List the four states of matter.
Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma
What is solid
this phase has a definite shape and and definite volume, the particles do not move much and are close
Changing from a solid to a liquid by adding heat.
Melting
Which phase change is when a liquid change to a solid by removing heat.
Freezing
A phase change from Phase A to Phase B is known as:

Condensation
Compare the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the sample during interval BC to the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the sample during interval DE.
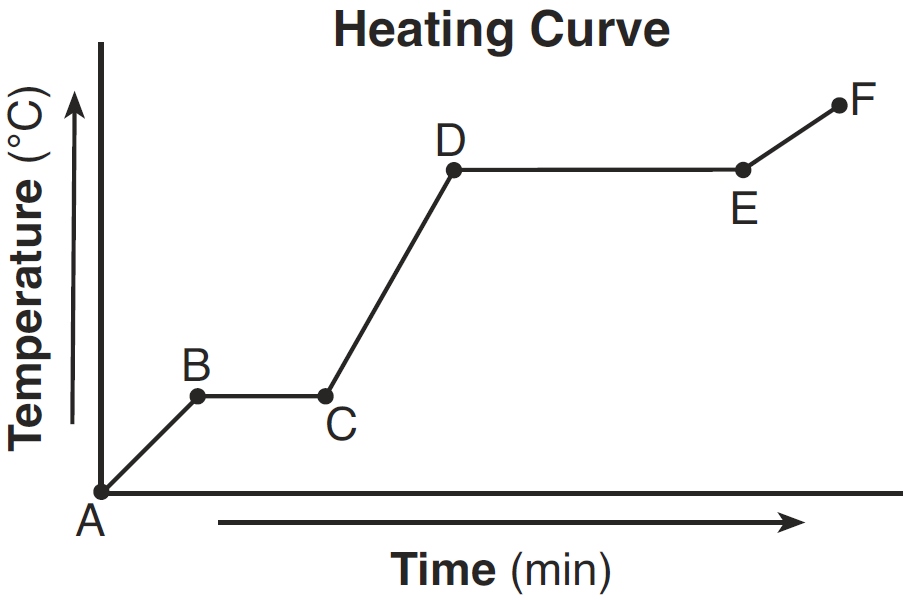
- The average kinetic energy of the molecules during interval BC is less than the average kinetic energy of the molecules during interval DE.
— During interval DE, the average kinetic energy is higher.
Which gas law describes the relationship between temperature and pressure at a constant volume?
Gay-Lussac’s law
Which state(s) of matter have no definite shape or volume?
gas
What is gas?
this phase does not have a definite shape or volume, the particles tend to move fast and are far apart
Which phase change is when a solid turns into a gas without ever becoming a liquid?
sublimation
At 30 atmospheres pressure, the boiling point of this substance is:

50 ºC
A phase change from Phase C to Phase B is known as:

Melting
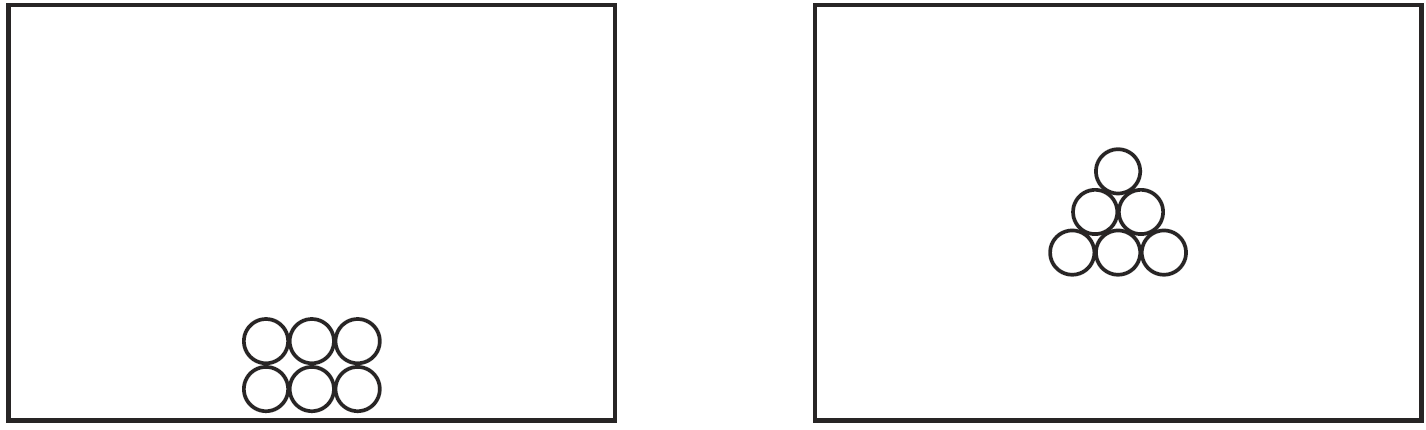
Draw a particle diagram to represent the sample during interval AB. Your response must include at least six molecules

Which statement is a description of Charles’s law?
a. The temperature and volume of a gas are directly proportional when pressure is constant.
b. The temperature and volume of a gas are inversely proportional when pressure is constant.
c. The volume and pressure of a gas are directly proportional when temperature is constant.
d. The volume and pressure of a gas are inversely proportional when temperature is constant.
a. The temperature and volume of a gas are directly proportional when pressure is constant.
Gold’s natural state has a definite shape and a definite volume. What is gold’s natural state(s)?
solid
What is liquid?
this phase does not have a definite shape but has a definite volume, the particles are free to move
Which phase change is when a gas turns into a solid without ever becoming a liquid
Deposition
At 30 atmospheres pressure, the melting point of this substance is:

0 ºC
A phase change from Phase B to Phase C is known as:

Freezing
What is happening to the average kinetic energy of the particles during segment BC?
It does not change.
JyQue makes the diagram below to compare Gay-Lussac’s law and Charles’s law.

