In Stage 2 of the DTM, what happens to death rates?
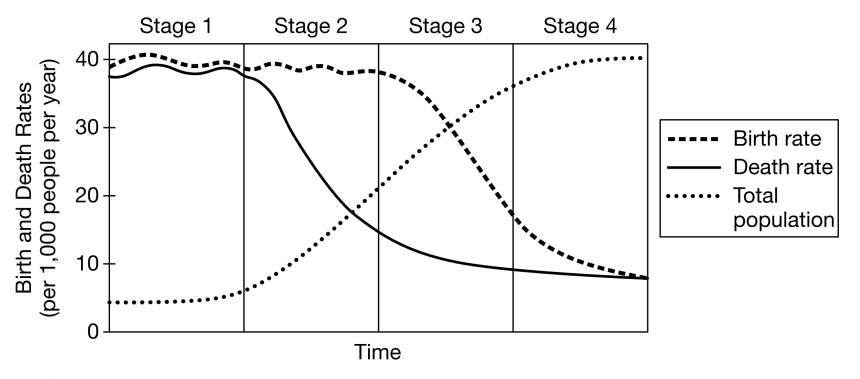
Decrease They fall.
What growth pattern corresponds to a J-shaped curve?
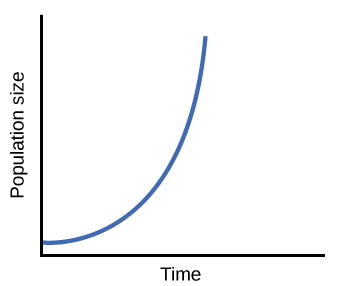
Exponential growth.
What survivorship curve do humans typically display?
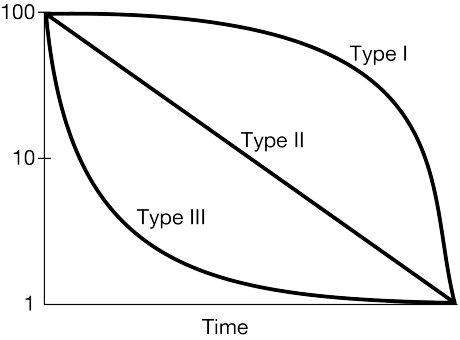
Type I.
A species with few offspring and long parental care is likely what?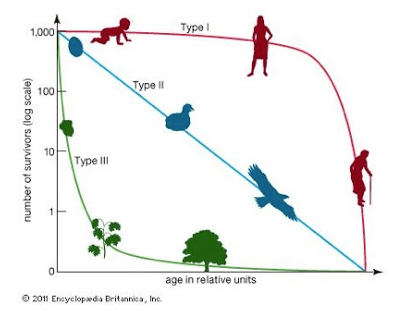
A K-strategist with a Type I curve.
Why do developed nations have lower fertility rates?
Higher education and healthcare access.
What does the DTM describe?
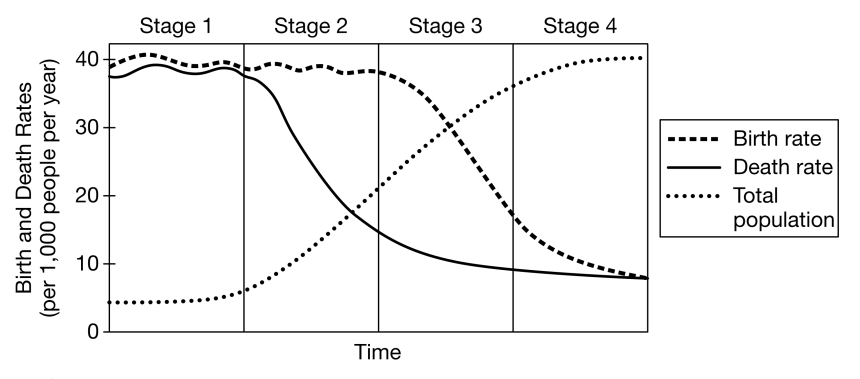
The shift from high birth/death rates to low birth/death rates.
Which age structure diagram shape typically shows negative growth?
