What is the definition of Psychology?
The scientific study of behavior and mental
processes.
How is science explained by Goodwin?
A way of knowing characterized by the
attempt to apply objective, empirical methods
when searching for the causes of natural
events
What type of medical equipment is used in relation to measuring/graphing the brain?
CT Scan, PET Scan, MRI, EEG.
How is consciousness defined?
A state of knowing or being aware of internal
and external experiences
What are sensations?
Messages we receive from our senses due to stimulation of various receptors
Who is considered the father of Psychology?
Wilhelm Wundt
What would the following coefficients represent?
a) .80
b) .06
c) -.40
a) Strong correlation
b) Weak correlation
c) Weak correlation (Inverse relationship because of -).
What are the four lobes of the brain?
Parietal, Frontal, Occipital, Temporal
What are the ranges of consciousness in sensory awareness? (High to Low)
High Awareness
Focuses awareness (focused attention)
Fully alert and completely engrossed in the task at hand
Middle Awareness
Aware, but minimal attention required
For example, daydreaming, divided attention tasks
Low Awareness
Minimal to no awareness
For example, sleeping
Unconscious—lowest level of awareness due to head injuries, disease,
anesthesia, or coma
What are the 5 external world senses, and 2 internal world senses?
External: Visual, auditory, taste (gustatory), smell (olfactory), and touch (tactile, temperature, pain, vibration).
Internal: Vestibular (position of the head in space, sense of balance) Kinesthesia (the sense that tells you where the parts of your body are).
What two movements dominated early psychology?
Functionalism and Structuralism
Differentiate between Independent Variable and Dependent Variable.
Independent Variable
A variable that is manipulated by an
experimenter
EX: Fertilizer
Dependent Variable
A variable that is measured to show the
influence of the independent variable
