Which of the following scales is the easiest to use for an initial assessment of delirium in the geriatric population?
A. Confusion Assessment Method
B. Montreal Cognitive Assessment
C. Mini-Mental Status Examination
D. Geriatric Mental State Schedule
E. Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale
A. Confusion Assessment Method
Which of the following disorders is associated with hypocretin-1 deficiency?
A. Narcolepsy
B. Sleep terrors
C. Klein-Levin syndrome
D. Obstructive sleep apnea
E. Hypersomnolence disorder
A. Narcolepsy
Which of the following neurotransmitters is thought to play a key role in fine-tuning working memory function in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex?
A. Serotonin
B. Dopamine
C. Nitrous oxide
D. Acetylcholine
E. Norepinephrine
B. Dopamine
What is the leading cause of death in persons with severe mental illness?
A. Cancer
B. Suicide
C. Diabetes
D. Accidents
E. Cardiovascular disease
E. Cardiovascular disease
A typically developing 24 month old would show the ability to:
A. Copy a circle
B. Draw people with 4 limbs
C. Copy a triangle
D. Build a tower with 6 blocks
E. Follow 2-step instructions
E. Follow 2-step instructions
A 24-year-old patient presents to the emergency department reporting ringing in the ears, and nausea and vomiting. Respirations are noted to be deep and rapid. During questioning the patient admits taking an overdose of numerous, unidentified pills. Which of the following did the patient most likely ingest?
A. Aspirin
B. Trazodone
C. Propranolol
D. Lorazepam
E. Acetaminophen
A. Aspirin
The validity scales of the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-II measure which of the following?
A. Face validity
B. Construct validity
C. Parallel form reliability
D. Standard error of measurement
E. Test-taking attitude of the patient
E. Test-taking attitude of the patient
Which of the following is considered a risk factor for suicide attempt in transitional-aged youth with schizophrenia?
A. Manic symptoms
B. Loose associations
C. Higher level of education
D. Adherence with medications
E. Reduced expectations of performance from others
C. Higher level of education
A 32-year-old patient has episodes of irresistible sleepiness, and falls asleep while driving. The patient reports experiencing episodes of paralysis and hallucinations upon awakening. These symptoms are best explained by a deficiency in which of the following?
A. GABA
B. Orexin
C. Cortisol
D. Melatonin
E. Adenosine
B. Orexin
Which of the following infant characteristics has been found to be associated
with marijuana use during pregnancy?
A. Attention deficit
B. Low birthweight
C. Increased irritability
D. Reduced wakefulness
E. Avoidance of human contact
B. Low birthweight
The developmental tasks of young adulthood include all of the following except:
A. Experience the third individuation
B. Develop age- appropriate play
C. Create a work identity
D. Establish new outlooks on time
E. Cope with the death of significant loved ones
E. Cope with the death of significant loved ones
Which of the following antipsychotic medications carries the lowest risk of QT prolongation on electrocardiogram?
A. Quetiapine
B. Haloperidol
C. Ziprasidone
D. Aripiprazole
E. Thioridazine
D. Aripiprazole
Which of the following is a neuropsychological test of sustained attention?
A. Differential Ability Scales
B. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
C. Rey-Osterreith Complex Figure Test
D. Conners' Continuous Performance Test
E. Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System
D. Conners' Continuous Performance Test
Which of the following neurochemical abnormalities has been described in patients with depressive disorders?
A. Reduced circulating levels of GABA
B. Increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of somatostatin
C. Upregulation of pre-synaptic beta-adrenergic receptors
D. Decreased activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
E. Exaggerated thyroid-stimulating hormone in response to thyroid-releasing hormone stimulation
A. Reduced circulating levels of GABA
What neural pathway has been most consistently found to mediate reactive aggression?
A. Septal nuclei-hypothalamus-pituitary
B. Hippocampus-fornix mammillary body
C. Hippocampus-amygdala-orbitofrontal cortex
D. Amygdala-hypothalamus-periaqueductal gray
E. Caudate-globus pallidus-subthalamic nucleus
D. Amygdala-hypothalamus-periaqueductal gray
A patient who takes quetiapine develops diabetes. Treating the patient with metformin is an example of what kind of prevention?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
C. Tertiary
By the age of about 15 months, typically developing children begin to achieve which of the following milestones?
