Pubic bone borders the prostate ________________
Anteriorly
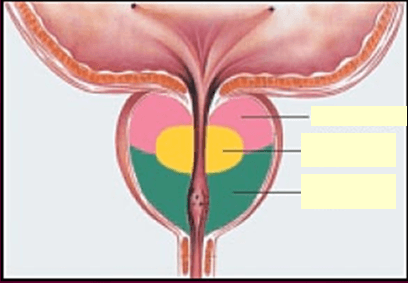
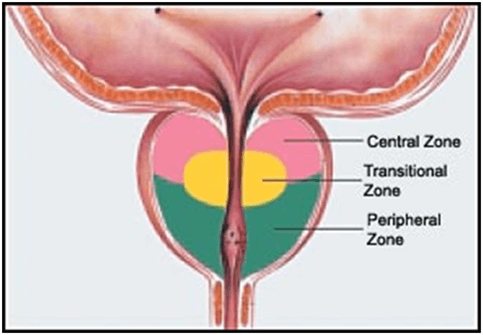
Peripheral zone is situated ____________________ next to the ____________
Posteriorly; rectum
Urogenital diaphragm borders prostate __________
inferiorly
AKA for urogenital diaphragm
triangular ligament
BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
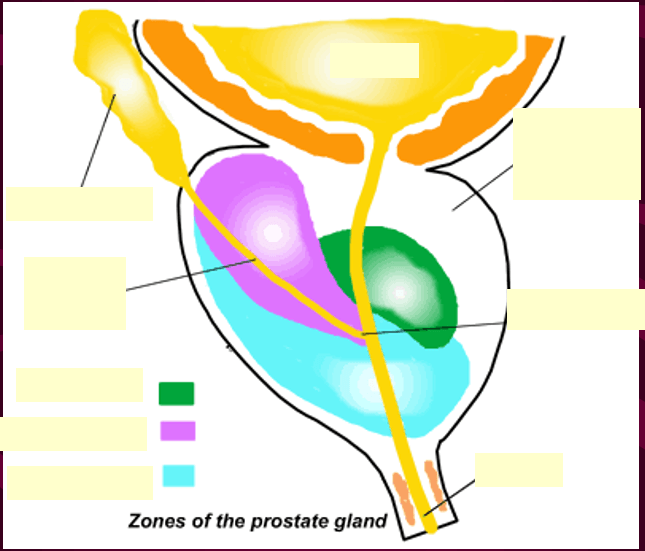
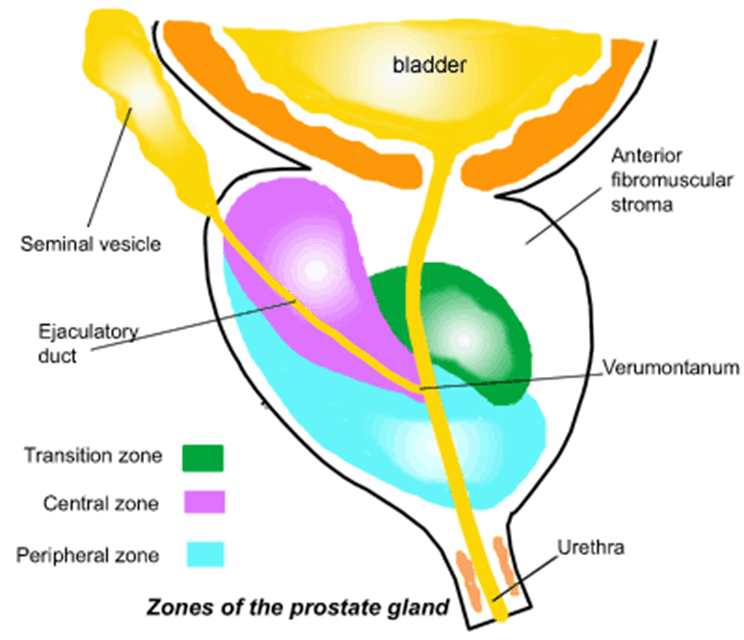
This zone is the 2nd largest consisting of ~ 35% of glandular tissue
Central Zone
Rectum borders prostate ______________
Posteriorly
AKA PSA
Prostate Specific Antigen
This involves direct placement of multiple radioactive seeds into the prostate via the transperineal approach
Brachytherapy
Urinary bladder borders prostate ____________
Superiorly
How large does the prostate become after puberty?