EX: Plant growth
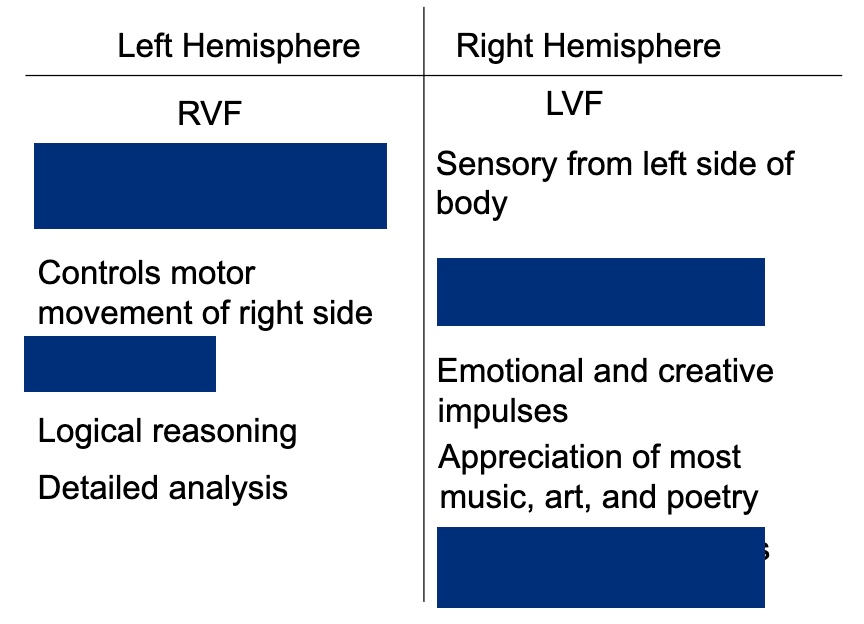
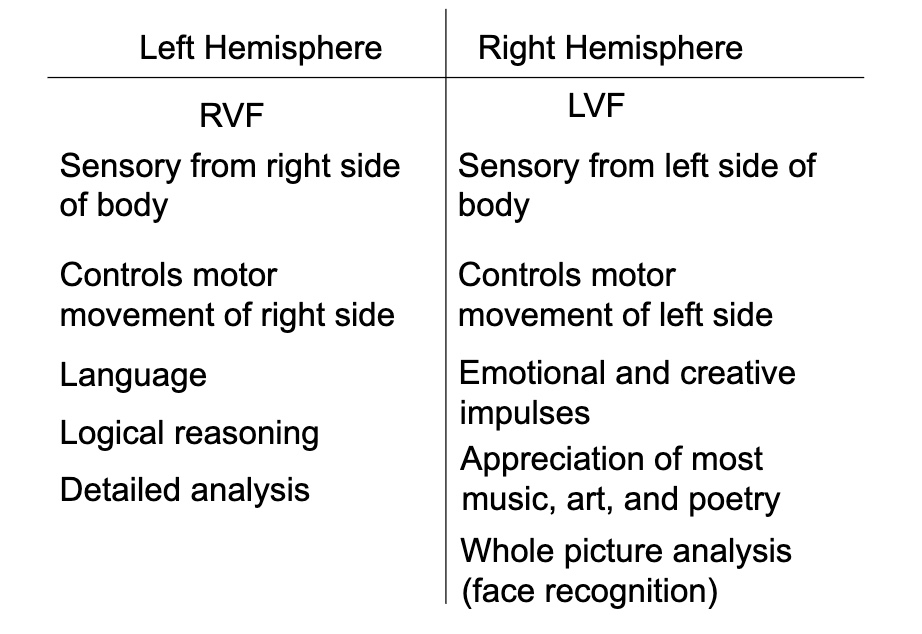
Differentiate between Broca's Area and Wernicke's Area.
Wernicke's Area
- temporal lobe of left hemisphere (near visual and auditory cortex) - Area associated with speech comprehensionBroca's Area
- frontal lobe of left hemisphere- Area associated with speech production
Sleep may be studied and recorded through different types of equipment, name the four (abbreviations) and what they do.
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
Recording of brain waves
EMG (Electromyograph)
Measure muscular activity and tension
EOG (Electrooculograph)
Measures eye movements
EKG (Electrocardiograph)
Measures the contraction of the heart
Does this image represent, binocular or monocular? Explain why and define.
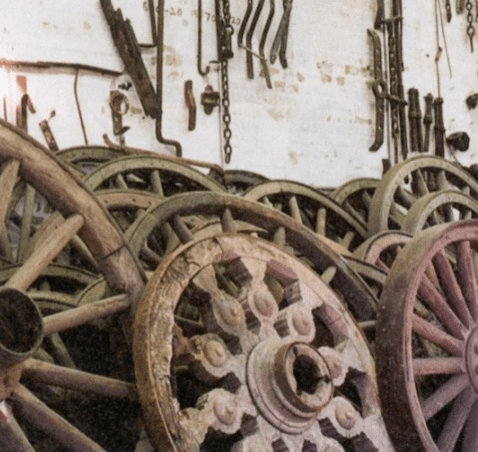

Monocular: Perception through a singular eye.
Closer objects block the view of farther objects.
Briefly explain Functionalism and Structuralism, share one of the criticisms as well.
Functionalism - Focuses on how an object or phenomenon is used.
Criticism:
Introspection is too subjective
Not much application to the real world
Structuralism - Breaking conscious experience into its basic sensations.
Criticism:
Overapplication, not a depth understanding.
Deemed too basic.
What is a Case Study, what is an advantage and what is a disadvantage?
Case Studies: Detailed examination of an existing
situation dealing with a unique individual,
group, or event
Advantages
Only way to learn about unique, rare events
In depth study, so lots of information (details)
Good starting point for generating ideas and
theories
Disadvantages
Post hoc nature of case studies
--- Relies on memories for what happened
Highly influenced by researcher bias One unique circumstance, don’t know what
other influences may have been presen Cannot draw causal conclusions
Fill in the missing blanks to this lateralization Image.
