Hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized speech that persist for under a month and resolve completely. Define this short-lived psychotic illness.
What is brief psychotic disorder?
Affected neurons contain Lewy bodies: intracellular eosinophilic inclusions composed of _________?
What are alpha-synucleins?
Most common cause of restless leg syndrome?
What is iron deficiency anemia?
This atypical antipsychotic is unique for its ability to reduce suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
What is clozapine?
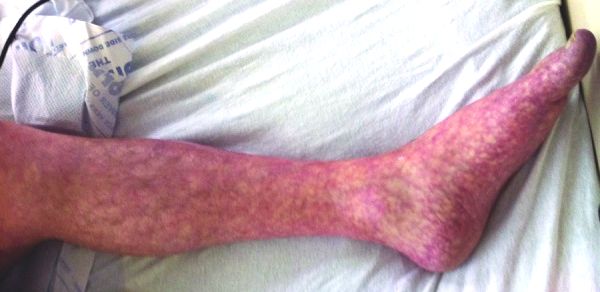
Parkinson Drug that can cause the above as a side effect.
What is amantadine?
Trinucleotide repeat for Huntington's Disease
What is CAG?
A patient has been on haloperidol for 2 weeks and develops fever, elevated creatine kinase, elevated WBCs, and lead-pipe rigidity. These drug(s) are used to reverse the life-threatening reaction.
What is dantrolene or bromocriptine?
High doses of carbidopa-levodopa can cause psychosis. What is the next best step in management?
What is "Decrease dose of carbidopa-levodopa"?
Name one medication that can treat restless leg syndrome.
What are:
- gabapentin, pregabalin (gabapentinoids)
- dopamine agonists (pramipexole)
- carbidopa/levodopa (used in intermittent/milder cases)?
This atypical antipsychotic can cause galactorrhea, amenorrhea, and gynecomastia due to elevated prolactin levels.
What is risperidone?
A 52-year-old man with Parkinson disease presents to the emergency department with a sudden, severe headache, palpitations, nausea, and profuse sweating. His blood pressure is 240/130 mm Hg, and pulse is 120/min. He recently started a new medication to help with his "off" episodes between doses of levodopa. On further questioning, he reports attending a wine-and-cheese party the previous evening. Give the immediate first-line pharmacotherapy.
What is Phentolamine (IV)?
*Immediate management:
Discontinue the MAO inhibitor (selegiline).
Administer a short-acting α-adrenergic blocker:
Phentolamine (IV) — competitive, nonselective α-blocker
→ ↓ peripheral vasoconstriction
→ ↓ BP rapidly
If unavailable: Nitroprusside (direct vasodilator) or nitroglycerin can be used.
Supportive care: Oxygen, cardiac monitoring, IV fluids (as needed).
Dementia + visual hallucinations + parkinsonism.
What is lewy body dementia?
This first-line pharmacotherapy is used for a patient on an antipsychotic for over 2 years who has started to experience involuntary, erratic, jerky, uncontrolled, and repetitive facial muscle movements.
What are VMAT2 inhibitors (valbenazine or deutetrabenazine)?
*adjunct therapy: benzo or botulinum toxin injections
A 54-year-old man with Parkinson disease presents with agitation, tremors, diaphoresis, and hyperreflexia. His temperature is 39.4 °C (103 °F), heart rate is 118/min, and blood pressure is 165/95 mm Hg. He recently began taking an over-the-counter herbal supplement for “mood enhancement” while continuing his prescribed selegiline. Give 2 drugs that can manage this case.
What are benzos or cyproheptadine?
The combination of selegiline (MAO-B inhibitor) and St. John’s Wort (serotonergic herbal agent) leads to serotonin syndrome.
The immediate step in management is discontinuation of all serotonergic agents and supportive care (IV fluids, cooling, benzodiazepines).
Cyproheptadine is the specific antidote, but it is used after stabilization if symptoms persist or worsen.
Parents of an 8-year-old child who has a 50% risk of inheriting HD request genetic testing for their child. NBS?
What is "recommend against predictive testing"?