A radiograph taken to demonstrate the upper ribs should be exposed:
A. At the end of full inspiration
B. At the end of expiration
C. During shallow breathing
D. During heavy breathing
A. At the end of full inspiration
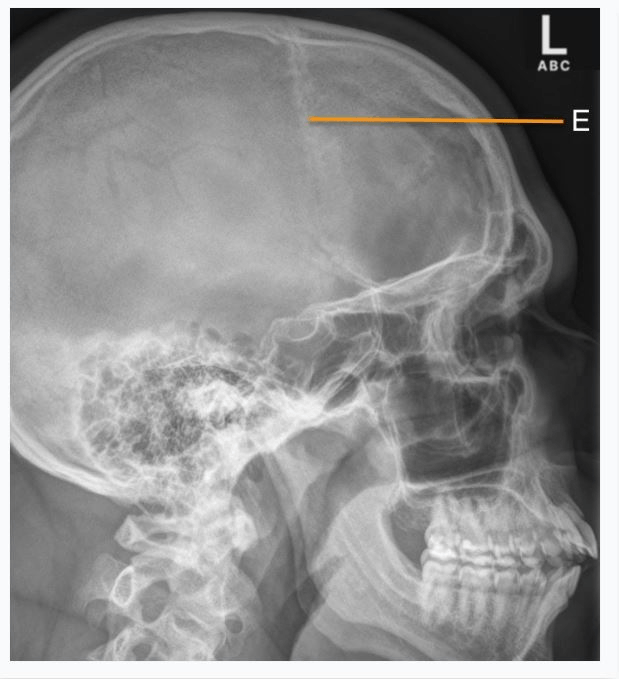
Identify the structure that is represented by the letter (E)
A. Sphenoid sinus
B. Coronal suture
C. Sella Turcica
D. Lambdoidal suture
B. Coronal suture
An "apple core" lesion typically is related to which of the following pathologies?
A. Colon cancer
B. Renal calculi
C. Chondrosarcoma
D. Cirrhosis
A. Colon cancer
The cuboid bone articulates with which of the following bones?
A. Talus
B. Medial cuneiform
C. 5th metatarsal
D. Proximal phalanx of 5th digit
C. 5th metatarsal
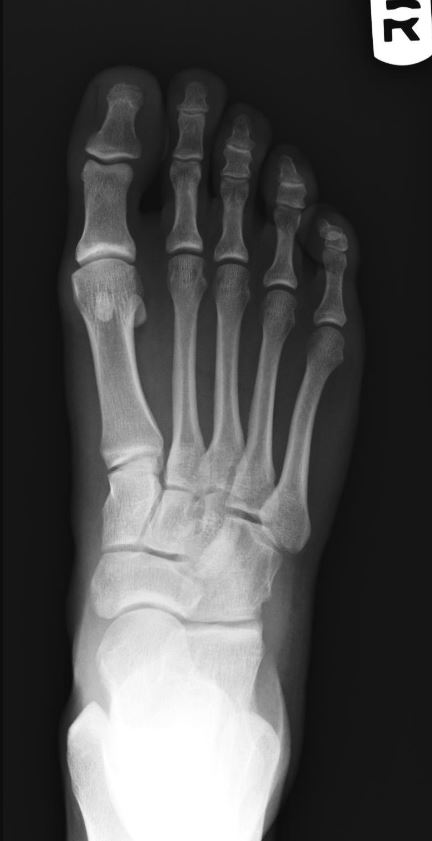
The cuboid bone articulate with the calcaneus, navicular, lateral cuneiform, and the bases of the 4th and 5th metatarsals
From the following options, choose three structures that are normally located in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) of the abdomen? (Select three)
A. Gallbladder
B. Liver
C. Tail of pancreas
D. Adrenal gland
E. Appendix
A. Gallbladder
B. Liver
D. Adrenal gland
Which projection of the shoulder best demonstrates the greater tubercle in profile laterally?
A. AP with internal rotation
B. AP with external rotation
C. Grashey
D. Scapular Y
B. AP with external rotation
An elderly patient has potentially suffered a stroke and arrives in the emergency department (ED) completely unable to speak and form words. This is a condition called:
A. Dysphasia
B. Dysphagia
C. Aphasia
D. Aphagia
C. Aphasia
Aphasia is the complete loss of the ability to speak. Dysphasia is a term that refers to a moderate language and speaking difficulties
What is the name of the anatomic structure that controls the passage of food from the small bowel into the large bowel?