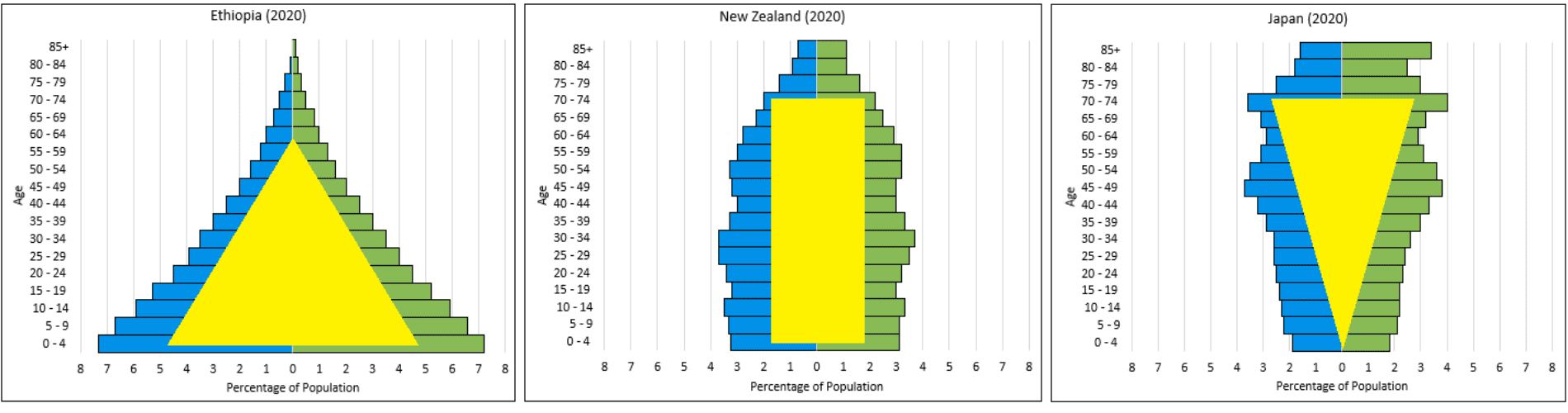
Narrow base compared to upper age groups (inverted pyramid).
Which survivorship curve shows high infant mortality?
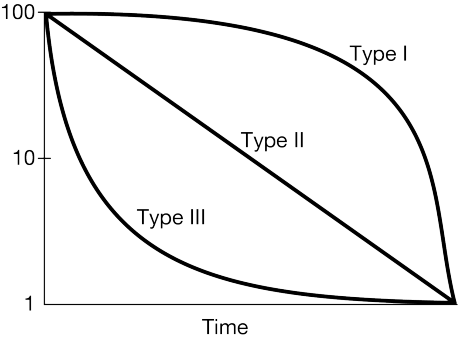
Type III.
Which strategist typically has many offspring and little parental investment?
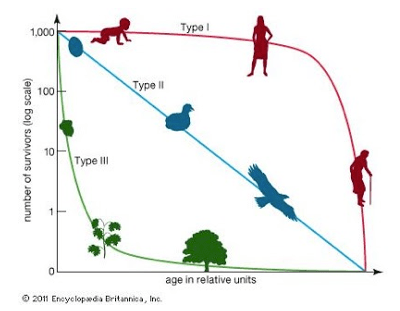
r-strategist.
How does industrialization correlate with environmental impact?
More industrialization usually increases environmental impact.
Why do developed countries typically show low birth rates?
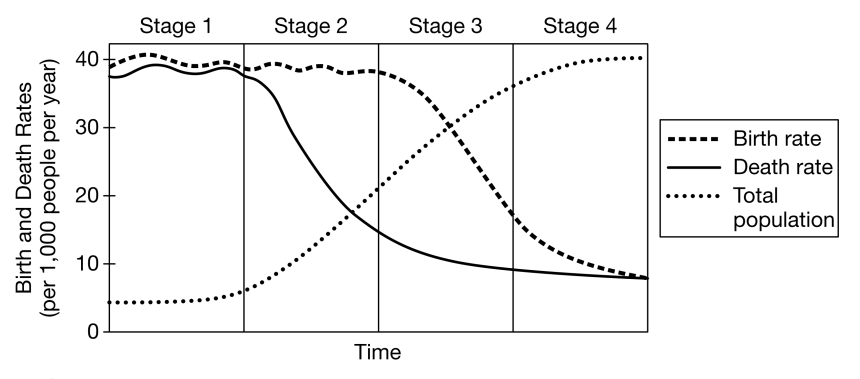
Higher education levels and access to healthcare reduce fertility.
If a population has many young individuals and few elderly individuals, what future trend is likely?
It will grow rapidly.
Why do Type III species produce a large number of offspring?
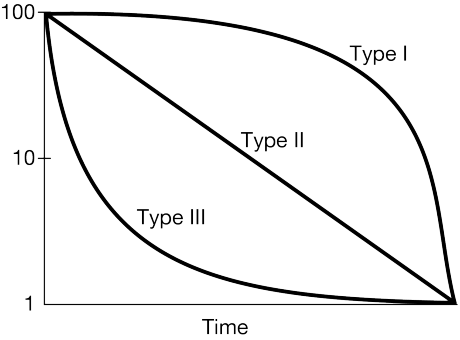
To compensate for high early-life mortality.
Why might an r-strategist thrive after a natural disaster?
Their rapid reproduction helps them recolonize unstable environments.
Why do developing nations tend to have higher birth rates?
Limited access to education, healthcare, and family planning.