What are the FIVE prominent sleeping disorders? briefly describe.
Narcolepsy
Also called “sleep attacks”
Sleepy all of the time and fall asleep without realizing it
Sleep Apnea
Intermittent loud snoring frequently accompanies the disorder because the sleeper struggles to fill the lungs with air.
Sleep Terror Disorder (Night Terrors)
EX: Child wakes up with a blood-curdling scream
Sleep Walking
Walking or performing other activities while seemingly still asleep
Insomnia
Cannot fall asleep or cannot stay asleep
Which of Gestalt's principles is this? why?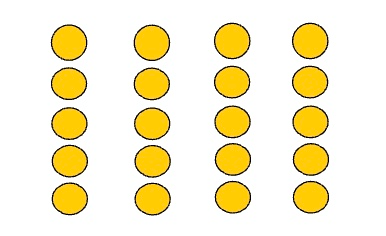
Similarity
Items that are similar in style tend to be
grouped together
Name all SEVEN perspectives of Psychology, and a brief explanation.
Psychodynamic
Looks at Internal conflicts, primarily unconscious, behaviors and mental processes we exhibit.
Behavioral
Looks to the role of learning (the influence of the external environment)
Humanistic
Looks to the value of individual’s potential for growth and stresses that the choices people make are determined by their unique perspectives. (Free will)
Biological
Approach assumes that behavior and mental
