Define the categories of ribs (based on costal cartilage)
True (1-7): vertebrosternal
False (8-10): vertebrochondral
Floating (11-12): vertebral
Name the layers of the abdominal wall
Skin
Camper's fascia
Scarpa's fascia
Muscles
Transversalis fascia
Peritoneum
Describe the significance of the two lumbar triangles
Spaces that do not contain all of the muscular layers
Superior: rib 12, quadratus lumborum, int oblique
Inferior: lat, ext oblique, iliac crest
Describe the blood supply of pec major
Dominant: pectoral branch of thoracoacromial trunk
Secondary: IMA perforators (medial), intercostals and lateral thoracic (lateral)
Which artist/anatomist/inventor first drew and described the anatomy of the spine?
Leonardo da Vinci
Name the muscles of the anterior chest wall
Intercostals (3), pec minor, pec major
Subscapularis - internal rotation
Infraspinatus - external rotation
Teres minor - external rotation
Supraspinatus - abduction
Name the branches of the subclavian artery
Vertebral
Internal thoracic
Thyroscapulocervical (inferior thyroid, suprascapular, superficial cervical)
Costocervical (superior intercostal, deep cervical)
Dorsal scapular
What is the location (layer) of Cooper's ligaments and what is their function?
Superficial and deep subcutaneous fascia
Elevation of breast tissue / prevention of ptosis
What is the location (layer) of the neurovascular bundles supplying the intercostal muscles?
Between innermost and internal intercostal muscles
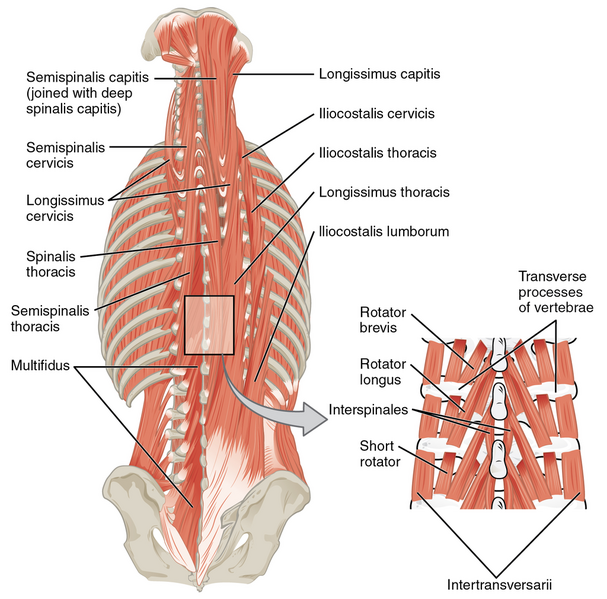
Describe the layers of the paraspinous muscles. Contents????
Deep (transversospinal): semispinalis, multifidus, rotators
Intermediate (erector spinae): spinalis, interspinalis, intertransverse, longissimus, and iliocostalis
Superficial (spinotransverse): splenius cervicis and capitis
Describe the course of DIEA
1. Branches off external iliac
2. Pierces transversalis fascia, runs along rectus
4. Divides at arcuate line to medial and lateral branches (and sometimes umb branch)
5. Perforators