During transcription _____ turns into ______
DNA turns into mRNA
What are the 2 main steps of protein synthesis called, in order.
Transcription then translation
T/F Genetic engineering is controlled
true
Charles Darwin conducted research in the Galapagos Islands
T/F once amino acids are linked during translation... that's it!
What is the main goal of translation?
During translation ______ gets read by _______
mRNA gets read by tRNA
Is a mutation considered genetic engineering?
No, because it is not controlled by a scientist
Evolution was originally called
Descent with Modification
What is a mutation?
A change in the genetic code/one or more DNA nucleotide
What is a codon?
A sequence of 3 nucleotides on mRNA that is read during translation
List the 3 sites of protein synthesis
nucleus to cytoplasm to ribosome
What was the goal of the human genome project?
To sequence the human genome, including the location of specific genes
What is a vestigial structure?
a body part that has lost much or all of its original function through evolution, yet still exists
Give an example of a genetic modified organism.
Pick one: Wooly mouse, glowing mouse, GMO crops, dolly the cloned sheep, the dire wolf, etc.
What is an anticodon?
The sequence of 3 nucleotides on tRNA that reads the mRNA codon
What amino acid is produced by the DNA code CGA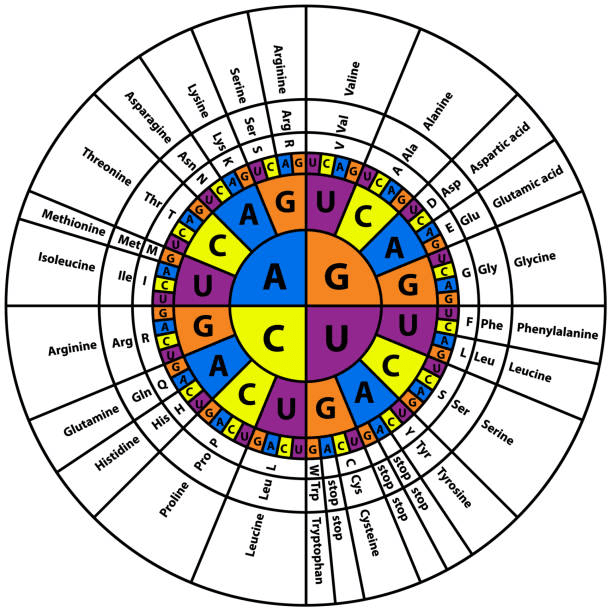
Alanine
Explain 2 potential benefits of genetic engineering.
Answers vary, some are listed below.
1) Modifying crops to become
*pest resistant
*nutritionally dense
*able to grow with less resources (more crops per area)
2) Personalizing medical treatment
3) Rebalancing environments that lack genetic diversity
Explain how homologous structures are evidence for evolution.
Homologous structures are anatomical structures in different species that share a similar underlying skeletal anatomy because they are derived from a common ancestor
Relate DNA to protein synthesis, genetic engineering and evolution
DNA is the template for protein synthesis, it is the code that is altered in genetic engineering, and it is one of the main ways to see how closely related different species are when analyzing evolutionary relationships.
No, it will not always have this impact.
There are many codons for each amino acid, so a change in one nucleotide does not always change the amino acid, so the protein may not be affected.
If the nucleotide change does change the amino acid that is placed, then the protein will be affected.
DNA codes for RNA, which determines amino acid sequences. The amino acid sequences become proteins which create the structures of the organism, including pigmentation (color), and shape.
Explain why genetic engineering is often considered ethically questionable.
Answers may vary- up to teacher discretion
**Goes against religious beliefs/playing "God"
**Removing variation of species
**No one standard of perfect
How is comparing DNA beneficial when studying evolution?
As DNA is the code for organisms, comparing DNA allows us to see how similar/closely related species are
Explain how fossils are used for genetic engineering AND as evidence of evolution
Genetic Engineering: Fossils are used to provide DNA that can be modified and inserted in modern/current species (EX: dire wolf)
Evolution: Fossils demonstrate how life forms have changed over time, showing similarities and differences of the organism to its ancestors