What was the Gestalt psychology approach to memory
Emphasised the active role of the remember and their internal representations of stimuli which are organised using perceptual principles and reasoning (eg. similarity)
Give an example of structural plasticity
Taxi driver have larger hippocampus
How can we observe the SPE in infants
They spend less time looking (more recognition) at faces they saw early and late. recency effect fades with delay
how do we know that binding is an automatic process?
because impairment of an additional task on recall was no greater for binding condition then it was in the single features condition
How did Sperling measure sensory memory? Hint: this addressed the limitation of forgetting where we know we saw more then we can remember after
Participants were presented with 3 rows of 4 letters, participants were not told in advance which would be tested (hence requiring the whole array to be encoded). The row to be recalled was specified by a a tone (e.g. low tone for top line). Their accuracy of recall for the specified line was multiplied by 3 since it represented their memory of the entire array. When tested immediately this provided an estimate of sensory memory capacity
What is the lag effect? And what is the non-monotonic lag effect?
The benefit of repeated study attempts increases as the lag between the two study ocassions increases. The non-monotonic lag effect is the tendency for the lag effect to first increase and then decrease if the lag gets to long (in the study the increase stopped after 20 days)
what study showed the peak end rule?
Cold pressor task: most people wanted to do the longer trial of putting hand in freezing water because for the last 30 seconds the water temp increased by a degree
what was Phillips study which showed change blindness and visuo-spatial stms limited capacity
ability to detect change decreased as the complexity increased 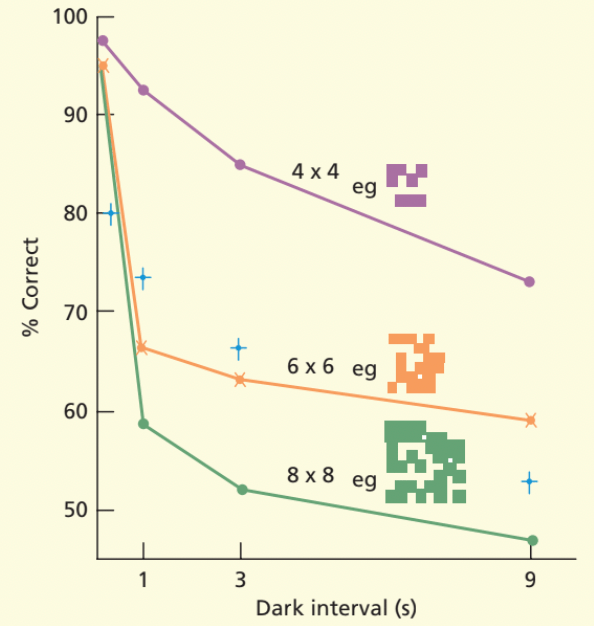
What is masking?
when the perception and storage of a stimulus is influenced by events occurring immediately before presentation (forward masking) or more commonly after (backward masking)
2 reasons why isn't spacing commonly used?
1. Spacing requires you to plan your study well in advance which is not always practical
2. Metamemory: People believe massed learning is better for them as it feels better and satisfactory
depression is characterised by ________ memory
overgeneral
what is the corsi span task and what does it measure
measures the spatial aspect of visuo-spatial memory by imitating the sequence of block tapping - typically around 5
What were the two types of masking investigated by Michael Turvey?
Brightness masking (masking/interference increases when the mask becomes brighter because it makes the target less distinct). This reflects early processing because the effect only occurs when the mask and stimulus are presented to the same eye.
Pattern masking (targets are followed by similar features which disrupts perception of the target before it can be processed). This reflects later processing because the effect occurs even when the mask is presented to the other eye since later visual processes binds the information from both.
what theories are favoured for why spacing/distributed practice works?
Deficient processing hypothesis and study phase retrieval hypothesis
what 2 things do memory span measures require?
remember what the item are, remember the order in which they were presented
what is the specious present
the tendency to extend or shorten the time frame of the present to best suit the events
How is serial recall differentially affected by errors for auditory vs visual presentation of stimulus?
Likelihood of errors systematically increases for visual presentation from beginning to end. Whereas, auditory presentation ALSO shows a recency advantage where the last 1 or 2 items are more likely to be correct than the middle items.
