33. An older adult presents to the emergency department with confusion after falling while walking. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Intracranial mass on MRI
B. Epidural hematoma on X-ray
C. Subdural hematoma on CT scan
D. Intraventricular hemorrhage on MRA
E. Subarachnoid hemorrhage on PET scan
C. Subdural hematoma on CT scan
Blood collects between the dura mater and arachnoid mater.
Risk factors include age, blood thinners, chronic alcohol use.
Sx include headache, confusion, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness.

19. An argumentative ten-year-old who displays persistent anger outbursts, vindictiveness, and deliberately annoys adults most likely has which of the following disorders?
A. Conduct disorder
B. Oppositional defiant disorder
C. Antisocial personality disorder
D. Intermittent explosive disorder
E. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
B. Oppositional defiant disorder
DSM-V Criteria of ODD:
A pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness lasting at least 6 months as evidenced by at least four symptoms from any of the following categories, and exhibited during interaction with at least one individual who is not a sibling.
Angry/Irritable Mood:
1. Often loses temper.
2. Is often touchy or easily annoyed.
3. Is often angry and resentful.
Argumentative/Defiant Behavior
4. Often argues with authority figures or, for children and adolescents, with adults.
5. Often actively defies or refuses to comply with requests from authority figures or with rules.
6. Often deliberately annoys others.
7. Often blames others for his or her mistakes or misbehavior. Vindictiveness
8. Has been spiteful or vindictive at least twice within the past 6 months.
Note: The persistence and frequency of these behaviors should be used to distinguish a behavior that is within normal limits from a behavior that is symptomatic. For children younger than 5 years, the behavior should occur on most days for a period of at least 6 months unless otherwise noted
For individuals 5 years or older, the behavior should occur at least once per week for at least 6 months, unless otherwise noted (Criterion A8). While these frequency criteria provide guidance on a minimal level of frequency to define symptoms, other factors should also be considered, such as whether the frequency and intensity of the behaviors are outside a range that is normative for the individual’s developmental level, gender, and culture. B. The disturbance in behavior is associated with distress in the individual or others in his or her immediate social context (e.g., family, peer group, work colleagues), or it impacts negatively on social, educational, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. C. The behaviors do not occur exclusively during the course of a psychotic, substance use, depressive, or bipolar disorder. Also, the criteria are not met for disruptive mood dysregulation disorder.
118. A 75-year-old patient reports brief episodes of recurrent jabs of pain in the left lower jaw. The pain is so severe that he winces with each bout. He has noticed that the pain can also be triggered when he shaves or brushes his teeth. Magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain shows no abnormalities to explain the symptoms. This patient will most likely benefit from treatment with which of the following medications?
A. Oxycodone
B. Sumatriptan
C. Indomethacin
D. Corticosteroids
E. Carbamazepine
E. Carbamazepine

52. Which of the following is an example of classical conditioning?
A. Verbal praise for patients who quit smoking
B. Contingency contracts with non-compliant patients
C. Response prevention for patients with compulsive hand washing
D. Chemotherapy patients who become nauseous when driving to the hospital
E. Patients receiving extra dessert at lunch for attending inpatient group therapy
D. Chemotherapy patients who become nauseous when driving to the hospital
74. A patient has recently begun to see a new psychiatrist for combined medication management and interpersonal psychotherapy. How should the psychiatrist record the information about these sessions?
A. Medication information should go in the medical record, and all information about psychotherapy should go into process notes.
B. Information about medication should go in the medical record; details of psychotherapy are private and it is not necessary to record them.
C. Everything should go in the medical record; process notes are not appropriate for a treatment that includes medication management.
D. Diagnosis, functional status, and treatment plan should be included in process notes, and everything else should go in the medical record.
E. Sensitive information exclusively relevant to the treating provider should go in process notes; other information about medication and therapy goes in the medical record.
E. Sensitive information exclusively relevant to the treating provider should go in process notes; other information about medication and therapy goes in the medical record.