Walnut size
Two sac like out pouchings of the vas deferens
Seminal Vesicles
The proximal urethral sphincter is up to_____ in diameter
How large is the prostate at birth?
Pea size
Where do most cancers occur?
Posteriorly
What zones are the inner glands?
Central and transitional
When does the prostate begin to enlarge?
mid 40s
This duct originates from the combination of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle
Ejaculatory duct
What zone do the ejaculatory ducts pass through?
Central Zone
What zone is the outer zone?
Peripheral
What is a non-glandular portion of the prostate anterior to the urethra and is NOT affected by cancer, prostatitis, or hyperplasia?
Fibromuscular stroma
The inferior portion of the gland situated superior to the urogenital diaphragm
APEX (Apex towards Anus)
Normal prostate:
diameter ___________
weight __________
D: 3-4 cm
W: ~ 20 grams
HIFU
High Intensity Focused U/S
Seminal vesicles are situated adjacent to what aspect of the vas deferens
Superior/posterior
The superior portion of the gland situated below the inferior margin of the urinary bladder
BASE (Base towards Bladder)
This zone contains ~5% of glandular tissue
Transitional zone
This treats prostate cancer by freezing it with the use of thermal probes inserted transperineally with TRUS guidance
Cryotherapy
A layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis
urogenital diaphragm
Zone that is the site for MOST prostate cancers
Peripheral
The peripheral zone extends to the ________-
apex
The prostate does not have a true membranous capsule but instead is covered with this
condensed connective tissue
This zone is less than 1% of glandular tissue
Periurethral zone
A small elevation of the urethral crest in which the orifices of the ejaculatory ducts are located on either side
Verumontanum
The transitional zone looks like _________
saddle-bags
The ducts of the peripheral zone enter the ______________
distal urethra
What sign is the junction of the ejaculatory ducts and the urethra at the verumontanum?
Eiffel tower sign
Demarcation between the inner glands and the outer glands
Surgical capsule
In what zone does BPH originate?
Transitional zone
This zone surrounds the ejaculatory duct
Central zone
What produces PSA
prostatic acinar cells
The ________________ branches into the Inferior Vesical Artery
Internal Iliac Artery
This zone is felt to be relatively resistant to disease because only 5% of prostate cancers start here.
Central zone
Most common prostatic and seminal vesicle cysts
1. degenerative cysts
2. retention cysts in the transition zone
From 50 what is the doubling time of the weight of the prostate?
10 years
Calcifications commonly seen in the inner gland of the prostate (NOT indicative of malignancy)
Corpora Amylacea
Chronic prostatitis may be associated with what?
Chlamydia
What artery supplies most of the blood to the prostate?
Inferior Vesical Artery
Proteinaceous debris in dilated prostatic ducts
corpora amylacea
Prostate volume formula:
Volume = Height*Width*Length*0.52
Seen in older men who develop atrophy and dilation of peripheral prostatic ducts; visible tubular structures in the peripheral zone at the capsule and radiating towards the urethra
Benign Ductal Ectasia
Scan orientation for transrectal: what is displayed at the bottom of the screen?
rectum (screen is flipped)
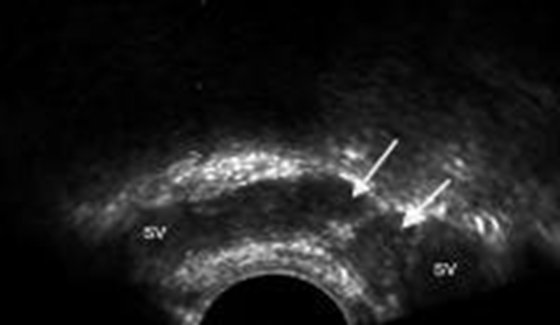 What are the white arrows pointing at?
What are the white arrows pointing at?
Ampulla of the vas deferens
The risk of prostate cancer is higher in what ethnic group?
African Americans
A prostate over __________ grams is considered enlarged in older men
PSA levels increase with these 2 things
1. age
2. prostatic volume
What gene is related to prostate cancer?
