Name 2 kinds of descriptive research
1. Case Studies (H.M)
2. Naturalistic Observation
As a reminder, descriptive research describes phenomena rather than manipulating variables.
What are two reasons someone conforms:
1) accuracy (informational influence): when a person believes that others are correct in their judgments
2) acceptance (normative influence): due to the desire to gain social acceptance
Give an example of a "personality" test you should not let your friends use
MBTI, Enneagram, Love Languages, Horoscopes, etc
Name two statistical tests/measures of mean differences
1. T-test
When t = or > 1.96, the difference is significant • p value
2. Effect size
Difference between means/std. dev. Most basic is Cohen’s d:
• small: d = .2
• medium: d = .5
• large: d = .8
What is Prejudice vs. Stereotype vs. Discrimination?
Prejudice: Positive or negative attitude
toward a group or its members
Stereotype: Belief about members of a group
Discrimination: Differential behavior toward one
group relative to another
What are the different types of memory?
- Sensory, short-term (George Miller: 7 +/- 2 chunks), long-term (vast, virtually unlimited)
- Implicit, explicit
- Semantic (learn about the Milgram experiment), episodic (find Edmunds room 114)
- Encoding, storage, retrieval
- Recall vs. recognition
What is Classical (Pavlovian) Conditioning?
• Unconditioned stimulus (US) → unconditioned response (UR)
• Conditioned stimulus (CS) + US → conditioned response (CR)
What is operationalization?
The process of turning an abstract concept into an observable and measurable phenomena/variable.
Examples?
What are the differences between conformity, compliance and obedience?
Conformity: Behavior change due to the real or imagined presence of others (low pressue)
Compliance: Behavior change due to a direct request
Obedience: Behavior change at request of authority figure (high pressure)
What are the Big-5 traits?
O: Openness to Experience
C: Conscientiousness
E: Extraversion
A: Agreeableness
N: Neuroticism
What do correlations tell us? What is small, medium and large?
1) direction of relationship (positive or negative)
2) magnitude of relationship (-1 to 1)
small: 0.2, medium: 0.3, large: 0.5
What is the difference between "Old-fashioned” Racism vs. Contemporary Racism?
"Old-fashioned” Racism:
• Blatant, overt
• Consciously endorsed
Contemporary Racism:
• Often unconscious, latent
• Powerfully influenced by the situation...
Neural bases of learning: difference between Synaptogenesis & Neurogenesis
Creation of new synapses between neurons vs. new neurons
Neurogenesis typically happens in utero/prenatally and infancy (it also continues to a much smaller extent in certain parts of the brain, such as the hippocampus, into adulthood), whereas Synaptogenesis happens every time we learn something new (occurs throughout life, particularly in response to learning and experience).
Describe Watson & Rayner (1920) findings (Little Albert)
US - Lound noise
CS - White rat
Other CS - Other stimuli similar to the rat (rabbit, fur coat)
UR - Fear of the CS and a more generalized fear response to other stimuli that are similar to the original CS, turning into a CR
What is the purpose of random assignment?
It controls bias.
The population has natural variation, this is expected to be the same in both groups if assignment is random.
What is the difference between a descriptive (2 types) and an injunctive norm?
Descriptive: perception of what is common
Static: explain the current state of behavior // Dynamic: explain how behavior is changing
Injunctive: perception of what is socially acceptable
What is the "lexical hypothesis" of personalities? (Allport & Odbert, 1936).
The idea the most important differences between individual people will be coded in the language that we use to describe people. Thus, all the words can be narrowed down into certain orthogonal dimensions (scores on one trait dimension doesn't predict scores on another dimension.
Name the three principles of the Belmont Report and their applications.
1) Respect for persons: voluntary participation, minimal coercion, informed consent
2) Beneficence: minimized risk < maximized benefit
3) Justice: fair distribution of benefits and risks (randoms selection of subjects)
Factors that contribute to bias
Motivational: Perceived conflict over resources, values
Socio-cultural: Media, cultural associations (Good/Bad)
Cognitive: Social categorization, automatic associations, attentional & memory biases...
What are the Core Tenets of Behaviorism?
(disclaimer --> not fully supported now—both nature and nurture)
1. Psychology is the science of observable behavior, not internal processes (emotion, cognition)
2. The sources of behavior are external (in the environment), not internal (in the mind)
3. Human and animal behavior is learned through conditioning
What is extinction? When is it used?
Occurs when a CR no longer occurs when a CS is presented
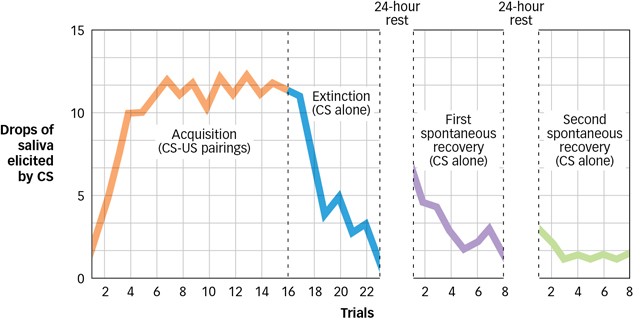
Repeatedly pairing an unconditioned stimulus and neutral stimulus will lead to a learned association (acquisition). The neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus. Presenting the conditioned stimulus without the unconditioned stimulus will lead to extinction. Over time, the learned response may reemerge, a process called spontaneous recovery.
What characteristics must be present in order for research to be "experimental"? What does experimental research tell us?
1. Manipulation: Independent variable(s), dependent variable(s)
2. Random assignment to conditions
Often, experimental studies include a:
3. Control group
Does X cause Y?
Describe an example of a descriptive norm experiment:
2) Food waste signs at Pitzer
What is the Person-Situation debate?
Are personalities based on "traits" or the "person," or rather are they based on the "context" of which the person developed and/or is currently existing in.
Name one problem with using correlations?
Third-variable problem: is there another variable that may be causing the results we found? (A mediating variable, but also could be a moderating variable)
Directionality problem: Which causes what?
What are the differences between System 1 vs. System 2 processing?
System 1 (implicit):
• Nonconscious
• Involuntary
• Effortless
• Fast
• Rooted in past experience, repeated exposure
➢ Assessed indirectly (e.g., via reaction time,
physiological measures --> IATs)
System 2 (explicit):
• Conscious
• Voluntary/deliberate
• Effortful (requires cog. resources)
• Slow
• Assessed via self-report
• Reflects cultural and
personal values
(Stroop Color-Naming Task: People are generally slower to name the color of words when they are incongruent with the meaning of the word)
How to get information from working memory into LTM?
Rehearsal is not enough (need for structure/organization) --> Deeper processing enhances memory
Examples:
– Chunking (e.g., chess masters)
– ‘Deep’ (semantic) versus ‘shallow’ (surface)
encoding
– Deeper processing facilitates encoding (e.g.,
vivid imagery)
–Mnemonics (get around on campus with my hippocampus OR CPR "Stayin Alive")
Describe: Operant (Instrumental) Conditioning
a learning method that uses rewards and punishments to modify behavior. It's based on the idea that behaviors that are rewarded are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors that are punished are less likely to happen again.