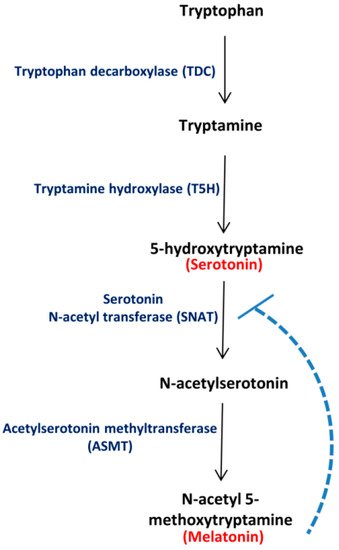
5. Melatonin is derived from which of the following neurotransmitters?
A. Serotonin
B. Histamine
C. Dopamine
D. Acetylcholine
E. Norepinephrine
A. Serotonin
144. Which of the following is the risk of individuals developing schizophrenia when a sibling has the disorder but the parents do not?
A. 1%
B. 10%
C. 50%
D. 90%
B. 10%
Most people with a close relative who has schizophrenia won't develop it themselves. The risk of developing schizophrenia increases by 10% if a parent, sibling, or half-sibling has it, and by 13% if one or more children have it.
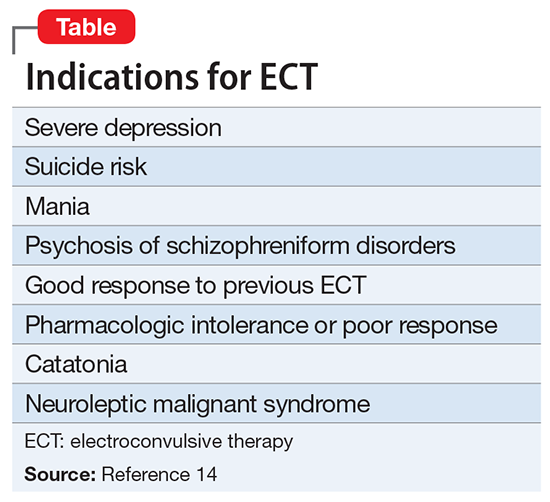
87. An 80-year-old patient with major depressive disorder is admitted to the internal medicine service for failure to thrive. The patient reports months of depression and anhedonia, spending all day in bed and sleeping up to 15 hours per day. For the last three weeks, the patient has been refusing nearly all food, resulting in a 20-pound weight loss. The patient has been consistently taking mirtazapine 45 mg every night, following unsuccessful courses of sertraline and fluoxetine. Which of the following is the best next step in treatment?
A. Switch to duloxetine
B. Increase mirtazapine dose
C. Start electroconvulsive therapy
D. Add olanzapine oral dissolving tablet
E. Refer to cognitive-behavioral therapist
C. Start electroconvulsive therapy
115. Which of the following is the goal of motivational interviewing in the treatment of substance use disorders?
A. Support abstinence
B. Encourage stress reduction
C. Engage in planning for change
D. Alter reward-seeking behaviors
E. Promote healthy social networks
C. Engage in planning for change
Goal of MI is to resolve ambivalence about behavior and increase internal motivation to make positive changes.

134. To a psychiatrist evaluating a person for purposes of Social Security Disability, which of the following criteria would support evidence of impairment-related functional limitations?
A. No current gainful employment
B. Treatment at mental health facility
C. Evidence of ongoing substance use
D. Marked restriction in activities of daily living
E. Comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension
D. Marked restriction in activities of daily living
Criteria to support evidence of impairment-related functional limitations for Social Security Disability (must be ongoing for at least 12 mons):
Marked restrictions in activities of daily living
Significant difficulties maintaining social functioning
Marked difficulties with concentration, persistence, or pace, frequent episodes of decompensation
Limitations in the ability to understand, remember, or apply information
Limitations in interacting with others
Essentially, any evidence demonstrating how a medical condition significantly impacts your ability to perform basic work activities in areas like physical movement, mental functioning, or social interaction
85. Which of the following waveforms is a characteristic of deep Stage 3 sleep on an electroencephalograph?
A. Delta
B. Alpha
C. Sigma
D. Spindles
E. Sawtooth
A. Delta
The third stage of sleep is also known as deep sleep.
