111. A patient is found to have decreased movement of the left arm. When asked about this, the patient states, "It is not my arm." Which of the following brain regions is associated with this phenomenon?
A. Cerebellum
B. Frontal lobe
C. Parietal lobe
D. Occipital lobe
E. Temporal lobe
C. Parietal lobe

Generally, if the right parietal lobe is damaged, patients will ignore the left side of their body.
132. Which of the following patient characteristics best differentiates bulimia nervosa from binge eating disorder?
A. Normal BMI
B. Duration of symptoms
C. History of laxative abuse
D. Degree of control over food intake
E. History of non-suicidal self-injurious behavior
C. History of laxative abuse
Bulimia Nervosa DSM-V Criteria:
Recurrent episodes of binge eating, as characterized by both:
Eating, within any 2-hour period, an amount of food that is definitively larger than what most individuals would eat in a similar period of time under similar circumstances. A feeling that one cannot stop eating or control what or how much one is eating.
Recurrent inappropriate compensatory behaviors in order to prevent weight gain such as self-induced vomiting; misuse of laxatives, diuretics, or other medications; fasting or excessive exercise.
The binge eating and inappropriate compensatory behaviors occur, on average, at least once a week for 3 months.
Self-evaluation is unjustifiability influenced by body shape and weight.
The disturbance does not occur exclusively during episodes of anorexia nervosa.
Binge Eating Disorder DSM-V Criteria:
Recurrent episodes of binge eating. An episode of binge eating is characterized by both of the following:
Eating, in a discrete period of time (e.g., within any 2-hour period), an amount of food that is definitely larger than most people would eat in a similar period of time under similar circumstances. A sense of lack of control over eating during the episode (e.g., a feeling that one cannot stop eating or control what or how much one is eating)
The binge-eating episodes are associated with three (or more) of the following:
Eating much more rapidly than normal. Eating until feeling uncomfortably full. Eating large amounts of food when not feeling physically hungry. Eating alone because of feeling embarrassed by how much one is eating. Feeling disgusted with oneself, depressed, or very guilty after overeating
Marked distress regarding binge eating is present.
The binge eating occurs, on average, at least once a week for 3 months.
The binge eating is not associated with the regular use of inappropriate compensatory behaviors (e.g., purging, fasting, excessive exercise) and does not occur exclusively during the course of anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa.
135. A 30-year-old woman with no past psychiatric history is hospitalized with symptoms of mania. She informs the treating psychiatrist of her plan to become pregnant soon. Which of the following medications should be avoided if at all possible?
A. Olanzapine
B. Lamotrigine
C. Ziprasidone
D. Valproic acid
E. Lithium carbonate
D. Valproic acid
Use of Valproic acid in pregnancy may lead to:
Birth defects: Including neural tube defects, heart defects, cleft lip, spina bifida, atrial septal defect, cleft palate, hypospadias, and polydactyly.
The risk of neural tube defects is 1-2% when valproic acid is taken during the first trimester of pregnancy, which is 10-20 times higher than the general population
Cognitive impairment: Including lower cognitive test scores and autism spectrum disorders
Other pregnancy-related problems: Including low birth weight, temporary low blood sugar levels, and temporary behavior changes in the newborns
90. Which of the following refers to a process in which an infant acquires basic emotions through interactions with others?
A. Mimicry
B. Empathy
C. Attachment
D. Self-regulation
E. Goodness of fit
A. Mimicry
Mimicry is the tendency of infants to unconsciously and spontaneously copy others' actions.
Infants primarily learn about basic emotions through interactions with others, particularly by mimicking facial expressions and emotional cues displayed by caregivers.
Emotional mimicry allows them to gradually understand and express emotions themselves as they develop.
9. Which of the following often provides the strongest evidence for clinical decision making?
A. A randomized control trial
B. Several well-designed cohort studies
C. A meta-analysis of relevant randomized control trials
D. The opinions of authorities and/or expert committees
E. A systematic review of descriptive and qualitative studies
C. A meta-analysis of relevant randomized control trials
61. Orexin-producing neurons originate in what area of the brain?
A. Pineal gland
B. Raphe nuclei
C. Hypothalamus
D. Locus coeruleus
E. Pontine reticular formation
C. Hypothalamus
Orexin (aka hypocretin) regulates wakefulness, appetite, reward seeking, and pain.
It is not adequately produced in narcolepsy.
The hypothalamus also secretes the following hormones:
54. A three-year-old child with seizure disorder presents for evaluation of language impairment. The clinician notes that the patient engages in purposeless hand movements and has difficulty ambulating. The child met all developmental milestones appropriately until one year of age with unchanged serial neuroimaging. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Rett syndrome
B. Down syndrome
C. Tuberous sclerosis
D. Angelman syndrome
E. Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
A. Rett syndrome
Rett syndrome: sx onset - 6-18 mons
Regression (during the first five years of age)
Repetitive hand movements
Mobility issues (walking, sitting, crawling, or balance, walking on the toes, or a wide-based gait)
Speech (loss of language skills)
Breathing complications
Others: irritability, sleep disturbances, seizures, scoliosis, decreased eye contact
Tuberous Sclerosis:
Brain tumors - Cortical tubers on the surface of the brain, subependymal nodules (SEN) in the walls of the ventricles (fluid-filled cavities of the brain), and subependymal giant-cell astrocytomas (SEGA), which develop from SEN and block flow of fluid in brain. Other tumors: rhabdomyomas
Seizures, cognitive difficulties from mild learning disabilities to severe impairment, behavior problems (aggression, ADHD, OCD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Skin: Ash leaf spots (hypopigmented macules), facial angiofibromas (consist of blood vessels and fibrous tissue), shagreen patches (thick leathery, pebbly skin, usually on the lower back or nape of the neck). Ungual/subungual fibromas (small fleshy tumors around and under the toenails or fingernails, appear later in life, ages 20-50.)
Renal cysts and angiomyolipomas (benign growths of fatty tissue and muscle cells) can sometimes grow so large that they cause pain or kidney failure. Bleeding from angiomyolipomas may also occur. Increased RCC risk.
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (cells increase in the lungs, and there is lung destruction with cyst formation) and multinodular multifocal pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH).
Angelman syndrome: deletion of 15q11-13→loss of maternal contribution; developmental delay, speech impairment, gait ataxia, happy demeanor (frequent laughing and excitability).
Lesch Nyhan: HPRT1 mutation leads to increased uric acid → gout, renal stones, poor muscle control, developmental delays, self injury (biting)
13. Which of the following tricyclic antidepressants are the least anticholinergic? (CHOOSE TWO)
A. Amitriptyline
B. Desipramine
C. Imipramine
D. Nortriptyline
E. Protriptyline
B. Desipramine and D. Nortriptyline
141. Which of the following refers to heritable differences underlying one's automatic response to danger, novelty, social approval, and intermittent reward?
A. Psyche
B. Character
C. Motivation
D. Personality
E. Temperament
E. Temperament

