What are the preventative components of a yearly physical exam for men and women? Name 3 for each
depression screen
•Men
•Depression
•Colon Cancer
•Lung cancer
Diabetes
•Depression
female:
•Chlamydia
•Breast Cancer
•Colon Cancer
•Cervical Cancer
•Diabetes
Lung cance
Name 3 important vaccines in adulthood one should consider
•Influenza
•Pneumococcal
•HPV vaccination
•Zoster
•Tdap
At what blood pressure do we diagnose hypertension
•Diagnosis > 140/90 on at least two consecutive visits. Unless sbp >210, dbp >120, end organ damage
What are types of contraception and what are contraindications to them
oral contraception- estrogen and progesterone
: hx venous thrombosis, cardiovascular dz, brest ca, liver disease, undx vaginal bleeding, lactation, smoking
Depo
IUD
nexplanon
nuvaring
How do you diagnose diabetes
•FBS greater than 126 on two or more occasions
•Random glucose of over 200 with symptoms
•2 hour post prandial greater than 200
•Prediabetes/IFG fasting 100-126
•A1C >6.5%
When do pap smear screening start and how often does a woman have them?
•Start over age 21
•Don't do if hysterectomy (including cervix) done for benign reasons
•Every 3 years (unless abnormal)
•Stop age 65 (USPSTF) if no abnormal in last 10 years
•HPV testing for over 30 and reflex testing ascus or greater
•Colposcopy if acus +hpv, hgsil, lsil , consider +hpv and >30 yo
•
How often do you get a TDAP vaccine?
every 10 years
at what age are we concerned about secondary HTN when we diagnose HTN and what is the workup
age can tell you a lot- 40 and up I dont do a workup but under this you need: renal US, aldosterone/ renin ratio/ CMP, and a good history
What vaccines do all pregnant women get
TDAP
how do you diagnose COPD? What specifically on testing shows COPD
you need a PFT- •FEV1 and ratio of FEV1: FVC reduced ( < 70%)
GOLD criteria-
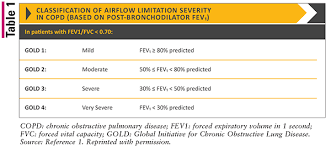
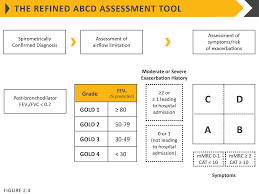
When does someone get a colon cancer screening?
fobt annual, flex sig with or wihtout q 3 years
Colonoscopy 10 years stop 75-85.
start at 45
Cologuard every 3 years starting at 45
it all depends on what the find on colonoscopy-
2 main classes of precancerious lesions serrated and conventional adenomas ( adenomas are 70% of the precursors to cancer)
villous adeonomas more likely to cause cancer
When do you start shingles vaccine? Do you ever start earlier
age 50 - never earlier
name the classes of HTN medications
ACE/ARB
beta blocker
CCB
diuretics
•Centrally acting sympatholytic inhibitors
•Alpha blockers
when is a triple screen offered and what does it include
•HCG
•estriol
•AFP
•High- neural tube defect or spina bifida or inaccurate dates
•Low-down syndrome , trisomy 18
•
Inhibin A ( quad screen)
what preventative measures are important for diabetics and COPD patients
vaccines: they need PCV
vitals: known about HTN is important, oxygen status
smoking cessation is key for both
What are criteria for low dose lung CT screening
age 50-80 hx smoking 20 pk year and quit whin past 15 years. Stop once you have not smoked for 15 years.
why are HPV vaccines important and what are the age ranges to get one and how many vaccines are there
prevent cervical cancer, testicular and esophageal cancer from strains HPV 16, 18, 21
Male 9–26 years and females aged 9–45 years
If before 15 can get 2 vaccines 15 and older 3
tell me common side effects of :
ACE
beta blocker
CCB
ACE- cough
beta blocker- SOB in asthma or erectile dysfunction in males
CCB- swelling in legs
What testing happens during 26-28 weeks during pregnancy
glucose challenge test
hemoglobin test for RH factors
GBS is at 35 weeks
what are the specific care guidelines for diabetics
•Annual foot exam (technically every visit)
•Annual ophthalmology exam
•Annual measurement of microalbumin
•Blood pressure, lipids, AIC, renal function
•Vaccinations: influenza, pneumococcal
•Discuss diet/exercise goals
•Smoking cessation
Consider ABI/eval for PAD
What is the depression screen name and what are the components of it ( name 4 components )

When do you start pneumococcal vaccine- and which is first
what are special circumstances to start early and which do you start first
Pneumococcal copd, asthma, dm earlier than 65 then once after 65
23 before then 13 and 23 again
PCV 15 and 20 now in outpatient settings-
for those who have never received a vaccine- give PCV20 and vaccine schedule now complete
if 15 used then follow with one dose PCV 23 in 1 year
recevied just 23--> 15 or 20
splenectomy 2 month follow up after the initial vaccination • Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23 – Pneumovax 23) 0.5 mL IM • Meningococcal vaccine 0.5 mL IM • Meningococcal serogroup B 0.5 mL IM (> 1 month after first dose) Long-term follow up • Pneumococcal polysaccharide 0.5 mL IM 5 years after the first dose of this vaccine • Meningococcal vaccine 0.5 mL IM recommended every 5 years • No additional haemophilus vaccine is needed • Seasonal influenza vaccine is indicated annually
What are guidelines for hyperlipidemia ( AKA when do we treat) - for healthy and for special populations
•Treatment if LDL >70 and diabetes, hx stroke, MI
•For healthy individuals, if LDL>190
•If LDL between 70 and 190, use risk calculator to determine 10 year risk.
•Select Statins first line
What testing is done at every obstetric visit
urine- only population you treat asymptomatic bacteria
how do you treat both COPD and diabetes- give me starting treatment for both


•Metformin is the standard
•Sulfonylureas
•Thiazolidinones (not used much)
•Dpp4 inhibitors
•GLP analogues
•SGLT2 inhibitors
•Add basal insulin AIC over 10, failure to reach goal
•Goal aic is 6.5, adjust if elderly