The brain primarily produces slow, large amplitude brain waves called delta waves.

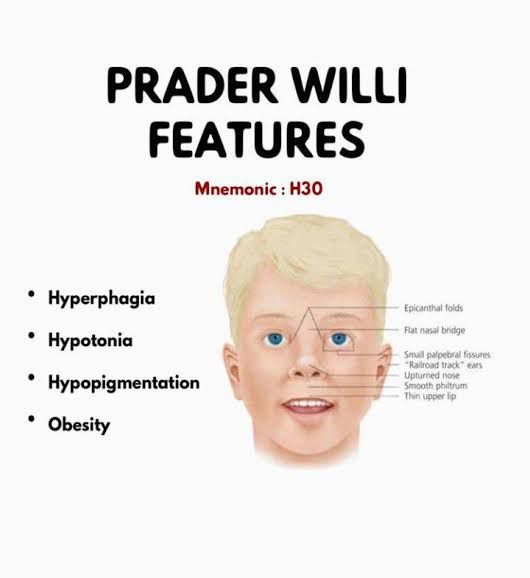
126. A patient presents with a history of failure to thrive in infancy, hyperphagia, early obesity. hypogonadism, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The patient is noted to have short stature with small hands and feet. This patient most likely has which of the following congenital syndromes?
A. Down
B. Williams
C. Fragile X
D. Angelman
E. Prader-Willi
E. Prader-Willi Syndrome
Chromosome 15 from father isn't inherited either via deletion or imprinting from mother's chromosome.

144. A patient with bipolar disorder is started on valproic acid and subsequently experiences rapid symptom improvement but has mild transaminase elevation up to 1.5 times the upper limit of normal on follow-up labs. The patient has no associated physical symptoms. What intervention should be performed by the psychiatrist?
A. Valproic acid should be continued, but the dosage should be decreased.
B. The patient should be sent to the emergency room for a more complete assessment.
C. Current dosage of Valproic acid should be maintained and Lactulose should be added.
D. Current dosage of Valproic acid should be maintained with more frequent monitoring of liver function.
E. Valproic acid should be discontinued immediately and alternative mood stabilization medication started.
D. Current dosage of Valproic acid should be maintained with more frequent monitoring of liver function.
-Valproate acid can cause asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes in 5–10% of patients (typically transitory and dose-related).
-If enzyme level increase is moderate but pt is asymptomatic, continue medication. Discontinue if symptomatic.
Stahls:
-Before starting treatment, complete blood counts, coagulation tests, and liver function tests
-Consider coagulation tests prior to planned surgery or if there is a history of bleeding
-During the first few months of treatment, regular liver function tests and platelet counts
-Can be shifted to once or twice a year for the remainder of treatment.
112. A four-year-old has all 20 primary teeth, a slim torso and long legs. The child can walk and run, but does so quickly and intensely, often walking up on toes. The child is ambidextrous and can ride a small bicycle with training wheels although appears a little uncertain when doing so. Which of these physical findings should raise a concern about the child's physical development?
A. Ambidexterity
B. Walking on toes
C. Presence of all baby teeth
D. Pace and intensity of walking
E. Uncertainty when riding a bicycle
B. Walking on toes
-It is common for children of 10-18 months to walk on tip toes when they are learning to walk as it can help with their balance. Some children can continue this up to the age 3 yo. Past that, it may be due to Muscular dystrophy, ASD, and CP.
-Children typically begin losing their baby teeth, also called primary teeth, around age 6, and usually finish by age 12.
-Training wheels acceptable from 2-3 yo. They can transition out of training wheels between 4-8 yo.
21. To be eligible for special education services a student must require specific interventions in order to make progress in school, and meet which of the following criteria?
