A fridge has 20 bottles of pop in it. 12 of them are colas, 6 are lemon/lime, and 2 are orange. If I draw one bottle at random from the fridge, what is P(orange)?
1/10 or 0.1
A bakery's cakes are normally distributed by weight, with mean weight of 3.2kg and standard deviation 0.05kg.
Give an upper and lower weight that covers the middle 95% of cakes.
3.1 to 3.3 kg
If P(sing | dance) =0.4 and P(sing) =0.4 then events "sing" and "dance" are...
Independent!
In a normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1,
P( 0 or less)=0.5
True! The mean is 0 and exactly half the area is below the mean.
In a normal distribution with mean 12 and standard deviation 6, what is the probability of a value being more than 18?
About 16%
Since 18= 1 standard deviation above the mean,
P(above 18) = 13.5+2.35+0.15
If using a calculator, P(18 or greater)= 0.1587
A fridge has 20 bottles of pop in it. 12 of them are colas, 6 are lemon/lime, and 2 are orange. If I draw one bottle at random from the fridge, what is the probability it is orange, given that I know it's not a cola?
2/8=1/4 or 0.25
Two events A and B are independent. You find out that P(A)=0.4 and P(not B) = 0.8 .
What is P(A and B)?
P(B)= ( 1-0.8)=0.2
P(A and B) =0.4* 0.2=0.08
If I try to estimate the mean of a population using the mean of a random sample, how can I find the margin of error?
Take the standard deviation of the sample and multiply by 2.
In a normal distribution with mean 3 and standard deviation 10, the percent of the area greater than 7 is about 0.655
False! P(less than 7) =0.655
So, P(greater than 7) =1-0.655=0.345
Are "Weekday" and "Lose" dependent?
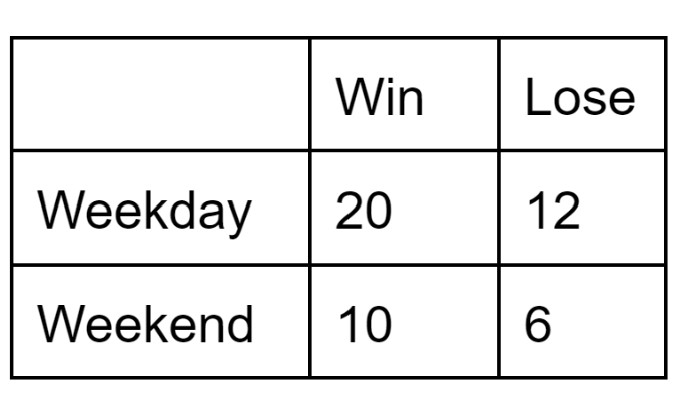
No, independent.
P(Lose| Weekday) = 12/32=0.375
P(Lose) =18/48=0.375
My closet has clothing of different types according to this two-way table. If I pick a piece of clothing at random, what is P(pant | red)?
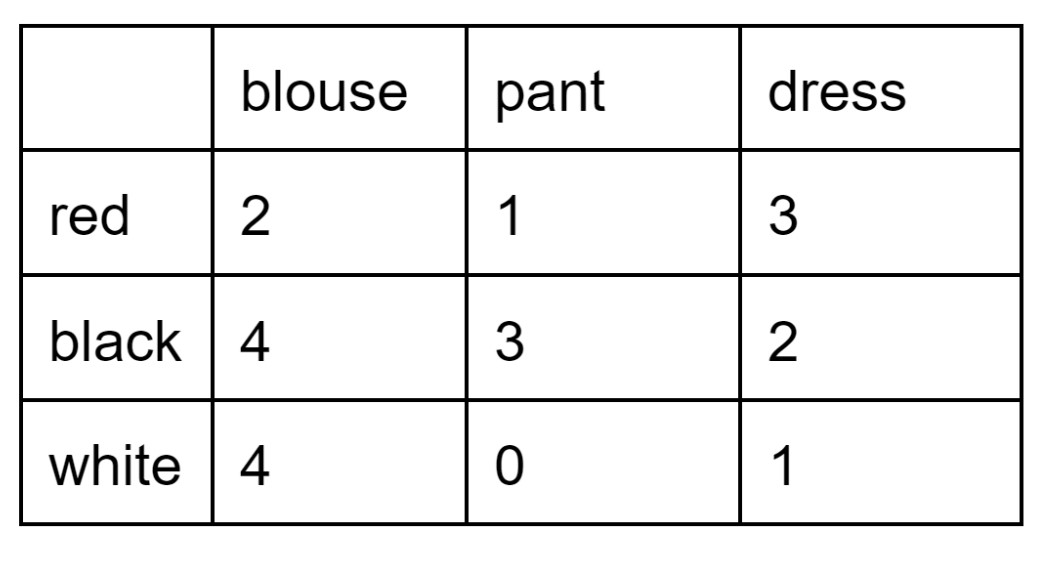
1/6
My closet has clothing of different types according to this two-way table. I pick a piece of clothing at random. Are "dress" and "red" independent events?
