What document would we consult to see the proportion of a distribution in the tail for a z-score of 1.47?
Unit Normal Table
0.50 (or 50.00%)
What is the mean of the Standard Distribution?
0
In a frequency distribution table, the column "p" represents proportion and is calculated by dividing f by N. What does the following equation always equal?
sum(p)
1
In addition to skewness, what's the other visual way we look for normality in a distribution?
Kurtosis
What is the correct interpretation for a z-score of 2.80?
The score is 2.80 standard deviation units above the mean.
What is the probability term for two events that are said to be mutually exclusive?
Disjoint Events
What is another name for the mean of the distribution of sample means?
Expected Value of the Mean
Assume that you care about your relative score on a biological psychology exam (relative to your classmates), and you want to do as well as possible. The average test score was a 70 and you scored an 82. Which of the following standard deviations would make you feel the best about your score?
SD = 5
or
SD = 15
SD = 5
In a normal distribution, approximately what percentage of scores are between 1 SD above the mean and 1 SD below the mean?
~68% of scores.
What are the two components of a z-score?
Sign (+ or -) and magnitude
A researcher is interested in seeing if people in Cleveland prefer country music more or prefer rock & roll music more. The researcher sets up a stand outside the Rock and Roll hall of fame and collects data from people that walk by. Using a concept we discussed in Unit II, why is this potentially problematic?
Random Sampling issues
What are the two conditions for when the distribution of sample means will be a normal distribution?
If:
(a) the original population is a normal distribution
or
(b) the sample size is sufficiently large
Given X = 15, µ = 18, and σ = 4, calculate z.
Without context, how would you interpret that z score?
z = -0.75
The raw score is 0.75 standard deviation units below the population mean.
In what two ways is the formula for z-score for sample means different from the formula for z-score for a single raw score?
1. The deviation score (the numerator) is calculated by subtracting the population mean from the sample mean.
AND
2. The measure of variance (the denominator) is standard error of the mean, not standard deviation.
What are the three components required to calculate the z-score of a population?
The population mean (µ), the population standard deviation (σ), and the raw score (X).
Which mathematical operation is necessary to calculate probability for random sampling with replacement?
Multiplication
For a normal population with µ = 50 and σ = 5, which of the following samples is less likely to be obtained?
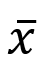 < 42 for a sample of n = 5
< 42 for a sample of n = 5
or
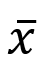 < 42 for a sample of n =100
< 42 for a sample of n =100
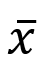 < 42 for a sample of n =100
< 42 for a sample of n =100
Last week, Aubrey had an exam on classical music theory. His score was 85, the class had a standard deviation of σ = 7, and his z-score was 2.5. What was the class average on the exam?
67.5
(µ = X - [σ * z])
How is probability related to proportions?
They represent the same concepts using different language
In relative terms, which of the following scores is "better?"
A GRE of 160 by a psychology student with a z-score of +1.57.
A GRE score of 120 by a communications student with a z-score of -1.59.
A GRE score of 165 by an engineering student with a z-score of 0.28.
A GRE of 160 by a psychology student with a z-score of +1.57.
(The z-score with the highest positive magnitude).
Demonstrated by "Rule 3," which mathematical property is demonstrated in a dichotomous approach to modeling the probability of an event?
Subtraction
P(not A) = 1.00 - P(A)
As n increases, the standard error of the mean decreases. What concept does this statement represent?
Law of Large Numbers
In a bag of M&Ms, 10 are orange, 8 are blue, 7 are green, 5 are red, and there are no other colors.
You draw and eat an M&M at random, and then draw and eat another M&M at random.
What is the probability that the first M&M was blue and the second M&M was red?
0.05 or 4.60%
P(blue) * P(red)
0.2667 * 0.1724
0.0460
When would it not be appropriate to use the unit normal table?
On a non-normal distribution