A. Have failed at least one grade
B. Be under a psychiatrist's care
C. Have a documented disability
D. Require pharmacologic treatment
E. Have failed all other less restrictive alternatives
C. Have a documented disability
-Disability: The child must have a disability
-Need: The child must need special education services to benefit from education as a result of their disability
-Severity: The disability must be severe enough to require special education services
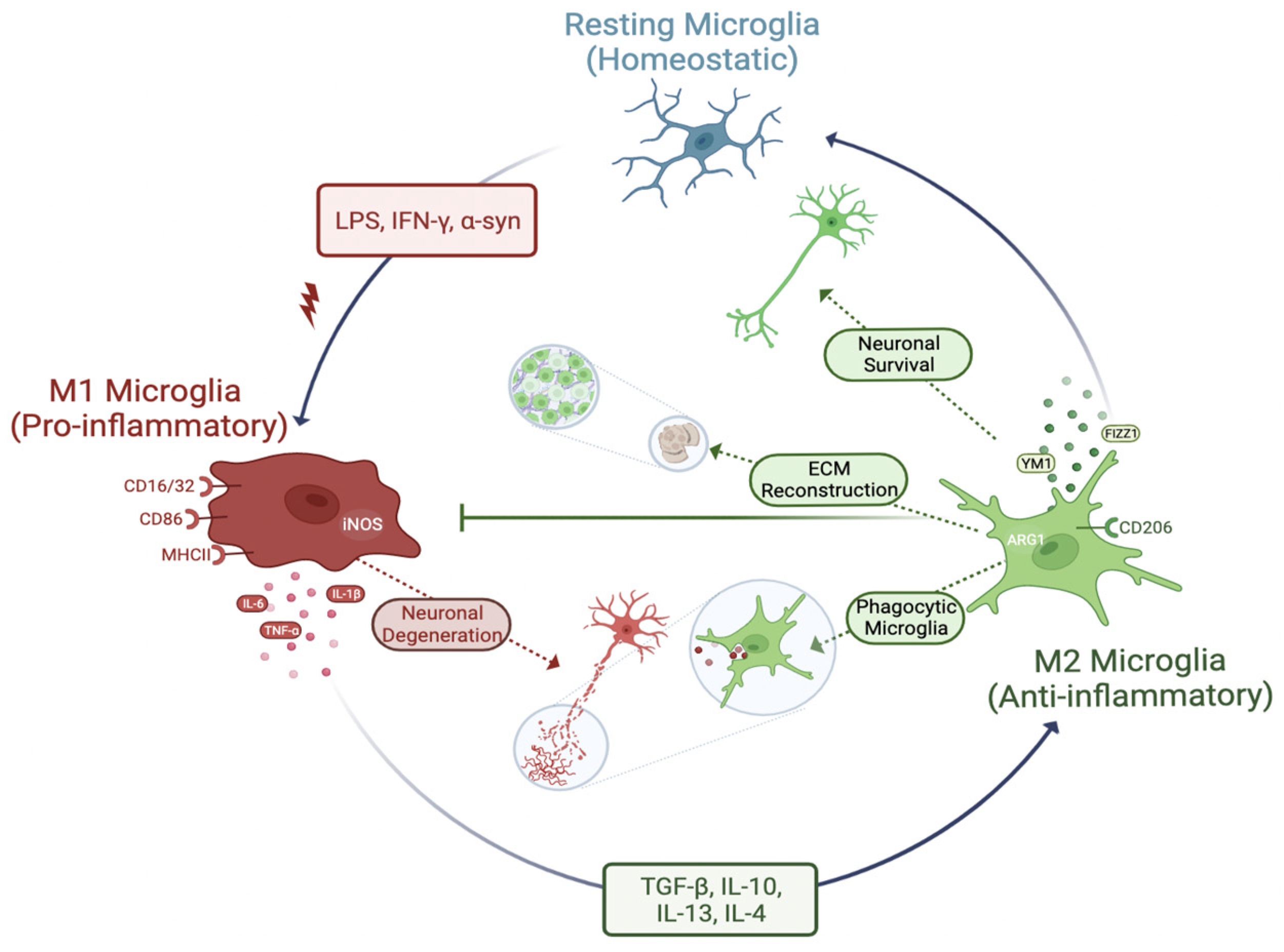
82. Which of the following types of cells secrete the innate proinflammatory cytokines TNF-a and IL-1ẞ in patients with inflammatory conditions that affect the brain?
