Older adults are at greater risk of for adverse reactions to procedural sedation. Why?
Decreased renal function, decreased hepatic function, relative loss of muscle, comorbidities
What is the PASS score required for discharge?
In general, PASS of 13-14 OR the patient returns to within 1 point of baseline PASS score for the first 5 categories (consciousness, activity, circulation, respiration, O2 sat) and achieve baseline or improved score for pain/emesis
Name 3 things the RN should assess prior to procedure.
-Allergies
-Vitals
-Pain (baseline)
-PASS (baseline)
-Weight
-IV patency
Name at least 3 emergency items to have available during procedural sedation.
-Crash cart, Ambu bag/mask, reversal agents, wall suction regulator/setup
Definition: a drug-induced depression of consciousness during which patients respond purposefully to verbal commands, either alone or accompanied by light tactile stimulation. No interventions are required to maintain a patent airway, and spontaneous ventilation is adequate. Cardiovascular function is usually maintained.
Moderate Sedation (Level 2)
Determine this patient's PASS score: What is this patient's PASS Score? (Appendix B in policy, pg 17) Relevant Data: Patient is awake and responsive, moving but appears weak. BP stable at 125/85 (baseline ~115), mild dyspnea. Current saturation 96% on 4L NC, no pain reported, mild nausea with no vomiting.
Answer: Score of 11. Patient is awake and alert, responsive to voice (2), Activity is weak for age or development (1), Stable BP within 15% of presedation level (2), Dyspnea with limited breathing (1), Require supplemental O2 to maintain sat >95% (1), No pain reported (2), mild nausea with no vomiting (2)
True or false: RNs can administer deep sedation.
False. Deep sedation is administered only by licensed independent providers (i.e. anesthesia).
During a procedure, your patient starts snoring, with occasional brief periods of apnea. What are some possible actions to take?
-Head tilt chin lift; jaw thrust
-Stimulate patient, reposition
-Consider oropharyngeal airway if persists
-repeat vitals, assess capnography and SpO2
Additional invasive airway measures/drug reversal as appropriate/ordered
True/False: Continuous sedative infusions given to intubated/ventilated patients are considered procedural sedation.
False. Other situations that are NOT considered procedural sedation include: meds given in immediate life threatening situations (i.e. code, emergency intubation), preprocedural anxiety management
You are caring for a patient in a persistent vegetative state getting a PEG tube . Baseline PASS is 11: Consciousness - 1, Activity - 0, Circulation - 2, Respiration - 2, O2 Sat - 2, Pain - 2, Emetic - 2.
After procedure, you notice that consciousness is now 0. Can this patient be discharged?
Yes. The patient just needs to be within 1 point of baseline for the first 5 categories, and baseline or better for the last two.
What is the minimum number of times vital signs should be obtained after procedure?
Answer: VS should be assessed and documented at least twice during the recovery period.
You are doing preprocedure chart review for a patient admitted for bowel obstruction. Other history includes diabetes, liver failure with ascites, and esophageal stricture. What sedation/anesthesia complication is this patient at risk for?
This patient's listed conditions are all risk factors for aspiration with anesthesia.
True/False: An RN administering sedation can take a verbal order from a provider for incremental dosing.
True. Incremental dosing can be used to achieve/maintain desired level of sedation.
Name all 7 elements of the Procedure and Anesthesia Scoring Scale (PASS).
Consciousness, Activity, Circulation, Respiration, O2 Saturation, Pain, Emesis.
During procedures, BP and HR must be documented every __ minutes. SpO2, EtCO2, and respirations are documented at least every __ minutes.
During procedures, BP and HR must be documented every 5 minutes. SpO2, EtCO2, and respirations are documented at least every 15 minutes. Also document with any unanticipated changes -pain, LOC, cardiac rhythm, O2 needs.
During a drain placement under moderate sedation, the monitor suddenly shows this rhythm. What are your initial interventions? What potential treatments might you expect?
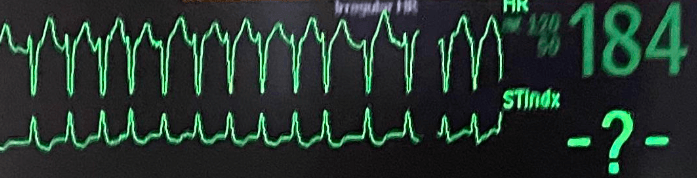
Initial intervention: assess patient, get a BP, put on O2. Is the patient stable or not? Depending on that (+ nature of procedure), stop and treat.
-Vagal maneuvers.
-Rate control - BBs, CCBs
-If symptomatic, persistent, and new onset (<48 hrs) may consider cardioversion.