Temperament refers to the innate, biological aspects of a person's behavioral style, essentially how they tend to react to situations.
Personality is a broader concept encompassing a person's unique set of traits, behaviors, and thoughts that develop over time through life experiences.
Temperament is more rigid than personality, which can evolve with age and life changes.
Psyche is the totality of the human mind, conscious and unconscious.
68. Which of the following best describes the difference between "sanity" and "competency to stand trial" in the forensic setting?
A. Sanity is a medical term, while competency is a legal term.
B. A person who is found to be insane can often be restored to sanity, but incompetency is usually permanent.
C. The evaluating psychiatrist determines whether someone is competent to stand trial, but sanity is determined by the court.
D. Sanity refers to the defendant's mental state at the time of the crime, while competency refers to the defendant's current mental state.
E. It is not necessary to have an underlying mental illness to be found lacking sanity, but a psychiatric illness is a prerequisite for incompetency.
D. Sanity refers to the defendant's mental state at the time of the crime, while competency refers to the defendant's current mental state.
106. Which of the following polysomnogram findings would be expected after a period of sleep deprivation?
A. Sleep onset REM
B. No change in REM
C. Reduced overall REM
D. Shortened REM periods
E. Increased movements during REM
A. Sleep onset REM
REM Rebound is a compensatory response that occurs with sleep deprivation that causes increased REM sleep than normal (increased REM sleep frequency, intensity, and depth).
It can also include vivid dreams or nightmares.
REM rebound can be caused by sleep deprivation, stress, drug withdrawal, or recreational drug and alcohol use.
7. Which of the following disorders arises from a defect in the mitochondrial genome?
A. Rett syndrome
B. Phenylketonuria
C. Friedreich ataxia
D. Huntington's Chorea
E. Lysosomal storage diseases
C. Friedreich ataxia

