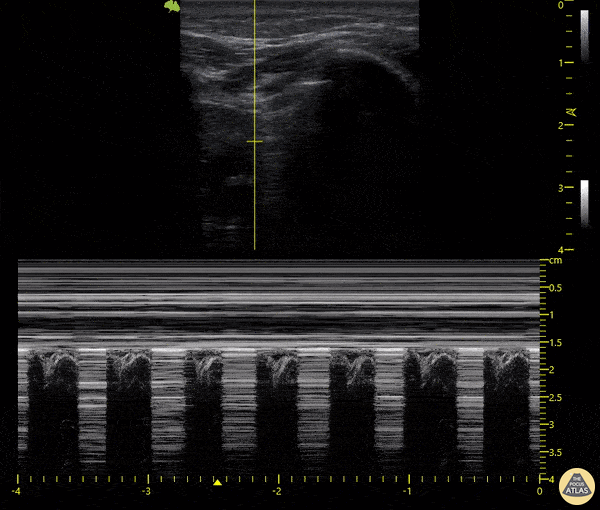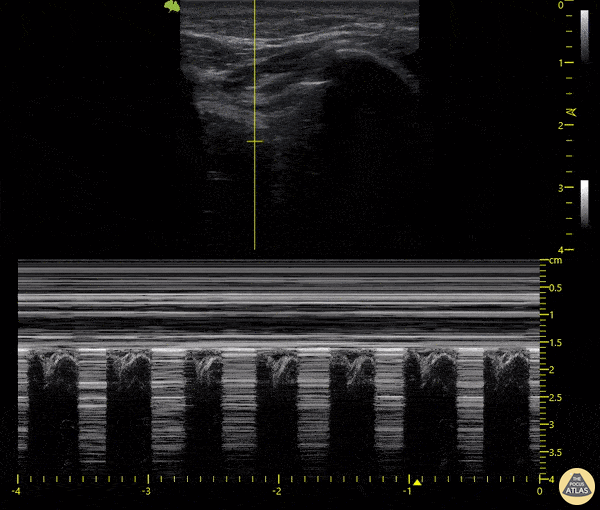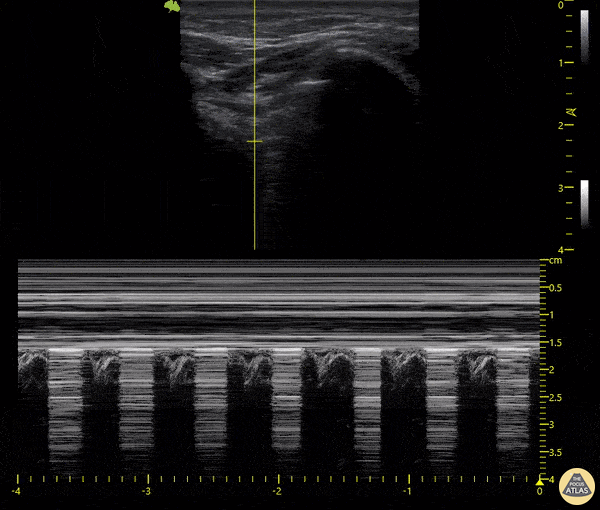
Pneumothorax
Finding shown here:
VSD
Mitral stenosis with mitral regurgitation with the classic MV "hockey stick" sign seen classically in which disease?

Rheumatic mitral valve disease
Why was this foley not draining: (Watch full clip)
Lodged in bladder diverticulum
Cardiac sign seen on this PLAX view:
McConnell's sign
Whats wrong with this patient: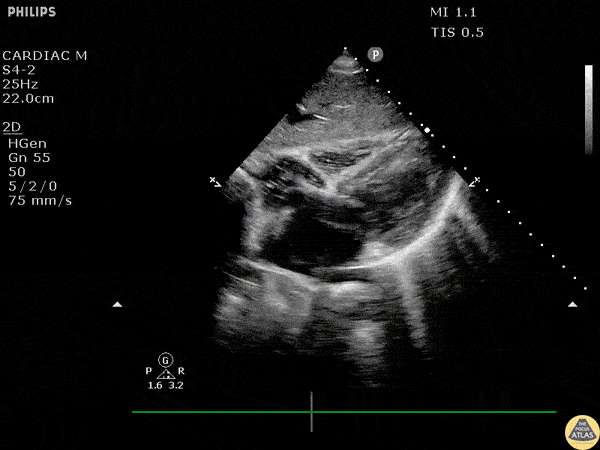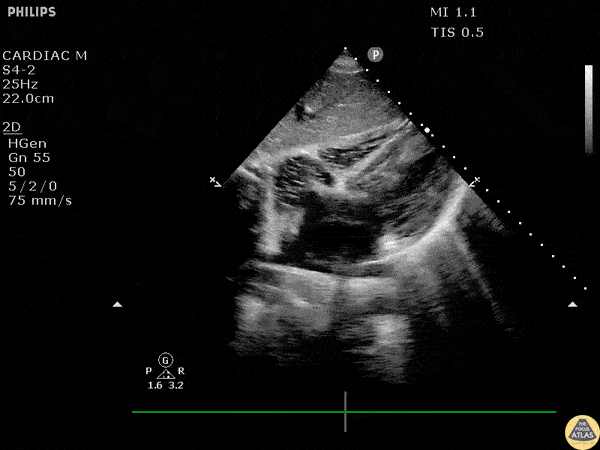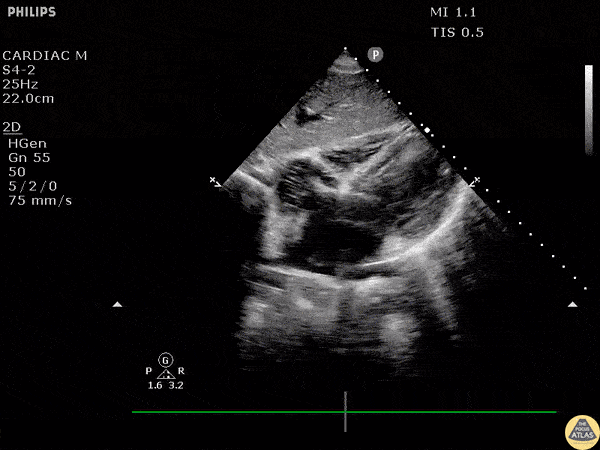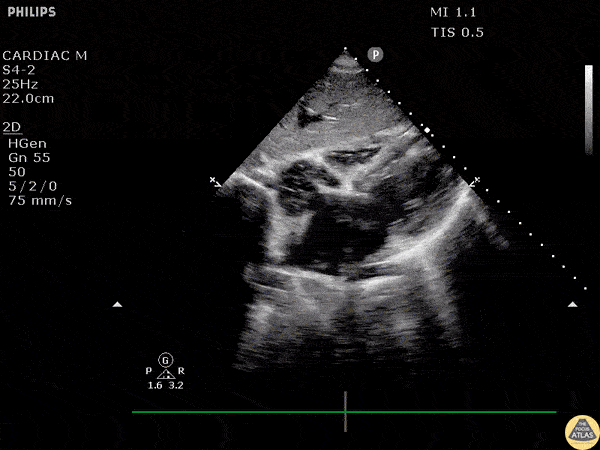
Vfib Cardiac Arrest/ Accept death
This ultrasonographic finding, first described in the 1990s, can be seen in both severe tricuspid regurgitation and cardiac tamponade. It refers to abnormal diastolic movement of this structure due to elevated right-sided pressures and may be missed unless you freeze-frame during ventricular diastole.
What is RV trampolining of the lateral wall and or intra-ventricular septum.