A. Microglia
B. Neuroblasts
C. Interneurons
D. Pyramidal cells
E. Oligodendrocytes
A. Microglia
Microglia are the primary cells in the central nervous system responsible for secreting innate pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) when activated by injury, infection, or other pathological stimuli; essentially acting as the immune response within the brain by releasing these signaling molecules to initiate inflammation.
67. Which of the following conditions is a risk factor for the future onset of neurodegenerative synucleinopathies?
A. Restless leg syndrome
B. Periodic limb movements
C. Insufficient sleep syndrome
D. Psychophysiologic insomnia
E. REM sleep behavior disorder
E. REM sleep behavior disorder
-Synucleinopathies include Parkinson’s, LBD, or multiple system atrophy
-REM sleep behavior disorder associated with alpha synuclein protein aggregation
REM sleep Behavior Disorder DSM-5 Criteria:
A) Repeated episodes of arousal during sleep associated with vocalization and/or complex motor behaviors.
B) These behaviors arise during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and therefore usually occur more than 90 minutes after sleep onset, are more frequent during the later portions of the sleep period, and uncommonly occur during daytime naps.
C) Upon awakening from these episodes, the individual is completely awake, alert, and not confused or disoriented.
D) Either of the following: REM sleep without atonia on polysomnographic recording OR a history suggestive of REM sleep behavior disorder and an established synucleinopathy diagnosis (e.g., Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy).
E) The behaviors cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning (which may include injury to self or the bed partner).
F) The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g. - a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition.
G) Coexisting mental and medical disorders do not explain the episodes
137. Which of the following medications may induce the metabolism of mirtazapine?
A. Carbamazepine
B. Fluoxetine
C. Lithium
D. Paroxetine
E. Sertraline
A. Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is a CYP450-3A4 inducer. Mirtazapine is partially metabolized by CYP450-3A4 → decreased serum mirtazapine concentration.
146. According to Mary Ainsworth's work on social development, which of the following types of infant attachment is most strongly correlated with a history of maltreatment?
A. Secure
B. Avoidant
C. Ambivalent
D. Disorganized-disoriented
D. Disorganized-disoriented
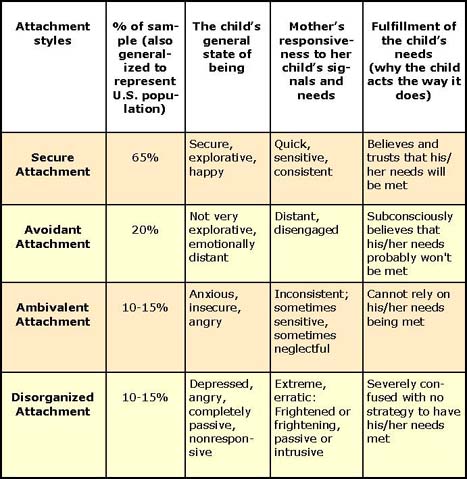
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/attachment-styles-2795344-v1-5c61db3346e0fb0001ca8cb1.png)
32. The issue of "dual loyalty" is a particularly prevalent problem in which system of care?
A. Private practice
B. Correctional settings
C. Public hospital systems
D. Integrated behavioral health
E. Community mental health centers
B. Correctional settings
Dual loyalty is the clinical role conflict between professional duties to a patient and obligations, expressed or implied, to the interests of a third party such as an employer, an insurer, or the state.