A. Vermiform appendix
B. Ileocecal valve
C. Cecum
D. Ligament of Treitz
B. Ileocecal valve
Which imaging study of the urinary system is a structural study rather than a functional study?
A. Intravenous urography
B. Nephrotomography
C. Voiding cystourethrogram
D. Retrograde pyelogram
D. Retrograde pyelogram
A retrograde pyelogram is a structural imaging study of the urinary system. Functional studies demonstrate both the anatomy and physiologic workings of an organ, such as how the kidneys filter contrast from the blood or how the bladder empties.
The acromion process is part of what bone?
A. Clavicle
B. Humerus
C. Scapula
D. Sternum
C. Scapula
A patient cannot extend their neck for an open-mouth odontoid view. What is the best alternative projection?
A. Judd method
B. Swimmer's lateral
C. AP axial (Caldwell)
D. Fuchs method
D. Fuchs method
Which projection and position are used to evaluate the scaphoid with minimal foreshortening and maximum elongation?
A. PA wrist with radial deviation
B. PA wrist with ulnar deviation
C. Lateral wrist
D. Oblique with external rotation
B. PA wrist with ulnar deviation
Identify the structure that is represented by the letter (A)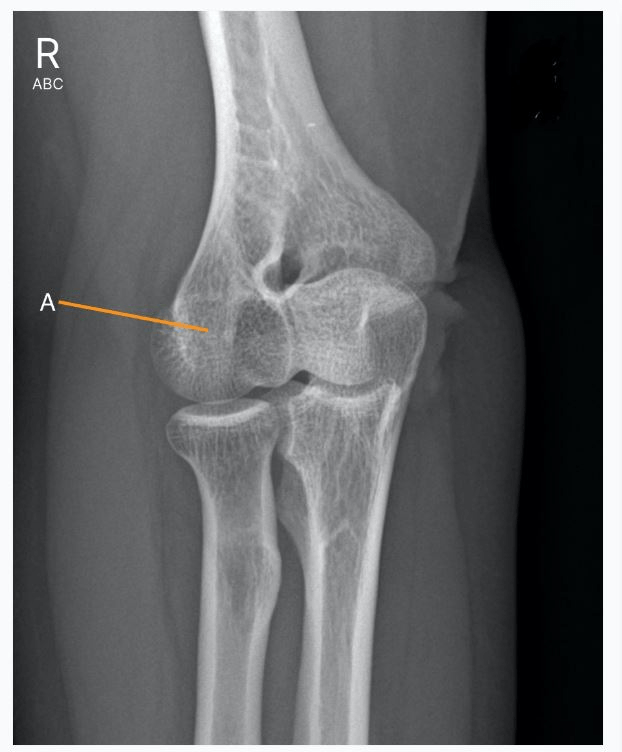
A. Capitulum
B. Head of radius
C. Radial Tubercle
D. Lateral epicondyle
A. Capitulum
Which two bones form the flat bony partition between the sides of the nasal cavity?
A. Nasal bones
B. Ethmoid and palatine
C. Ethmoid and vomer
D. Vomer and maxilla
C. Ethmoid and vomer
Gout most commonly affects what area of the lower extremity?
A. Subtalar joint
B. Ankle
C. Base of the first toe
D. Plantar surface
C. Base of the first toe
Which three of the following statements are true when positioning for an anteroposterior (AP) open-mouth projection of the cervical spine? (Select three)
A. The central ray is angled 15 degrees cephalad
B. The occlusal plane is perpendicular to the image receptor
C. The midsagittal plane (MSP) is perpendicular to the image receptor
D. The image demonstrates cervical vertebrae C1 through C5
E. The image demonstrates the atlantoaxial joint
B. The occlusal plane is perpendicular to the image receptor
C. The midsagittal plane (MSP) is perpendicular to the image receptor
E. The image demonstrates the atlantoaxial joint
(the occlusal plane is the line from the bottom of the upper incisors to the base of the skull)
Which structure is best seen with the Settegast method?
A. Intercondylar fossa
B. Patellofemoral joint
C. Tibial plateau
D. Tibial tuberosity
B. Patellofemoral joint
True or False: The Gaynor-Hart method is used to evaluate the navicular.
False
visualizes the carpal tunnel
On a lateral ankle image, the technologist notices the fibula superimposing the anterior half of the tibia. What, if any, mistake has been made?