A country just developed new medical technology that reduces infectious disease deaths. How would this likely shift their stage in the DTM?
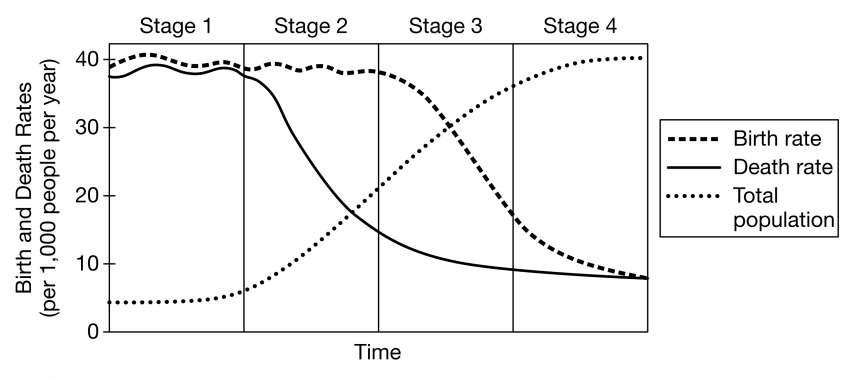
It would reduce death rates and push the country from Stage 1 → Stage 2.
Explain how a country like Japan can have a declining population even with good healthcare.
Low birth rates outweigh the number of people surviving to older ages.
Compare Type I and Type II survivorship in terms of parental care.
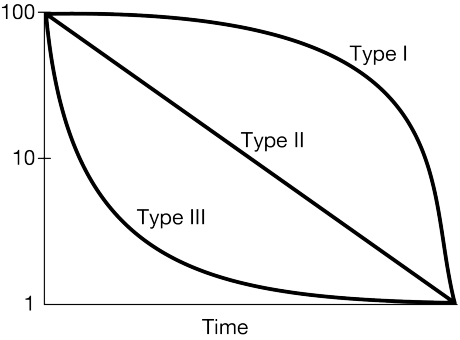
Type I species invest heavily in parental care; Type II species show constant mortality regardless of parental investment.
Describe why K-strategists are more vulnerable to habitat destruction than r-strategists.
They reproduce slowly and cannot quickly recover lost population size.
Explain how improved medical technology can shift a developing country’s demographics.
It lowers mortality, leading to rapid population increase.
Predict how a developing country’s population structure would change over 30 years if its birth rate remains high but its death rate rapidly declines.
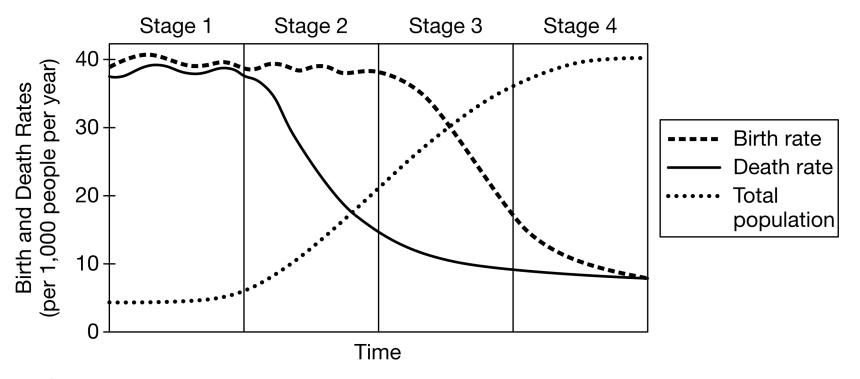
The population would grow rapidly, forming a pyramid-shaped age structure and increasing total population dramatically.
Using the concept of carrying capacity, explain why a population might level off after a period of exponential growth.
Resources become limited, shifting the population from exponential to logistic growth.
A population of seabirds has constant mortality across all ages. Propose which survivorship curve it fits and justify it using ecological traits.
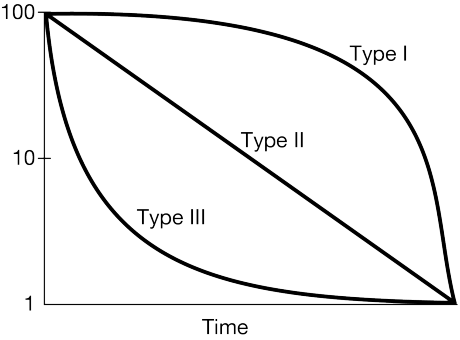
Type II; these species often face constant predation and environmental hazards across their lifespan.
A population of seals begins leveling off as it approaches 7,500 individuals. Explain why this is expected for a K-strategist species.
As resources become limited, growth slows and stabilizes at carrying capacity—typical of K-selected species.
A country introduces major healthcare and education reforms. Predict changes in fertility, mortality, and long-term population size.
Fertility and mortality decrease; population growth slows and stabilizes over time.