Which label belongs in the region marked X?
They both involve changes in temperature
Which state of mater is this changing from and to; and change of state is shown in the model?

Gas --> Solid
Sublimation
What is plasma?
this phase is quite rare on Earth but common in the universe
Which phase change is when a liquid turns into a gas?
evaporation or vaporization
A phase change from Phase A to Phase C is known as:

Deposition
The triple point of this substance occurs at:
- 15 ºC and 6 atmospheres
Identify the process that takes place during line segment DE of the heating curve
–boiling –vaporization – vapor equilibrium
Which formula represents Charles’s law?
a. 
b. 
c. P1V1 = P2V2
d. V1T1 = V2T2
a. 
This chart shows descriptions of the atoms for four different substances.

Which substance is a solid?
Object 3
Free-Points
Free-Points
when heat energy is added particles tend to...........
particles began to move faster or quicker
A phase change from Phase B to Phase A is known as:

Vaporization
The area of the graph that represent the solid phase is:
C
State what happens to the average kinetic energy of the molecules in the sample during the first 3 minutes.
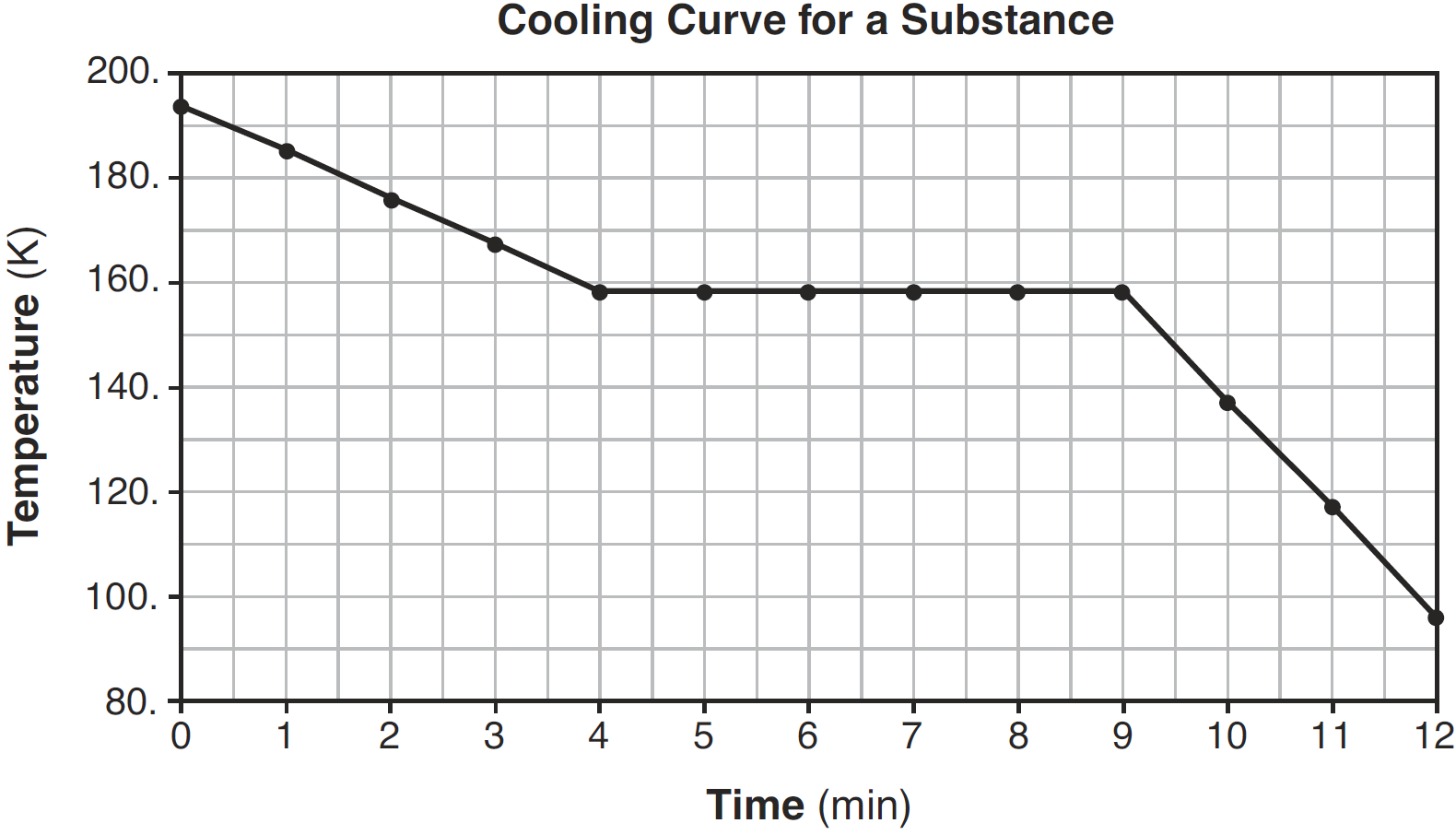
— The average kinetic energy decreases.
— The average KE goes down.
Loni makes a diagram to help organize what she has learned about the gas laws.

Which label belongs in the region marked X?
a. involves changes in temperature
b. has a constant volume
c. shows an inversely proportional relationship
d. does not describe pressure changes
c. shows an inversely proportional relationship