Name 3 risk factors for developing a pressure Injury 
Poor nutrition, dehydration, sensory impairment,
obesity, smoking, low toe pressures
prior pressure injuries
hypoxia, peripheral vascular disease
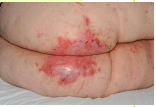
Redness or skin breakdown, usually found beneath abdominal folds and in the groin area, associated with moisture.
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis - IAD
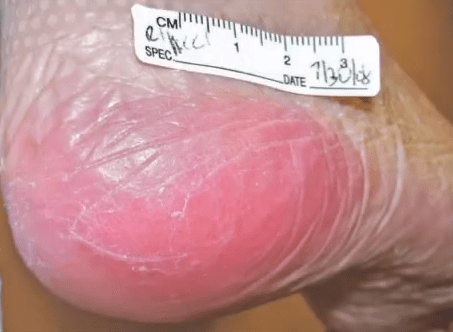
Intact, non-blanching redness found on a bony prominence.
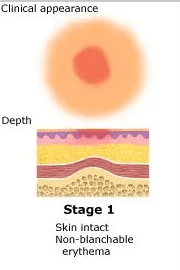
Stage 1 Pressure Injury
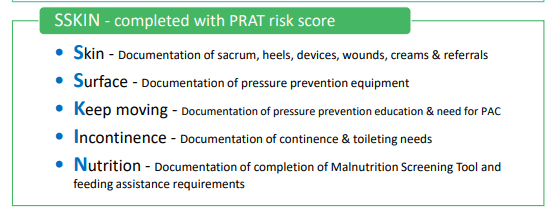
This Documentation is completed BD and assists staff to complete a full skin assessment and ensure relevant PI prevention equipment and referrals are in place.
SKINN Bundle
These devices reduce the risk of pressure injuries by keeping linen off the toes and feet
Bed Cradles
Greatest risk factor for pressure injury development
Immobility

List 5 medical devices that should be checked and adjusted each shift (or sooner) to reduce the risk of them causing a pressure injury.
IDC, NGT, PICC, HFNP tubing, Oxygen tubing, NIV masks, TED's, IVC's, Pulse Oximeter, drain tubes, NPWT, ICC
A pressure injury that can appear as a non blanching bruising or a blood filled blister. Often feels boggy on palpation.
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury

By typing this phrase, staff can fill in an auto text template to describe a NEWLY found Pressure Injury
.PressureInjury
This Intervention should be recommended for offloading pressure from patients heels
Pillow/Wedge
The amount of time needed for immobility to cause tissue ischemia.

20 minutes
*although ongoing research is suggesting 15mins now.
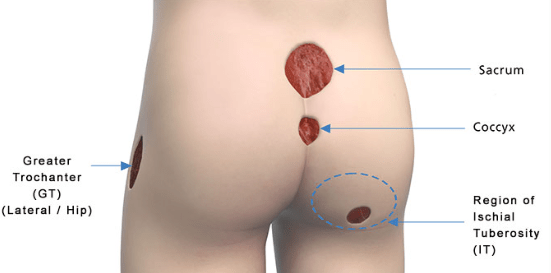
Two most common anatomical areas for developing pressure areas/pressure injuries.
Heels and sacrum
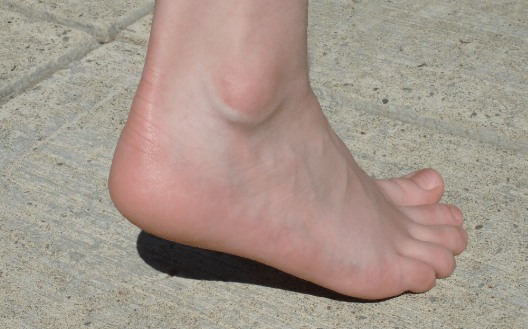
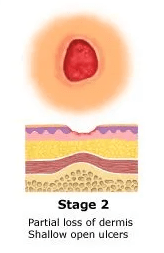
A pressure injury stage where the dermis has been damaged but subcutaneous tissue is not visible. May also present as an intact or broken serous filled blister.
Stage 2 Pressure Injury
After completing the braden score, staff can use this box to assign a pressure risk score using their own clinical judgement.
Clinicians Risk Assessment
This brochure can be given to patients and carers in conjunction with verbal education about pressure injury prevention
"Working together to prevent a pressure injury"