38. Which of the following selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor augmentation agents would be the best choice for a 58-year-old female patient with depression and pronounced psychomotor retardation?
A. Lithium
B. Estrogen
C. Olanzapine
D. Mirtazapine
E. Liothyronine
E. Liothyronine
Several controlled trials have indicated that liothyronine (25-50 mcg/day) use converts about 50 percent of antidepressant non-responders to responders.
(From Synopsis of Psychiatry)
64. Normal morphological changes within the brain during adolescent development include:
A. increased synaptic formation,
B. increased myelination of axons.
C. increased regulation of the amygdala to aversive stimuli.
D. accelerated maturation of the prefrontal and frontal cortices
E. reduced activation of the nucleus accumbens in response to reward stimuli.
B. increased myelination of axons.
Increased myelination during adolescence can lead to improved information processing and thinking skills.
Myelin is a fatty, white substance that insulates nerve cell axons, allowing electrical impulses to travel along them faster.
This process, called saltatory conduction, allows information to pass along a myelinated axon about 100 times faster than a non-myelinated axon.
Myelination also reduces the amount of energy needed to maintain this process.
137. What is the American Psychiatric Association's position on the possession of guns by individuals with a psychiatric diagnosis?
A. Guns should be banned for all individuals with any psychiatric diagnosis.
B. Individuals with a psychotic disorder should be banned from owning guns.
C. Individuals who present an increased risk of violence should be banned from owning guns.
D. Guns should be banned for anyone who has ever been hospitalized for psychiatric reasons.
E. Once an individual has lost the right to own a gun due to mental illness, that restriction should remain in place indefinitely.
C. Individuals who present an increased risk of violence should be banned from owning guns.
(See APA Position Template PDF)
22. Which of the following white matter tracts connects the temporal and orbitofrontal cortices?
A. Cingulum
B. Arcuate fasciculus
C. Uncinate fasciculus
D. Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
E. Superior longitudinal fasciculus
C. Uncinate fasciculus

The uncinate fasciculus is a hook-shaped tract that runs through the temporal stem and connects the orbitofrontal cortex and polar frontal cortex to the anterior temporal lobe
88. A patient presents with a chief complaint of tremor in both hands and arms, more pronounced on the right side. The tremor has interfered with writing and certain motor tasks such as buttoning a shirt. On examination, there is no noticeable tremor when the patient rests, but on the finger-nose-finger maneuver a high-frequency tremor is apparent bilaterally. What is the first line of treatment for this condition?
A. Benztropine
B. Gabapentin
C. Hydroxyzine
D. Levodopa
E. Propranolol
E. Propranolol

56. A patient who is dependent on heroin and whose last use was two hours ago requests to start buprenorphine. The psychiatrist explains that they must wait until the patient exhibits signs of withdrawal. Which of the following justifies the psychiatrist's directions?
A. Buprenorphine dissociates very slowly from u opioid receptors
B. Buprenorphine is a full opioid antagonist and competes with heroin
C. Buprenorphine will precipitate withdrawal by displacing full agonists
D. Buprenorphine has a lower affinity than heroin for μ-opioid receptors
E. Buprenorphine, if taken too soon, will not prevent euphoric effects of heroin
C. Buprenorphine will precipitate withdrawal by displacing full agonists
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor and an antagonist at the kappa receptor.
It has very high affinity and low intrinsic activity at the mu receptor.
It displaces full agonists from receptors, but because it does not activate the receptor, there is a net decrease in agonist effect, resulting in withdrawal.
79. While driving a tank during a combat deployment, a veteran experienced a landmine explosion. Since then, the veteran has developed anxiety, palpitations, and shortness of breath when traveling on major roads, and now avoids highway travel at home to prevent these symptoms. This behavior is a result of which of the following?
A. Positive punishment
B. Negative punishment
C. Positive reinforcement
D. Unconditioned stimulus
E. Negative reinforcement
E. Negative reinforcement
Reinforcement: used to encourage behaviors
Negative: remove or avoid negative stimuli to encourage certain behaviors. Ex. Nagging child to do homework, so the child does homework to AVOID nagging.
Positive: add positive stimuli to encourage behaviors. Ex. Getting an A on a test.
Punishment: used to discourage behaviors
Negative: removing desirable stimuli to discourage behaviors. Ex. Losing access to electronics after disobeying parents.
Positive: adding negative stimuli to discourage behaviors. Ex. Scolding student for listening to music in class.
109. In a trial studying the effectiveness of a behavioral treatment for anxiety, subjects experiencing a clinically significant response to treatment by week 16 are randomized to continue the treatment or to receive clinical monitoring alone for an additional 24 weeks. All subjects are then monitored for relapse of anxiety symptoms. The second stage of the trial is an example of what type of study?
A. Cohort
B. Survival
C. Cross-over
D. Case-control
E. Repeated measures
B. Survival
Survival analysis: studies the time between entry to a study and a subsequent event (could be death).
Cohort: a group of individuals sharing some characteristic is followed over time, and outcomes are measured at one or more time points. Uses relative risk.
Case control: a retrospective study that compares patients with a disease or outcome of interest (cases) to patients who do not have the disease or outcome (controls). Uses odds ratio.
63. Hyperphagia and aggressiveness can be observed with lesions to which hypothalamic nucleus?
A. Lateral
B. Anterior
C. Posterior
D. Premammillary
E. Ventromedial
E. Ventromedial

