Techniques used to summarize and interpret large amounts of information (data) to answer questions
What is STATISTICS?
The z-score formula for a sample of individual scores.
What is (X - M)/s ?
The type of graph that represents data using vertical bars of various heights that indicate frequencies for continuous data.
What is a Histogram?
The level of measurements where items are classified by categories or traits (such as eye color)
What is NOMINAL?
The mean from the set of data 2, 8, 10, 16, 18, 20
What is 12.3
The z-score for a batter who normally averages .3, with a standard deviation of .05, if he scores .420 for one game.
What is 2.4?
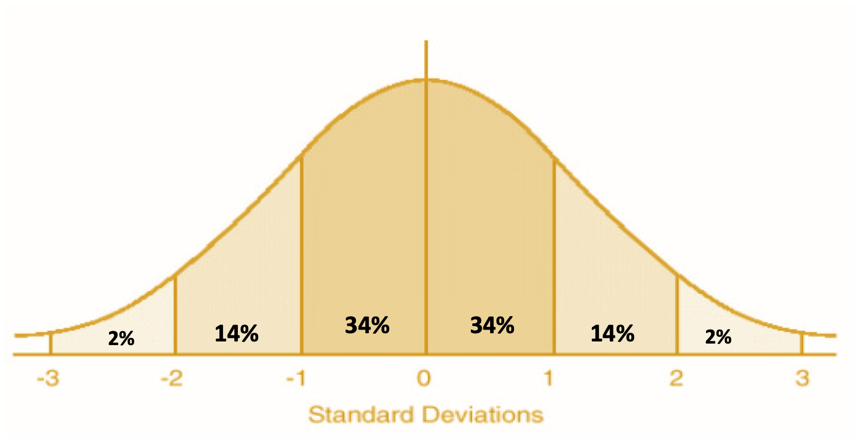
The estimated values for the proportions of scores that typically fall within 3 standard deviations of a mean, given that the scores are normally distributed. (Draw a curve and label!)
The level of measurement where there exists a true zero.
What is RATIO?
Variability calculations such as standard deviation and variance measure the _______ of scores.
What is spread?
A z-score tells us the number of these a score is from a mean.
What are standard deviations?
According to the Central Limit Theorem, if N is large (N = 30 or more), then the mean of the distribution of sample means is called the Expected Value of M (μM) and is equal to _________.
What is the population mean (μ)?
The type of study where a researcher manipulates one an independent variable and tries to determine how it influences other variables.
What is EXPERIMENTAL?
A z-score distribution has a mean of ____ and a standard deviation of _____.
mean = 0, sd = 1
For a sampling distribution of µ = 50 and σ = 10 for samples of n = 25, what is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of lower than 49?
30.85%
(z= -.5)
The size of the standard error (σM) decreases as the size of the sample _________.
What is increases?
A sample is considered a good sample if it is ______.
What is representative?
The measure of central tendency that should be chosen to describe a data set that is severely skewed.
Find the IQR from the set of data 4, 8, 12, 20
What is 10?
(Q1=6; Q3=16)
The raw (individual) scores that mark the boundaries of the middle 30% of a normal distribution of M = 8, s = .3
X = 7.89, 8.11
The confidence interval (in APA format) for a group of students: (M=85, σ=6, N=30).
M = 85.00, 95%CI [82.86, 87.14]