This is being represented by the dotted line in the picture below.
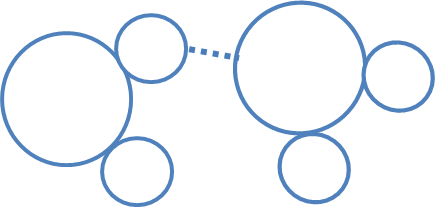
What is hydrogen bond?
These are the monomers of proteins or polypeptide chains.
What are amino acids?
These are proteins that speed up chemical reactions
What are enzymes?
A + B → C + D
A and B are examples of these
What are reactants?
These are the monomers of carbohydrates.
What are monosaccharides?
Any chemical that can speed up chemical reactions is called this.
What is a catalyst?
The what of a protein determines its function
Shape
This part of the enzyme is what binds to the substrate
What is the active site?
This type of reaction uses water to cut or break a big molecule into smaller molecules
What is hydrolysis?
These are the polymers for carbohydrates.
What are polysaccharides?
This property of water allows certain insects to stand on top of ponds or lakes
What is surface tension
Proteins differ in the number and type of this contained in their polypeptide chain(s)
What are amino acids?
"A" represents this in the image below
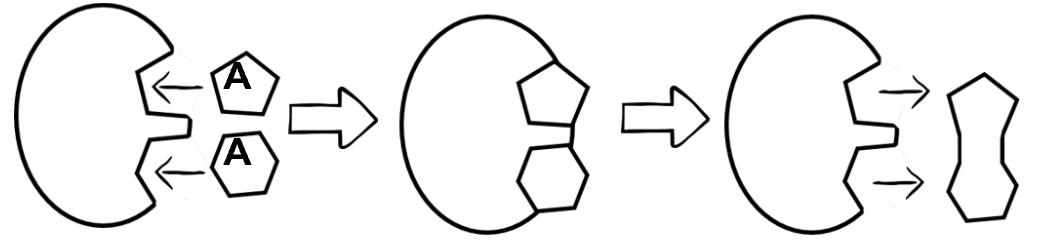
What is a substrate?
This type of reaction removes water to build smaller molecules into bigger molecules
What is dehydration synthesis?
This is the function for carbohydrates in the body
What is providing quick energy
This area of the enzyme is highlighted in purple
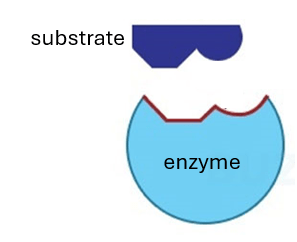
What is the active site?
The specific order of monomers in a protein is called this
What is primary structure?
This process changes the shape of a protein which changes the function
What is denaturing/denaturation?
This enzymatic reaction breaks up bigger molecules into smaller molecules which releases energy
What is catabolic reaction?
This term would be the best to describe the structure of starch
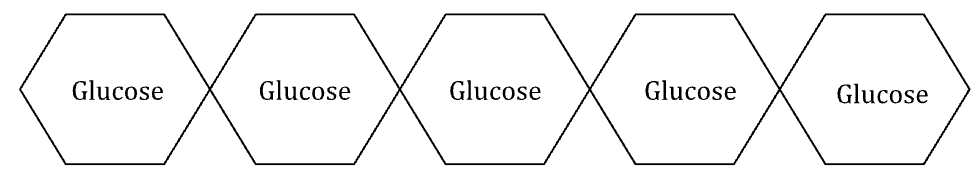
What is polysaccharide?
This forms when the substrate and enzyme combine
What is the enzyme-substrate complex?
This is the reason that the unique three-dimensional shape of the enzyme’s active site contributes to its function.
What is it provides a complementary fit to the substrate, facilitating enzyme-substrate binding?
These are the main two things that can denature enzymes
The image below represents this kind of reaction
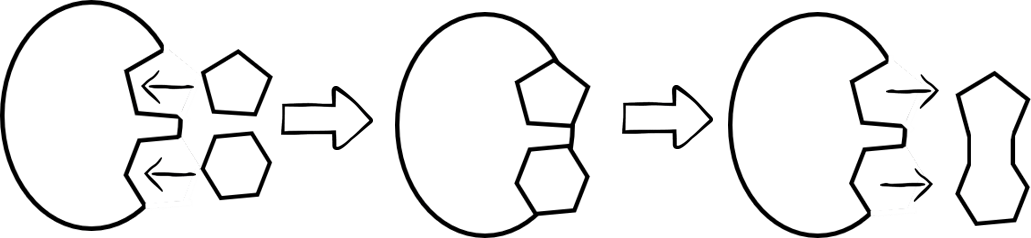
What is an anabolic reaction?
This carbohydrate helps make up plant cell walls and gives them their rigidity
What is cellulose?