53. An elderly patient presents with loss of smell beginning on one side of the nose and progressing to the other side. The patient also complains of slow deterioration of visual acuity. Family members have described increasing forgetfulness over the past one to two years. A magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain is diagnostic for which of the following?
(SEE IMAGE)
A. Meningioma
B. Glioblastoma
C. Neurofibroma
D. Ependymoma
E. Metastatic cancer
A. Meningioma
Meningioma:

Glioblastoma: most commonly found in the supratentorial region, which includes the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes.


Neurofibroma:
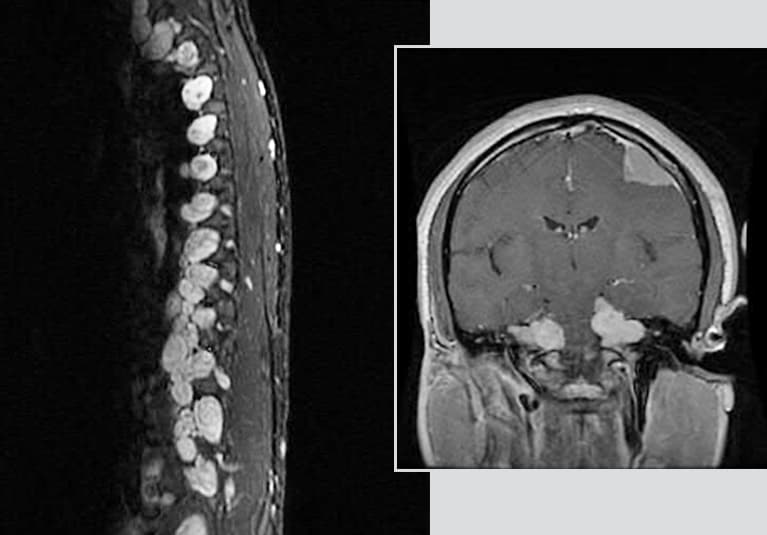
Ependymoma: glial cell tumors that commonly arise in the lining cells of the ventricular system

123. A patient with bipolar II disorder, who has been stable on lamotrigine for several years, presents to her psychiatrist at 32 weeks' gestation with a new depressive episode. She has good psychosocial support and sees her therapist regularly. What is the most likely explanation for her decompensation?
A. Use of a drug that is ineffective in pregnancy
B. Sleep deprivation secondary to late pregnancy
C. Estradiol-induced upregulation of glucuronidation
D. Increased metabolism by cytochrome P450 enzymes
E. Pregnancy-related increase in blood volume and glomerular filtration rate
C. Estradiol-induced upregulation of glucuronidation
Lamotrigine is normally converted into an inactive substance by UGT1A4 (an enzyme part of the glucuronidation pathway).
Estradiol, an estrogen, can increase the expression of UGT1A4.
Increased UGT1A4 expression → increased induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation in the liver → decrease in serum lamotrigine levels.
127. Which of the following best describes typical breast development in a girl in Tanner Stage 3?
A. Areola and papilla raised
B. Preadolescent breasts with elevation of papilla
C. Breast bud and small mound with increase in areola diameter
D. Breast and areola enlargement with no separation of contours between them
E. Breasts resemble adult female breast and areola has recessed to breast contour
D. Breast and areola enlargement with no separation of contours between them

125. In correctional settings, the right for inmates to access mental health services is directly based on which legal principle?
A. Pursuit of happiness
B. Freedom from discrimination
C. The principle of equal access
D. Prohibition of deliberate indifference
E. Protection against cruel and unusual punishment
D. Prohibition of deliberate indifference
Deliberate indifference is a standard that prohibits prison staff from intentionally ignoring a prisoner's safety or medical needs.
It is considered a violation of the 8th Amendment, which prohibits cruel and unusual punishment.