processes are based on biological processes.
Evolutionary
This approach investigates how evolutionary
processes affect and shape our behavior.
Cognitive
Looks at the mechanisms by which people process
information and how that mental process influences
behavior. (How we think, hear, remember, etc).
Sociocultural
Looks at the importance of social and cultural
influences have on our behavior and thoughts
What are all of scientific study categories? Give a type for each
Empirical Research:
-Descriptive Research, Correlational Research, Experimental Research
Descriptive Research:
Naturalistic Observation, Non-participant observer, participant observer, Case Study, Survey method
Label the parts of this neuron.
Explain the function of the Soma, Nucleus, Axon Hillock, Myelin Sheath, and Dendrites.
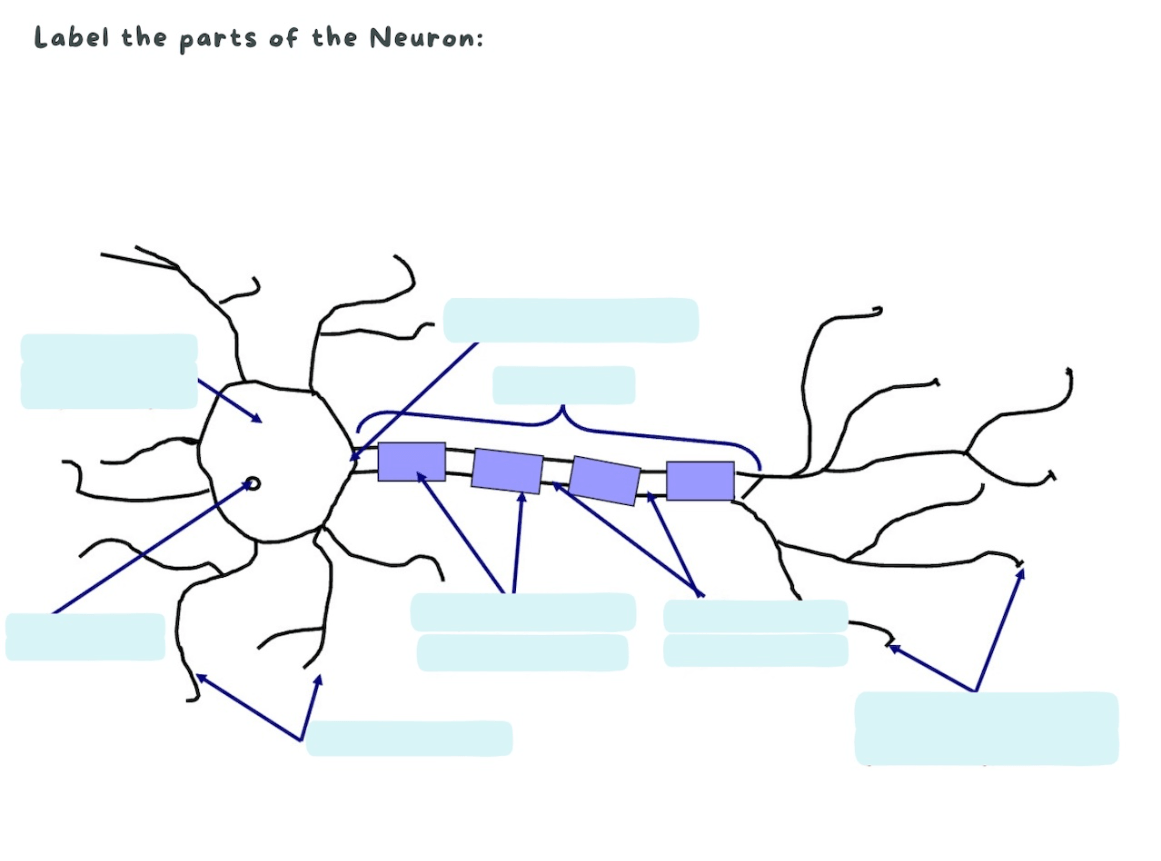
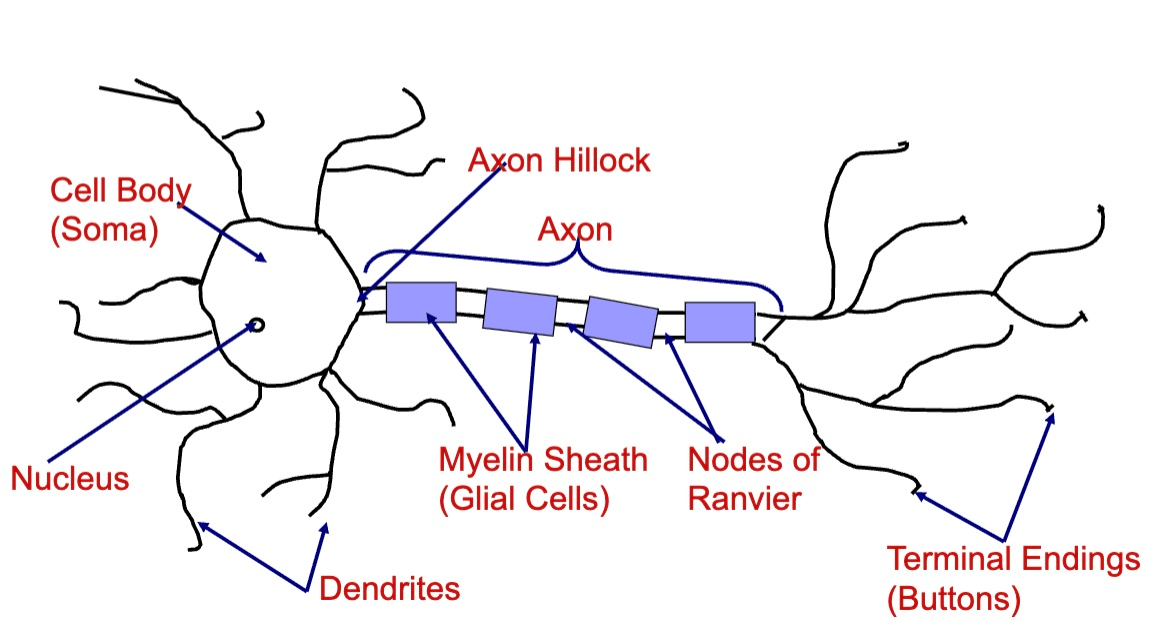
Dendrites—Receive information from other neurons
Cell body (Soma)—Receives information from dendrites
Nucleus—Contains genetic material (DNA)
Axon Hillock—measures stimulation of neuron; if
sufficiently excited, neuron fires. Myelin Sheath - speed up the process of a neuron.