A. No mistake was made
B. Knee was elevated too much
C. Leg was internally (medially) rotated
D. Leg was externally (laterally) rotated
C. Leg was internally (medially) rotated
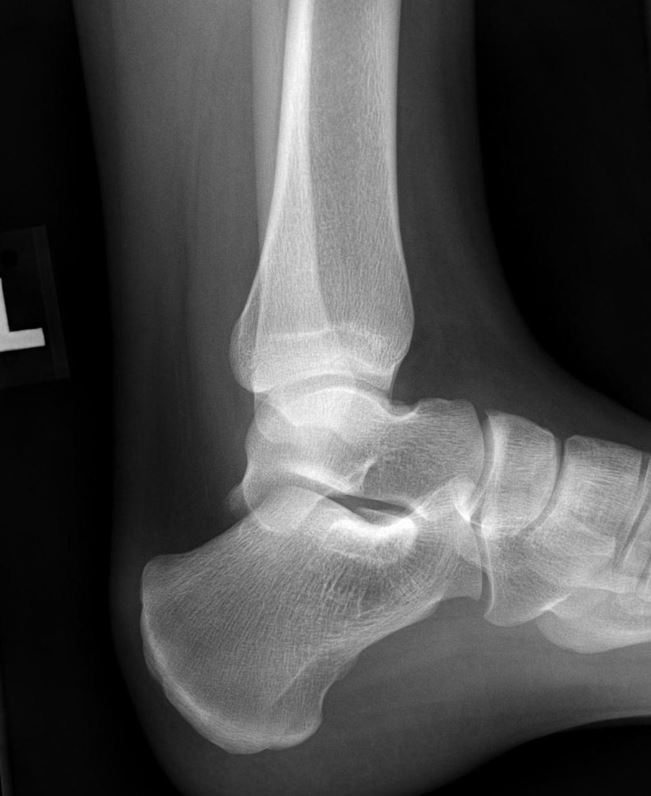
Example of a correctly positioned lateral ankle
The dorsum sellae is projected within the foramen magnum in which projection of the skull?
A. PA skull
B. PA axial skull (Caldwell method)
C. AP axial skull (Towne method)
D. Lateral skull
C. AP axial skull (Towne method)
A lateral cervical spine image shows the mandibular rami superimposing the C1-C2 region. What should the technologist do?
A. Raise the chin
B. Tuck the chin
C. Increase SID
D. Decrease kVp
A. Raise the chin
Which four of the following would indicate appropriate positioning for an AP supine projection of the abdomen (select four)
A. Spinous processes are demonstrated free of superimposition
B. Iliac wings are symmetrical
C. Margins of the kidneys are visible
D. Faint shadows of the psoas muscles are seen
E. Inferior liver is included
B. Iliac wings are symmetrical
C. Margins of the kidneys are visible
D. Faint shadows of the psoas muscles are seen
E. Inferior liver is included
In which projection will the humeral epicondyles form a perpendicular plane to the image receptor?
A. AP elbow
B. Medial oblique elbow
C. lateral oblique elbow
D. Lateral elbow
D. Lateral elbow
In which projection of the ankle should the malleoli be equidistant to the image receptor?
A. Mediolateral lateral
B. AP oblique 15 degree medial rotation
C. AP oblique 45 degree medial rotation
D. AP
B. AP oblique 15 degree medial rotation
The malleoli will NOT be the same distance from the IR in the anatomic position with a true AP projection (the lateral malleolus is about 15 degrees more posterior).
Identify the structure that is represented by the letter (A):
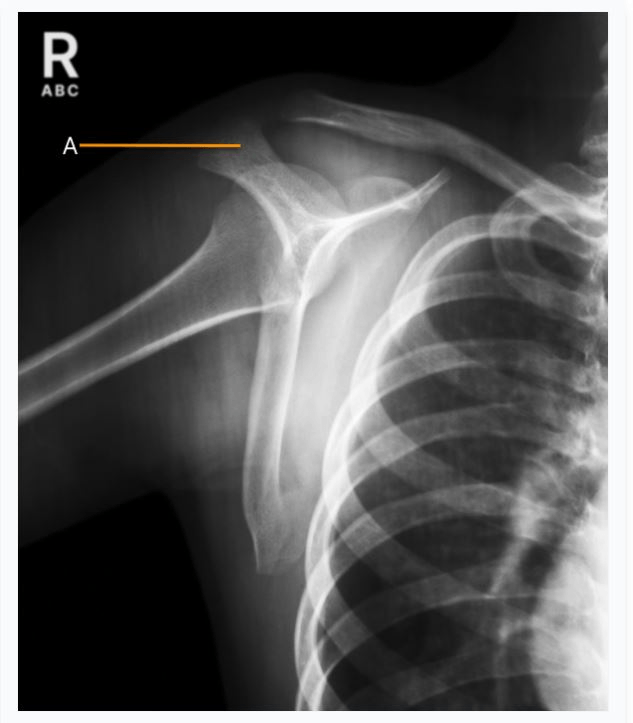
A. Head of humerus
B. Acromion
C. Coracoid process
D. Clavicle
B. Acromion
A technologist performs an AP axial clavicle with 30° cephalic angle on a hypersthenic patient. The image shows the clavicle projected above the apices. What is the likely issue?
