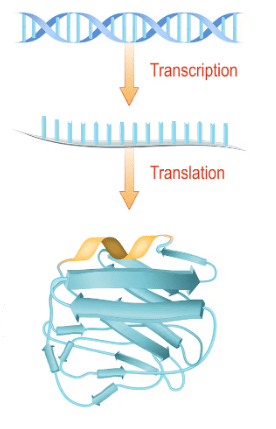
DNA
What is being shown in the image?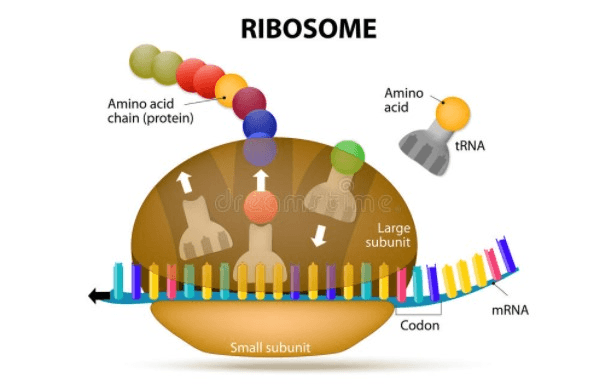
Translation
Where does transcription take place?
A base is deleted
Frameshift Deletion
DNA: TTG
MRNA: _ _ _
Amino Acid:___________
MRNA: AAC
Amino Acid: ASP
Uses Bases A, U, G, C and is single stranded
RNA
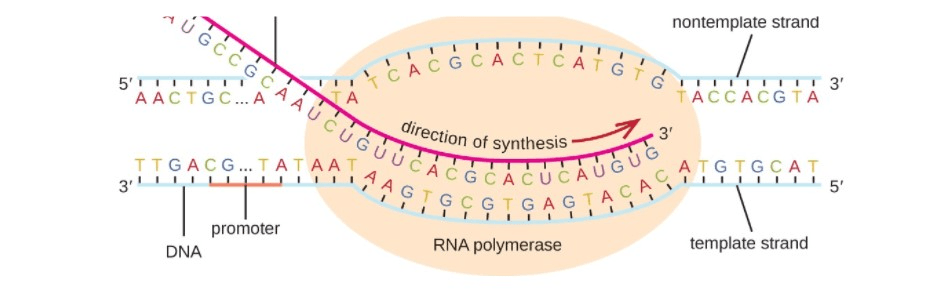 What process is happening in the diagram?
What process is happening in the diagram?
Transcription
Where does translation take place?
Ribosome
A base is added
Frameshift insertion
DNA: TAC
MRNA: _ _ _
Amino Acid: ___________
Amino Acid: Meth/Start
What process uses a segment of DNA to serve as a template for mRNA to copy.
Transcription
What type of mutation is being shown?
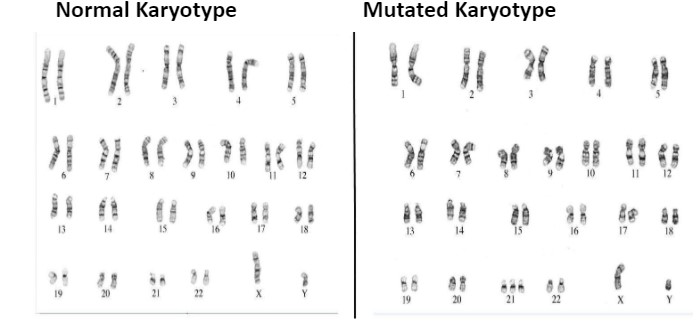
Chromosomal Mutation
What packages and sends the proteins to the correct locations?
Golgi Body
What effect is this:
Meth - STOP - ASP - ARG - CYS - STOP - ASP
Non-sense
DNA: GCG
mRNA: _ _ _
Amino Acid: _____________
mrna: CGC
Amino Acid: ARG
During what process are Amino acids joined together to make a protein (trait)
Translation
What is being created? 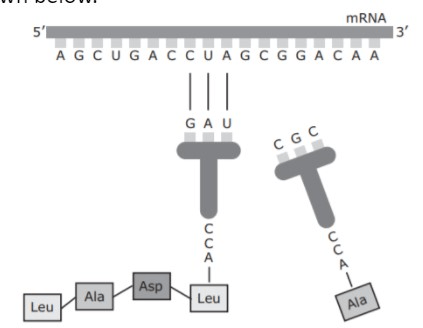
Amino Acids
What is the place that Ribosomes attach to and assist in making proteins?
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Chromosome mutation definition:
A change in structure or number of chromosomes
DNA: ATC
mRNA: _ _ _
Amino Acid: ____________
mRNA: UAG
Amino Acid: Stop
How many nucleotides make up a codon?
3
What is being created?
What cell type impacts future generations if a mutation occures within them?
Gametes
A letter is substituted within an RNA sequence. This amino acid ASP is changed to HIS. Other amino acids are not affected. What type of effect is this?
Effect: Missense
DNA: GAC
mRNA: _ _ _
Amino Acid: ____________
mRNA: CUG
Amino Acid:Leu