What do "H" and "L" mean on a weather map?
These symbols represent HIGH pressure and a LOW pressure systems on a weather map.
The boundary between two different air masses is called what?
A front
This older technology is still used to collect weather data from high in the atmosphere (but they must be replaced fairly regularly).
Weather balloons
What do we call a large region of the atmosphere in which all the air has similar properties throughout?
An "air mass"
The lines on a weather map that join places of equal pressure are called _____.
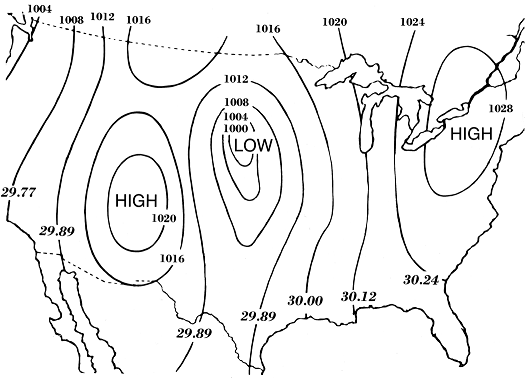
Isobars
What type of weather is found in a low pressure system?
Cloudy skies, storms, precipitation (and possibly even severe weather like thunderstorms, tornadoes, or hurricanes)
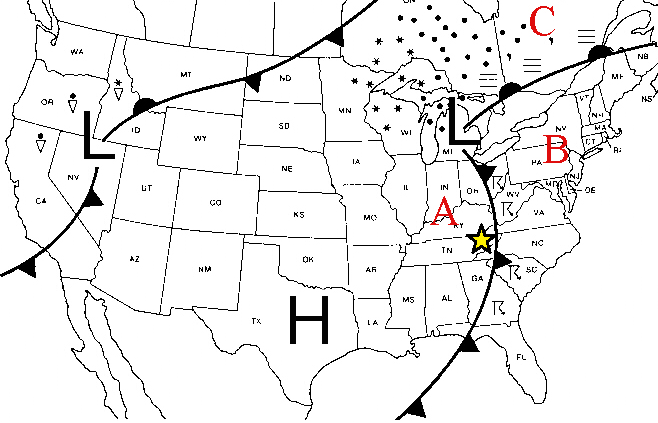
In THIS type of front, a mass of cold air moves in underneath a mass of warm air.
A cold front.
This technology sends photos from space back to earth and shows large weather patterns.
What is a satellite?
When two pockets of air (with different temperatures) collide, the cool air will always move in which direction?
Down (or "sinks" beneath the warm air)
What TWO descriptions would accurately describe our weather according to the map?
Cooler, clear skies
[not cloudy, not rainy, not warmer]
Clear skies with little or no clouds would be the typical weather during which type of weather system?
A high pressure system
THIS type of front involves cool air catching up with a warm front, moving underneath the warm front, and then catching up to another cold front, creating a raised "wedge" of warm air between two masses of cooler air.
Occluded front 
This ground-based technology is used to collect data about both precipitation and wind speed over large regions.
Doppler radar
Which type of air can hold more humidity: warmer air or cooler air?
Warmer air
Air will always move from ______ pressure areas to ______ pressure areas.
"high" --> "low"
What direction does a mass of warmer air always want to move?
Up (or "rise")
THIS type of front usually brings light but steady precipitation. After it passes, the weather is usually warmer and more humid.
A warm front 
What instrument is used to measure air pressure?
A barometer 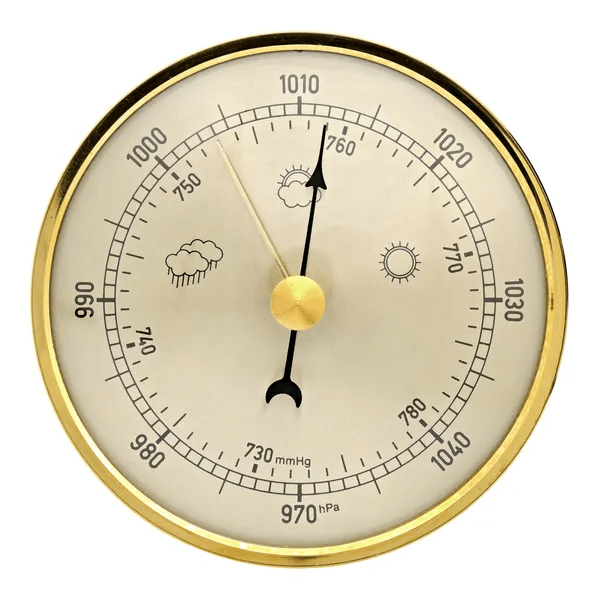
Warm air typically rises over cooler air because warm air is less ___________.
Dense
What phenomenon causes wind currents to occur?
Convection between warm and cold air...or movement from high pressure to low pressure
How is the pressure of a cool air mass different than that of a warm air mass?
Cooler air always has HIGHER air pressure than warm air
A cold front moving through will typically bring what TWO changes to the local weather?
Brief but heavy storms (or thunderstorms), a drop in temperature, and - after the front passes - weather that is clearer with cooler temperatures and lower humidity
Name one (specific) positive effect technology has had on weather forecasting over the last fifty years:
Greater accuracy, more detailed weather data, better predictions, forecasts can be made further in advance, better warning systems for severe storms...
Name TWO measurable properties of an air mass that help meteorologists forecast weather.
Temperature, humidity, and/or air pressure (also direction of movement)
What direction does most weather in the US usually travel (due to global wind currents)?
From the west to the east. --> -->