A. Patient is rotated
B. Too much angle used
C. Not enough angle
D. Tube was over-collimated
B. Too much angle used
Hypersthenic patients typically require less CR angulation (15-20 degrees per bontrager)
When evaluating a PA hand image, the technologist notices that the metacarpophalangeal joints are open, but the interphalangeal joints are not open. What should the technologist do?
A. Nothing, this is an acceptable image
B. Repeat the image the hand rotated slightly lateral
C. Repeat the image with the fingers extended and parallel with the image receptor
D. Repeat the image with the central ray angled 15 degrees cephalad
C. Repeat the image with the fingers extended and parallel with the image receptor
Which two of the following are part of the hip joint?
A. Ilium
B. Ischium
C. Sacrum
D. Coccyx
A. Ilium
B. Ischium
The hip joint consists of three bones; the ilium, ischium and pubis.
Which of the following bones articulates with the medial cuneiform of the foot?
A. Cuboid
B. First metatarsal
C. Calcaneus
D. Proximal phalanx of the first digit
B. First metatarsal
What portion of the spine contains demifacets?
A. Sacrum
B. Thoracic
C. Cervical
D. Lumbar
B. Thoracic
The demifacets of the thoracic spine articulate with the heads of the ribs
What part of the stomach communicates with the duodenal bulb?
A. Pyloric canal
B. Cardiac Sphincter
C. Body
D. Fundus
A. Pyloric canal
What is meant by the term, "orthogonal projections?"
A. The need for axial projections
B. Internal and external obliques
C. Supplemental projections
D. Projections 90 degrees from each other
D. Projections 90 degrees from each other
Identify the structure labeled "C":
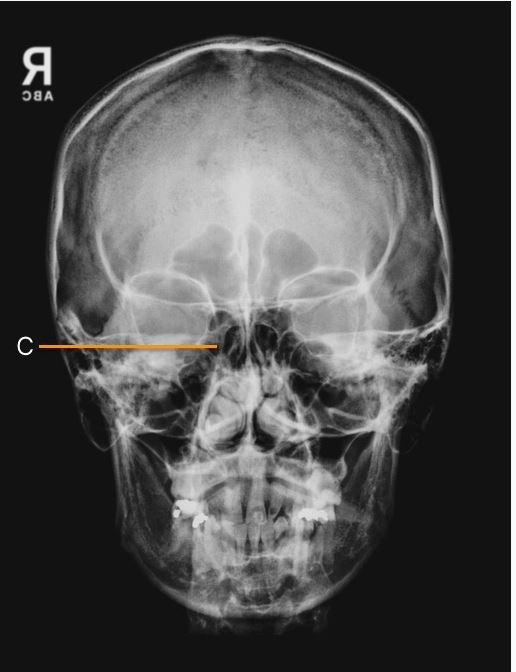
A. Sphenoid sinus
B. Petrous ridge
C. Frontal sinus
D. Ethmoid sinus
D. Ethmoid sinus
In which three of the following vascular structures does the direction of blood flow towards the heart? (select three)
A. Inferior vena cava
B. Superior vena cava
C. Pulmonary arteries
D. Pulmonary veins
E. Coronary arteries
A. Inferior vena cava
B. Superior vena cava
D. Pulmonary veins
Which of the following is the correct definition of chyme?
A. A hormone secreted by the kidneys
B. A hormone secreted by the pancreas
C. Chemically and mechanically altered food in the stomach
D. The byproduct of lipid digestion
C. Chemically and mechanically altered food in the stomach