HPC1
Histologic grading of prostate cancer is done using this
Gleason scoring system
The larger the lesion with prostate cancer, the _____________
higher the PSA
The periurethral zone is involved also in _______
BPH
Two positions of transrectal scanning:
1. LLD
2. Lithotomy
The border of a normal prostate appearance
highly echogenic, smooth and unbroken and sharply defined
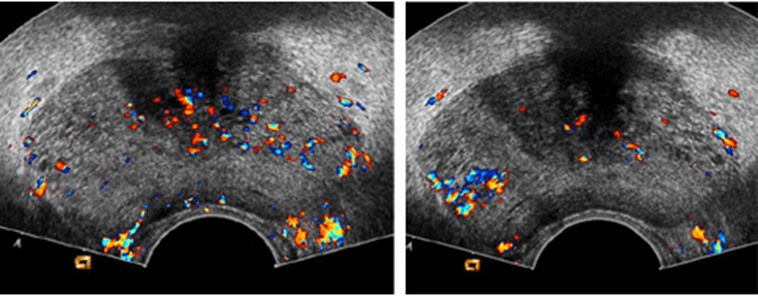 Hypoechoic, peripherally oriented lesion (May be hyperechoic/isoechoic)
Hypoechoic, peripherally oriented lesion (May be hyperechoic/isoechoic)
Prostate cancer
On the posterolateral margins the prostate capsule margin looks _______ because of these entering the prostate
ragged; neurovascular bundles
In this stage of prostate cancer tumors are NOT palpable clinically
T1
BPH occurs in what 2 zones?
1. Periurethral
2. Transitional (starts here)
What is the "classic appearance" of prostate cancer on us?
hypoechoic, peripherally-oriented lesion
When does prostate cancer screening begin?
age 50
2 Functions of the prostate gland:
1. Produces milky fluid to form semen with sperm
2. contains 5 alpha-reductase that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
Stage _____
PSA ______
Gleason score ______
prostate volume ________
Stage T1 or T2
PSA < 10
G Score < 7
Volume < 50mL
The LARGEST zone of the prostate (70%)
Peripheral
3 treatment options for prostate cancer
1. watchful waiting
2. radical prostatectomy
3. radiation therapy
Non-surgical interventions (5)
1. Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT)
2. Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA)
3. Transurethral Electovaporisation (TUEVP)
4. Laser Surgery
5. Prostatic Stenting
2 types of prostate biopsy
2. lesion directed
2 labs for prostate
1. PSA
2. Acid Phosphatase
What 4 things create the "fatty trapezoid area"
2. rectum
3. urethra
4. prostate
What 3 things are important to have before transrectal scanning?
1. history
2. digital exam results
3. PSA results
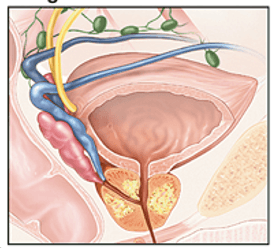
What stage of Prostate cancer is this?
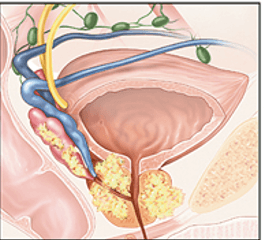
3 major risk factors for prostate cancer
2. family hx
3. ethnicity
The ducts of the transitional zone end in the _______________ at the level of the _____________________ which bounds the zone ______________
Proximal urethra
Verumontanum
Caudally
3 indications for a transrectal ultrasound
1. abnormal digital rectal exam
2. abnormal lab tests
3. biopsy guidance
What 2 tests are used for prostate cancer screening?
1. PSA levels
2. Digital rectal exam (DRE)
PSA labs:
normal __________
benign/borderline ___________
cancer ____________
N: <4 ng/mL
B/B: 4-10 ng/mL
C: > 10 ng/mL
What 2 things are preparations for prostate biopsy?
1. enema
2. antibiotics
How are the prostate measurements taken on transrectal us?
Maximal transverse width __________
Anteroposterior _____________
Length _______________
Max Trans width: right to left
AP: Anterior midline to rectal surface
Length: maximal head to foot
3 symptoms of BPH
1. Difficult initiation of voiding
2. Urinary frequency (nocturia)
3. Small stream of urine
4 prostatic zones?
1. peripheral
2. central
3. transitional
4. periurethral
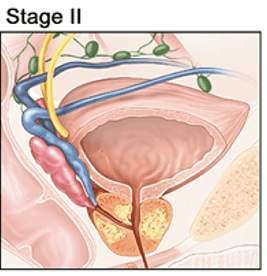
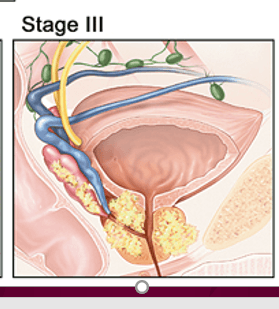
What stage of Prostate cancer is this?