Cognitive Load
Amount of information to keep in your mind.
Ex. 7 or 2 numbers
What is the reason for the difference in the following rates for organ donation rates? What does this tell us?
Germany: 12% effective consent
Austria: 99.98% effective consent
Austria has an opt-out policy for donating organs, making consent the default. Defaults are so powerful because it is less effortful to change the response and people infer a recommendation (to consent).
What is test-retest reliability? And how does it support the idea of personality traits?
T-R Reliability: consistency of a measure given to the same participants on different occasions
This supports the central idea that a "trait" should remain similar (stable) across time and situations (ex. E: 0.82, O: 0.80)
Describe Milgram (1963) series of studies in terms of the main type of study, IV, DV, results, as well as any ethical concerns this brought up.
Stanley Milgram's 1963 obedience study was an EXPERIMENT done in a lab made to investigate how far individuals would go in obeying an authority figure, even if it conflicts with their personal conscience.
IV: instructions given by authority figure
DV: max level of shock administered by participant onto the confederate
RESULTS: 65% of participants obeyed the authority figure and administered the highest level of shock (450V), indicating a strong tendency to obey.
ETHICAL CONCERNS: Lack of informed consent (thought the experiment was something else), Psychological Harm (thought they had hurt, even maybe killed, someone), Potential undue influence ("you must continue"), etc
What were the implications of the findings from the “ESP Study” by Gaertner & Dovidio (1977)?
"Racial discrimination may manifest in ambiguous situations where a response can be justified on the basis of ostensibly non-racial factors" (i.e., blame other witnesses for not helping).
Example bias interventions? (Hint: Dr. Jessica Eberhardt @Stanford)
– Counter-stereotype exposure
– Intergroup contact
• Greater exposure (quantity)
• Cross-group friendships (quality)
Implicit bias:
• Removing ambiguity, distraction, fatigue when making complex decisions (e.g., hiring, college admissions, jury decisions)
What are the different types of reinforcement schedules? Which is most effective?
Patterns of delivering a reward (reinforcer) to strengthen a behavior
• Continuous reinforcement
OR
• Partial reinforcement (fixed vs. variable)

Fill in the following blanks:
In _____ research, we specify a manipulation that defines the variable.
In _____ or _____ research, we define our variables by their measurement.
1) Experimental
2) Observational; Correlational
What are some of the major factors that affect obedience?
1) Emotional distance to the victim
2) Proximity of authority
3) Legitimacy of authority
O: Generally consistent, but increases with age
C: decreases around 15 and then increases with age
E: decreases around 15 and then remains consistent with age
A: decreases around 15 and then generally increases with age
N: Generally decreases with age
thanks for picking this one free points
good luck
What are the implications of social learning theory for bias (e.g., prejudice, stereotype, and discrimination)? In other words, how can we understand bias as a learned behavior, and hence as something that can be unlearned?
e.g.,:
Bias can be understood as a learned behavior because it is often developed through repeated exposure to societal norms, stereotypes, and personal experiences, ingrained in our minds over time. IATs can help as interventions allowing us to be aware of our biases and "unlearn" them by taking active steps to challenge those ingrained patterns, replacing them with more inclusive perspectives through conscious effort and exposure to diverse viewpoints.
Functions of the hippocampus, as exemplified by the London Cab Drivers study (Maguire et al., 2000)
-Short and long-term memory, learning, and spatial memory
- posterior HP bigger across time

Negative Reinforcement vs. Positive Punishment?
- Decreases the likelihood of an unwanted behavior by adding an aversive stimulus. For example, scolding a student for texting in class is a form of positive punishment.