A. Infer others' emotions and intent
B. Engage in reciprocal conversation
C. Display social smile and gesture in peer interactions
D. Understand that others have minds different from their own
D. Understand that others have minds different from their own
A patient is brought to the emergency department for altered mental status. She is currently prescribed sertraline, aripiprazole, and buspirone by a psychiatrist. She was discharged two days prior after a cholecystectomy, and has reportedly been taking a "pain killer" and ondansetron every eight hours since discharge. On mental status exam, the patient appears diaphoretic, is oriented only to person, and exhibits psychomotor agitation. Physical exam reveals hyperactive reflexes and inducible clonus at the ankles. She is febrile and hypertensive. Prescription of which of the following pain medications would most likely account for the patient's presentation?
A. Ibuprofen
B. Meperidine
C. Oxycodone
D. Codeine with acetaminophen
E. Hydrocodone with acetaminophen
B. Meperidine
A medical student on the psychiatric consult service is called to evaluate an 80-year-old patient in the ICU who is awake throughout the night, pulling out IV lines, and misidentifying the nurses as bank employees. The student wants to conduct a brief cognitive screen. In addition to questions of orientation, which of the following components of the Mini-Mental State Examination would be most helpful in confirming the patient's diagnosis?
A. Recall
B. Serial 7s
C. Metaphors
D. Registration
E. Sentence completion
B. Serial 7s
Which of the following features of schizophrenia has become less common in Western cultures?
A. Alogia
B. Catatonia
C. Stilted speech
D. Religious delusions
E. Disorganized thought
B. Catatonia
Disruption in cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuit function is most closely associated with what group of disorders?
A. Mood
B. Somatoform
C. Schizophrenic
D. Posttraumatic stress
E. Obsessive-compulsive
E. Obsessive-compulsive
According to reports conducted by the US Preventive Services Task Force, which of the following demographic groups has the highest prevalence of depression?
A. Males
B. College educated
C. Previously married
D. White Non-Hispanic
E. Persons 65 years or older
C. Previously married
A child is able to understand that he can use water to make ice cubes and that if he leaves the ice cubes on the counter they will melt into water. At what stage of cognitive development is this child?
A. Sensorimotor
B. Preoperational
C. Concrete operational
D. Formal operational
E. Hypotheticodeductive
C. Concrete operational
Which of the following options is correct regarding efficacy and tolerability
results from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness
(CATIE) trial Phase I?
A. SGAs were uniformly more effective than perphenazine.
B. The rate of premature discontinuation for all antipsychotics was about 75%.
C. Time to drug discontinuation due to lack of efficacy was shortest for olanzapine.
D. Amongst SGAs, olanzapine was most likely to cause anticholinergic side effects.
E. Perphenazine was more likely to cause extrapyramidal symptoms than second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs).
B. The rate of premature discontinuation for all antipsychotics was about 75%.
The psychiatrist who is assessing a patient's suitability for psychotherapy notes that the patient prominently uses the defenses of isolation of affect and intellectualization. The patient's description of many life events appears to involve reaction formation. Which of the following personality traits is most likely to characterize this patient?