Parallel friction force that occurs as patients are dragged during repositioning as opposed to being lifted and moved.
Shear
This term describes the development of a pressure injury because of a medical device
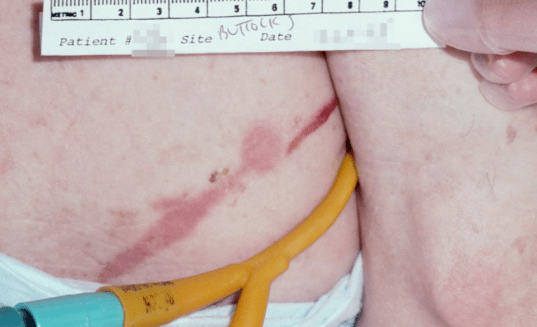
Medical device related pressure injury (MDRPI)
A pressure injury that has an obscured wound bed, may be obscured by slough or necrotic tissue.
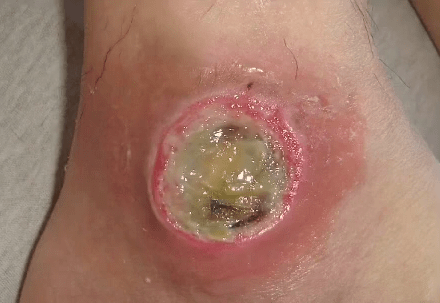
Unstageable Pressure Injury
This is the frequency in which the PRAT should be completed and repeated.

On Admission (if indicated)
+ weekly and/or change of condition
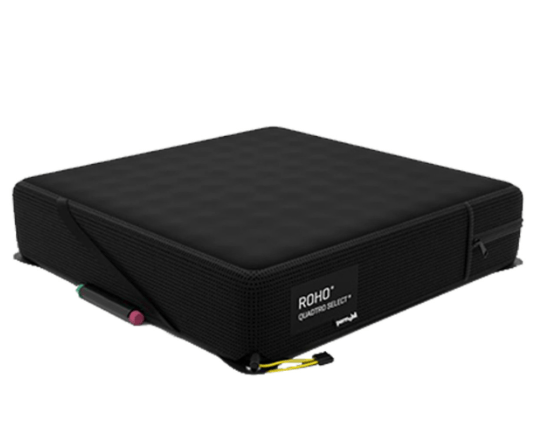
These devices have multiple adjustable valves to allow for a tailored fit.
They are the gold standard PI prevention production prescribed by OT's to prevent pressure injuries when patients are sitting out of bed.
ROHO Cushions

Two locations to develop a PI when a cervical collar is insitu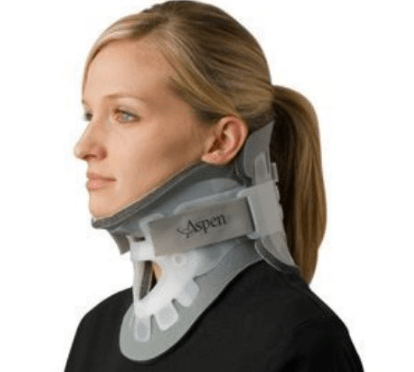
Mandible
Occiput
clavicle
upper chest
Name the 3 extrinsic factors that contribute to the development of a pressure injury
Moisture
Friction
Shear
This PRAT score should be automatically assigned when a patient has an existing pressure injury, or a history of pressure injuries.
HIGH to Very HIGH
The SKINN Bundle abbreviation relates to these words.
Skin, Surface, Keep Moving, Incontinence/Moisture and nutrition.
This type of dressing is used for pressure injury prevention.
5 layer silicone foam dressing