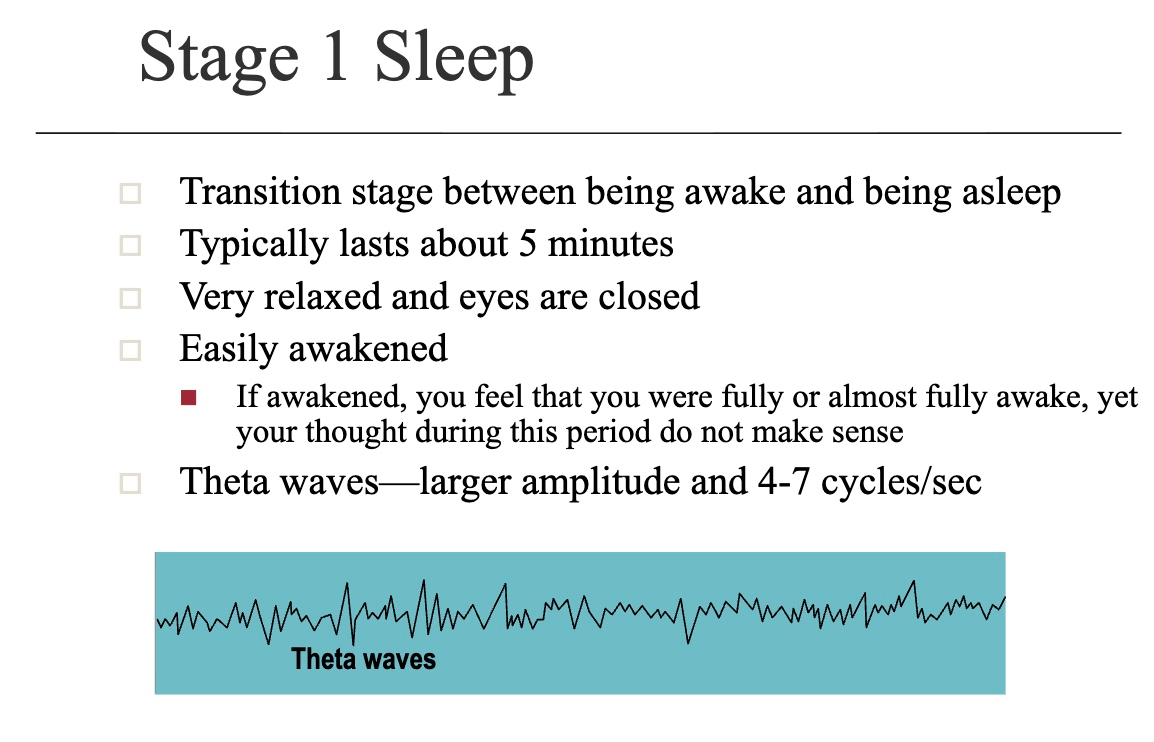
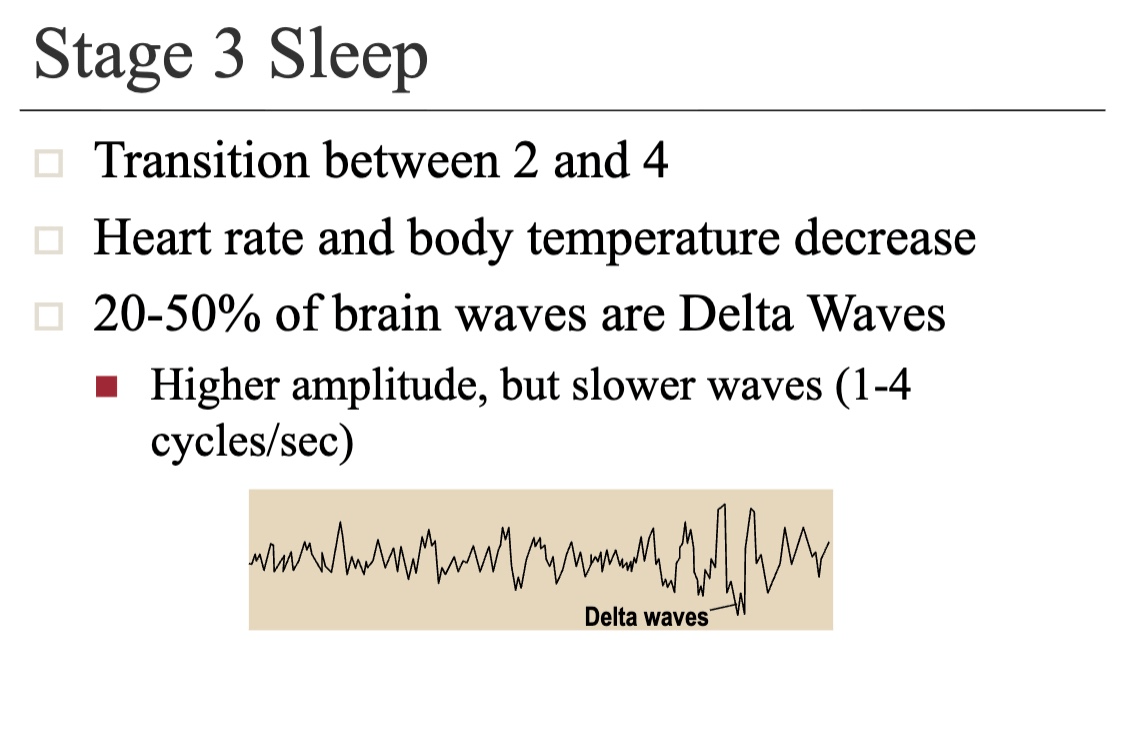
What are the 5 stages of Sleep? Briefly describe.