A. Schizoid
B. Paranoid
C. Histrionic
D. Narcissistic
E. Obsessive-compulsive
E. Obsessive-compulsive
A patient with social phobia avoids almost all social gatherings. The avoidance is regulated by a reciprocal connection between the amygdala and the:
A. hippocampus
B. locus coeruleus
C. parabrachial nucleus
D. periaqueductal gray
D. periaqueductal gray
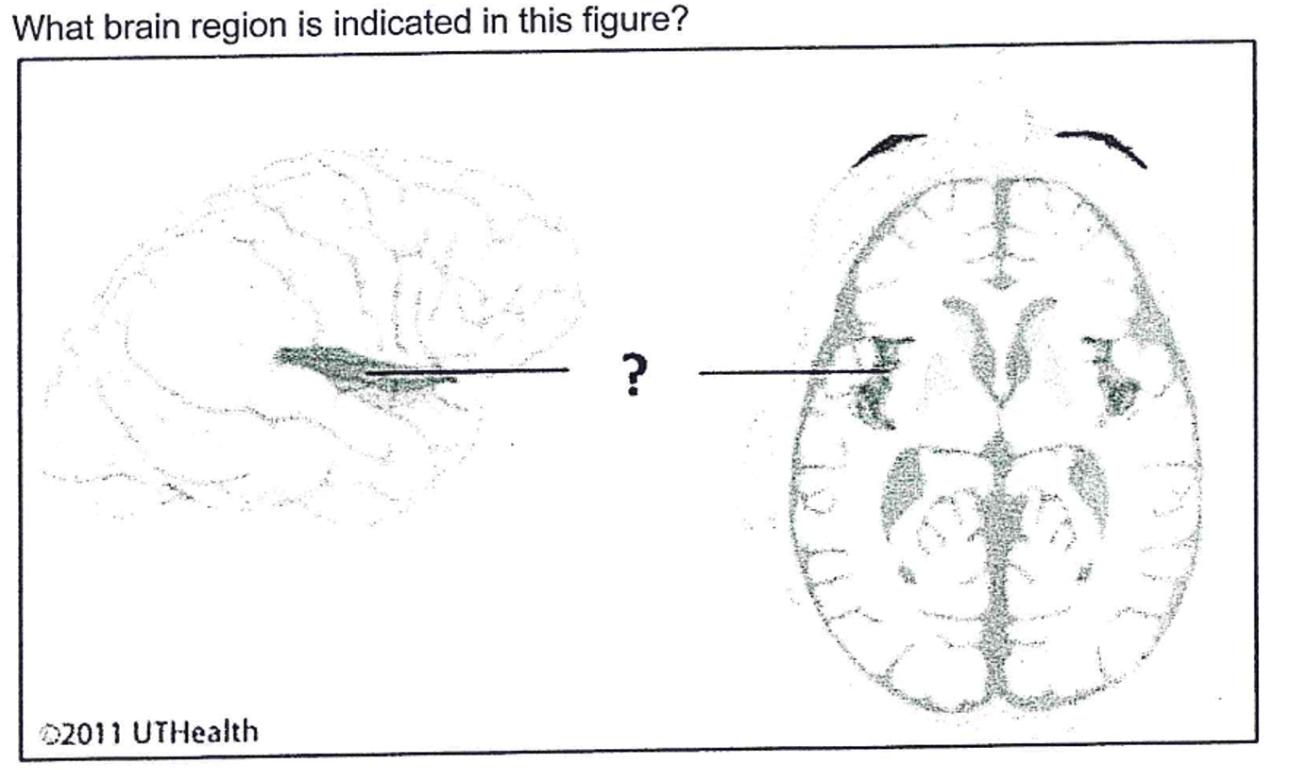
A. Insula
B. Habenula
C. Claustrum
D. Subiculum
E. Posterior cingulate
A. Insula
The Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness - Alzheimer's Disease (CATIE-AD) demonstrated that, relative to placebo, antipsychotic medication use for the treatment of behavioral disturbance in participants had which of the following effects in the majority of subjects by week 12?
A. Improved amotivation
B. Improved quality of life
C. Reduced suspiciousness
D. Improved functional status
E. Reduced caregiver burden
C. Reduced suspiciousness
Which of the following is a root cause of the phenomenon of infantile amnesia?
A. Immaturity of the medial temporal brain regions
B. Gradual maturation of the neocortex during infancy
C. Capacity for skill learning not developing until age three
D. Inability of adults to access early stored conscious memories
E. Declarative memory emerges before nondeclarative memory
B. Gradual maturation of the neocortex during infancy
A 35-year-old patient is brought to the emergency department with altered mental status and respiratory distress after overdosing on "alcohol and pills." The patient is medically stabilized after receiving flumazenil. This patient most likely ingested a medication that works in the amygdala via which of the following mechanisms?
A. Enhancing serotonin input
B. Alpha-2-delta ligand binding
C. Mu opiate receptor agonism
D. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation
E. Enhancing inhibitory actions at post-synaptic GABA-A receptors
E. Enhancing inhibitory actions at post-synaptic GABA-A receptors