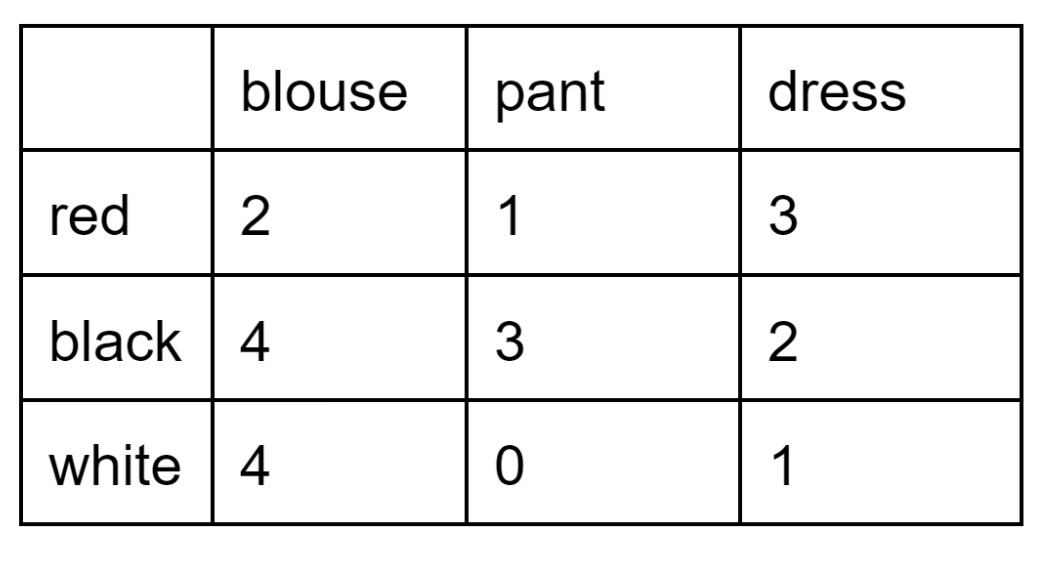
P(dress|red)=3/6 =1/2
P(dress)=6/20
P(dress|red) does not equal P(dress).
Dress and red are dependent events.
For a normal distribution, I can find probability or percent of values between, above, or below any point as long as I know these two things
Mean and standard deviation
If P(A |B ) = P( B| A), then A and B are independent.
False! You have to check P(A | B) compared to P (A ) to know if events are independent.
What is the formula for P(B |A)?
P(B | A) = (P(A and B) )/(P(A))
In the two way table below, we see the number of students taking electives (either Music or Drawing) during 1st, 2nd, or 6th period. Assume no students are taking more than 1 elective.
Find P(music and 2nd).
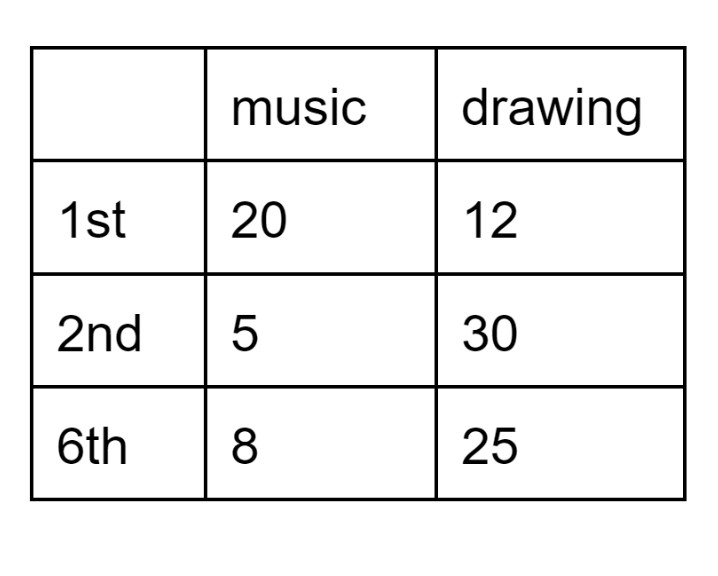
5/100= 0.05 or 1/20
Suppose in an experiment, Treatment mean= 19.1g
Control mean = 28g
I run a simulation 100 times. The difference of means distribution of my simulations has a mean of 3g and a standard deviation of 5g.
What is my experimental difference of means, and were my results significant? (Use a two-tail estimate)
Experimental difference of means: 19.1-28=-8.7
P(less than -8.7)=0.0096
P(greater than 8.7)= .127
Together this is a lot bigger than 5 % ( 0.05), so the results were not significant.
If I line up a collection of volunteers in order by height, and put the taller half in Group A and the shorter half in Group B, have I randomly assigned the groups?
No. I used height as a determining factor, as opposed to chance.
If the difference of means in an experiment is 5.2, and you run a simulation of 1000 trials with 14 resulting in a difference of means of 5.2 or greater, the experiment results were not significant and could be due to chance.
False! Your % simulations as extreme as your actual data are 14/1000=0.014 which is less than 0.05 (or 5%). Less than 5% tells us we can consider the experiment results significant.
Find P(Weekday or Win).
