What kind of shock is from fluid loss?
Hypovolemic shock
What are the three stages of shock?
Compensated Shock, Decompensated Shock, and Irreversible Shock
A patient tells you she has an allergy to sulfa drugs. What part of the SAMPLE history has she given you?
A-Allergies
What is the definition of pathophysiology?
the processes associated with disease or injury
How is an NPA measured for a patient?
tip of nose to tip of earlobe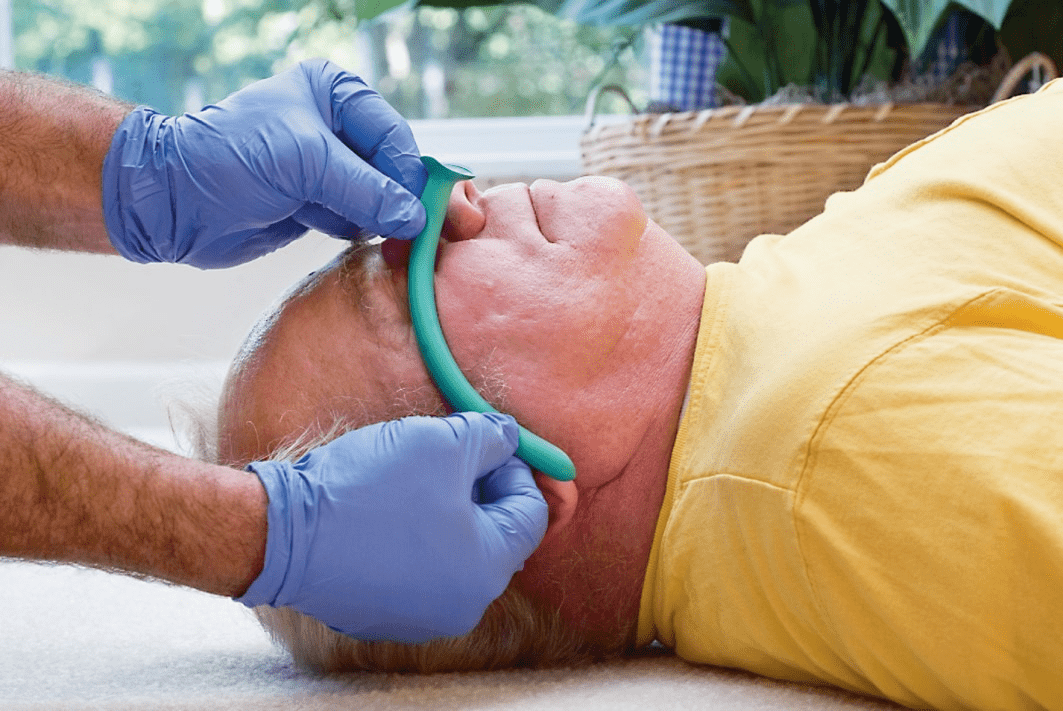
Your patient has admitted to ingestion of multiple alcoholic beverages, you note empty bottles of alcohol on the scene, and the pt has a strong odor of alcohol on their breath. They are AAOx2 and are refusing to go to the hospital. Can they refuse?
Nope
Heart or pump failure is what kind of shock?
Cardiogenic shock
What part of the cardiac pump function is the filling of the heart at the end of diastole?
Preload
A patient informs you that he had a bowl of walnut oatmeal ten minutes before his chest pain occurred. What two items from the SAMPLE history has he given you?
L and E-Last oral intake and Events leading up to the illness
What part of cellular metabolism occurs with oxygen? Which part occurs without oxygen?
aerobic-with oxygen anaerobic-without oxygen
Your patient is in the tripod position. Explain what this is and what it indicates.
difficulty breathing

You arrive on scene to an unconscious and pulseless patient. Under what consent can you treat this patient?
Implied Consent
What shock blocks blood flow or the ability of the heart to pump?
Obstructive Shock
What kind of shock is caused by massive widespread vasodilation and is treated with epinephrine?
anaphylactic shock
You are called to a section 8 housing apartment for a report of a domestic disturbance. You are the first unit on scene with Fire and PD closely behind. As you approach the building you hear a woman yelling. What are your next actions?
zero actions-scene safety first!
What is the major intracellular ion?
K+ Potassium
alveoli
How long is a PCR submissible in a court of law?
7 years
Structural issues with the "pipes" and their ability to channel blood to the body is what kind of shock?
Distributive shock
What specific aspect of a blood pressure would point to severe blood loss?
A narrow pulse pressure
Your patient has an arterial bleed that is hemorrhaging our of his left posterior thigh. She is also not breathing. Which item do you address first?
XABC-X=life threats
What does carbon monoxide do that when it enters the body?
It kicks off the oxygen from the red blood cells and bind more tightly to the RBCs.
Snoring respirations indicates what?
The tongue is blocking the airway
Your patient is found to be pulseless and apneic. Family is stating that they have a DNR but are unable to produce a physical copy. What are your next steps?
start CPR
What type of shock is identified with fever, altered mental status, tachycardia and an elevated white blood cell count indicating an infection?
Septic Shock
In the stage of shock known as irreversible shock there is wide spread failing and death of organs. This is called MODS. What does MODS stand for?
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
What are all the items of NEXUS criteria?
The initial steps of cellular metabolism is called what?
Glycolysis
What is the normal range for a capnometry reading?
35-45
You have a 16 year old female pt complaining of severe abdominal pain and reports she is in her second trimester. Her appearance matches her information and she is asking to be transported to the hospital. Parents state they do not want her transported. What is your next steps?
transport the patient
What two hormones are released by the adrenal glands that play a key factor in the sympathetic nervous system and the "fight-or-flight" response?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
What receptors does epinephrine bind to?
Alpha and Beta Receptors
You note a medical bracelet on a patient that says "Allergies PNC" on one side and "VWD" on the other side. What do these mean?
allergic to penicillin and Von Willebrand Disease
What occurs when there is severe muscle breakdown caused by the interruption of ATP production, the release of potassium and other compounds, and an overload of calcium?
Rhabdomyolysis
What is the name of the respiratory pattern often observed with patients that are in diabetic ketoacidosis(DKA)?
Kussmaul Respirations
What acronym is used to determine decision making capacity of a patient.
CURV-Choice, Understanding, Reason, and Values