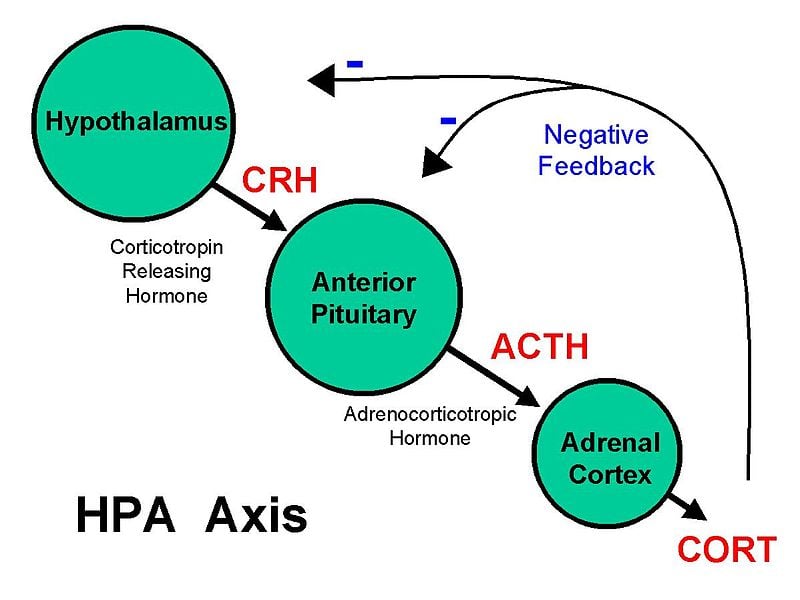
65. In which region of the hypothalamus is corticotropin-releasing hormone secreted?
A. Arcuate nucleus
B. Ventromedial nucleus
C. Paraventricular nucleus
D. Suprachiasmatic nucleus
E. Tubero-mamillary nucleus
C. Paraventricular nucleus
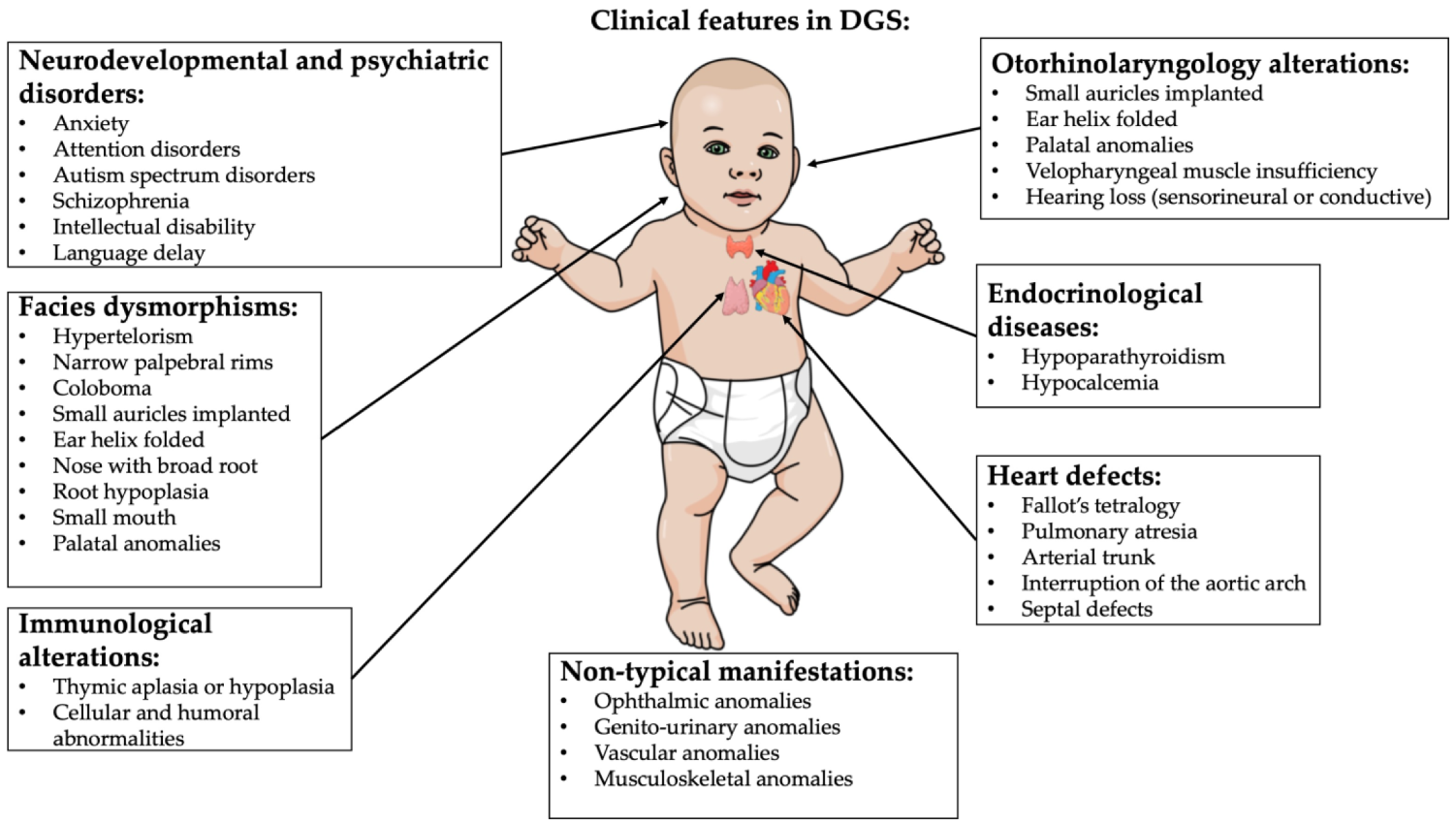
132. Chromosomal microdeletions, at region q11.2 of human chromosome 22 are most likely to present with symptoms of which of the following adult psychiatric disorders?"
A. Schizophrenia
B. Bipolar disorder
C. Major depression
D. Antisocial personality disorder
E. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
A. Schizophrenia
17. The risk of tardive dyskinesia depends partly on the blood concentration of which of the following?
A. Oxytocin
B. Estrogen
C. Testosterone
D. Progesterone
E. Growth hormone
B. Estrogen
Estrogen may play a role in tardive dyskinesia (TD), a condition that postmenopausal women are most likely to develop.
Estrogen may have neuroprotective properties that shield nerve cells from damage. When estrogen levels decrease, this protection may be reduced, making women more susceptible to the neurotoxic effects of antipsychotic medications, which can increase the risk of TD.
Estrogen may also act as an antioxidant and affect dopamine-related actions.
119. At what stage in Piaget's theory of cognitive development can a child recognize that when equal amounts of water are poured into a tall, skinny glass and a wide, short glass they hold the same amount of water?
A. Sensorimotor
B. Preoperational
C. Formal operations
D. Abstract reasoning
E. Concrete operations
E. Concrete operations

92. Which of the following has been found to reduce involuntary admissions for mental health treatment?
A. Integrated care
B. Treatment adherence therapy
C. Psychiatric advanced directives
D. Court-ordered outpatient treatment
E. Financial incentives to improve antipsychotic adherence
C. Psychiatric advanced directives
Patient autonomy: Allows patients to outline their preferences for mental health treatment and appoint a decision-maker to make treatment decisions on their behalf.
Improved communication
Early intervention: PADs can help healthcare providers respond quickly to crises by outlining warning signs and preferred treatment approaches. This can help reduce the severity and duration of crises, which can lead to fewer involuntary hospitalizations.
Prevent crisis situations: reduce the use of safety interventions like seclusion or restraint. When people with serious psychiatric conditions have mental health crises, they may be unable to communicate their needs or advocate for themselves, which can lead to treatment they wouldn't choose.
One study found that participants who used peer worker-facilitated PADs experienced significantly fewer compulsory admissions than those in a control group. Another study found that people who completed PADs had lower odds of experiencing coercive crisis interventions (CCIs), such as being involuntarily committed or transported by police to a treatment facility.