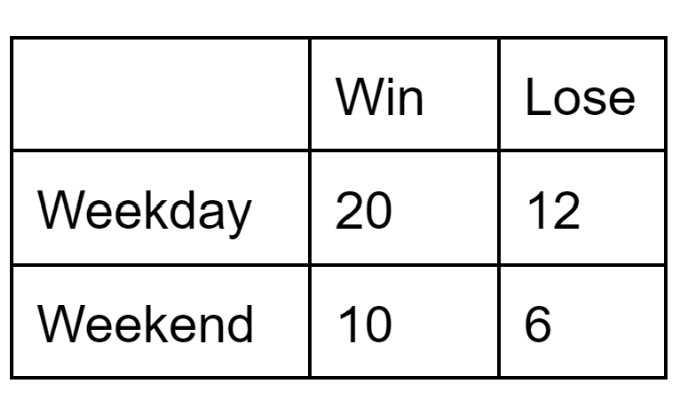
42/48 or 0.875
P(weekday) = 32/48 P(Win)=30/48
P(weekday & win)=20/48
P(weekday or win)=32/48+30/48-20/48
=42/48
The height of trees in the Frightful Forest is normally distributed with mean 12.8m and standard deviation 1.9m. A random sample of 400 trees are measured. Approximately how many trees will be less than 10m tall?
28 trees.
P( less than 10) =0.0703
400*0.0703=28.12 so about 28 trees.
What is the probability a student randomly chosen during 6th period is in drawing class?
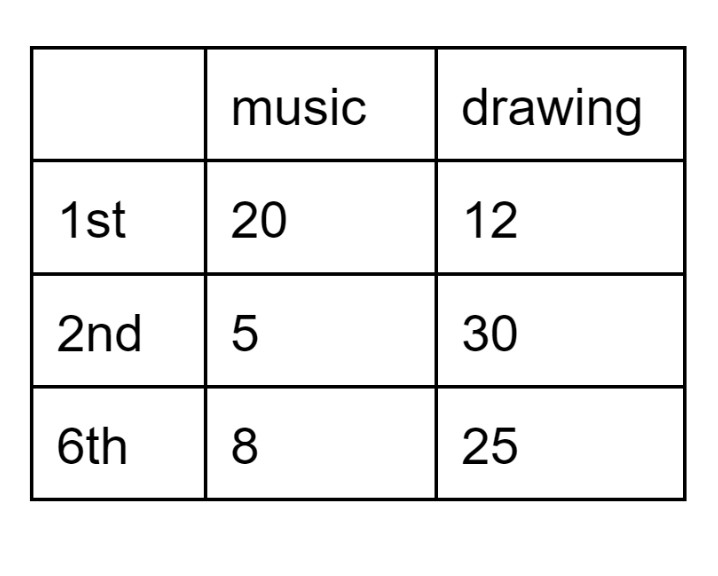
Total in 6th period = 8+25=33.
P(drawing | 6th) = 25/33 or about 0.7576
If an experiment results could happen by chance less than 5% of the time, what word describes the results?
Significant! It tells me my results may be related to my experiment and aren't just due to chance.
Below are students' elective choices (period and class). No one takes more than one elective.
True or false: 1st period students are 4 times more likely to be taking music.
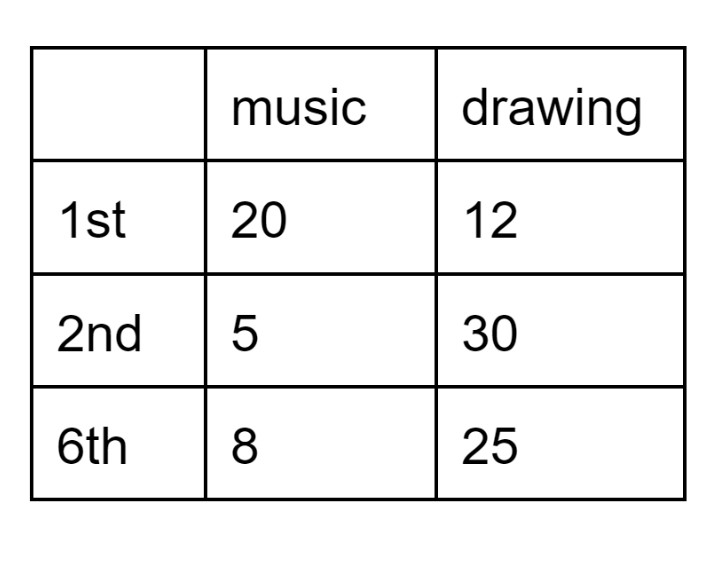
False!
P(music | 1st) = 20/32=0.625
P(music |2nd) =5/35 =0.143
0.625/0.143 = 4.37 which is not = 4.
Are these two groups significantly different? Explain how you could check.
Group A: 7, 7, 4, 3, 8
Group B: 5, 6, 4, 9, 4
Group A mean= 5.8 Group B mean= 5.6
Difference of means= 0.2
To test, regroup the data randomly, find difference of means, and repeat this a lot of times. Find % of simulations that have as extreme a difference of means.
Since the standard deviation of both samples is big (for A:2.17 and for B:2.07) compared to the tiny difference 0.2 in means, we can guess the result is not significant without doing the simulations.