Which of Gestalt's principle's does this represent?
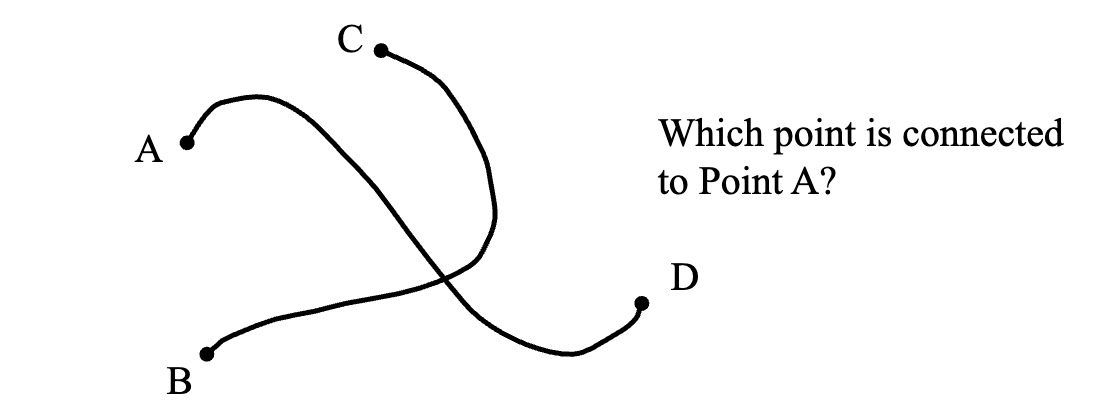
Good Continuation
We tend to perceive smooth, flowing forms
rather than disrupted forms