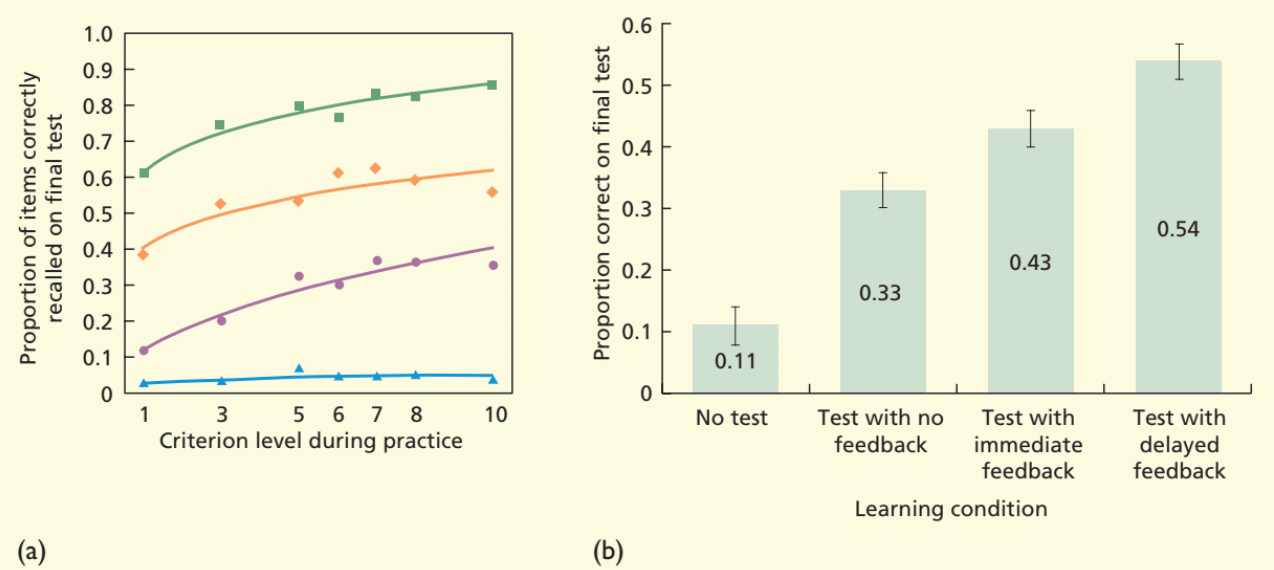
What is test enhanced learning?
Testing with feedback to correct mistakes and reinforce right answer especially when the feedback is given after all the questions instead of after each
how do we use chunking in memory span
by grouping things together into a chunk typically consistent with long term language habits (eg. natural rhythms in phone number)
in a study of subjective temporal distance, how did the length of the timeline surrounding the same date of a negative event affect how people rated themselves?
when people were given a longer timeline but the same date of event they rated themselves more negatively since it seems closer
How can the recency advantage of auditory presentation be removed and what study elaborated on this?
Having another spoken item/suffix between presentation and recall (even if the item isn't processed or relevant). This was elaborated in a study which showed that the nature of the suffix is crucial, eg. a buzzer sound did not disrupt recall only a spoken word
what is the changing state hypothesis in relation to the irrelevant sound effect
sounds that fluctuate in pitch disrupt verbal stm
What are examples of implict/non declarative memory
Priming, conditioning, procedural memory
how does the feature model explain forgetting
depends on interference of new items disrupting the features encoded of earlier items - explains similarity effect of phonological loop where items that have more similar features increases likelihood of retrieving wrong item
What is Ebbinghaus's 'total time hypothesis'?
The amount learned is a simple function of the amount of time spent learning
what happens to primacy and recency effects during short vs long delay of free recall task?
we see primacy in both conditions since they get transferred to LTM due to rehearsal but we only see recency effects in immediate recall since they are held in STM which decays
Why does Ericsson disagree with the 10,000 hour rule?
Because for many skill domains, performing a skill repeatedly will eventually lead to performance plateau where you will stop improving so much.
why do we know earlier items are stored in LTM? hint. what 5 variables that we know influence LTM also impact earlier items
1. presentation rate (slower is better)
2. imageability
3. word frequency - familiar words are better
4. age
5. physiological state
What is Ericsson's concept of deliberate practice and what study by Young and Salmela showed this effect?
Deliberate practice helps you move beyond the plateau of improvement by engaging with full concentration on improving a particular aspect with immediate feedback etc
Young and Samela showed that although national, club, and provincial runners spent the same hours training the national runners were the best because they devoted time to weight and technical training
what is the discrimination ratio
as you get further and further away (increased delay) the ability to discriminate between the most recent and the one before gets harder