What is the definition of Psychology?
The Scientific Study of Behavior and Mental Processes.
Does correlation imply causation?
No!
How do neurons function?
They are directional – electrical pulses travel down in one direction.
What is Developmental Psych?
The study of how human behavior and mental processes changes over the lifespan
Explain the Biological Perspective and Psychodynamic Perspective.
Psychodynamic: examines the unconscious role that internal conflicts on the behaviors & mental processes we have.
- Biological: Assumes that our behavior and mental processes are based on our biology. (Look at neurons, hormones, physiology, brain chemicals)
What two movements dominated Psychology?
Structuralism and Functionalism
What is the difference between a Non-participant Observer and Participant observer?
Participant is where the observer becomes involved in study. While, Non-participant is where the observer watches the study be conducted.
What makes up the cerebral cortex?
The frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital lobes.
Explain the Nature vs Nurture Argument.
Nature: Genetic or hereditary influences. Maturation
Nurture: Experiential or environmental influences. Learning
Both Nature & Nurture influence development.
Explain Conservation. And possibly the four ways to measure.
Volume, Matter, Number and Length.
Who is considered the father of Psychology?
Wilhelm Wundt
Identify scientific and non-scientific methods of research.
Scientific:
Empirical Method, Objective Method, Correlational Research, Experimental Research, Descriptive Research.
Non-Scientific:
Method of Authority, Method of Tenacity, Priori Method, Intuition, Personal experience.
Compare & Contrast Broca's area and Wernicke's area.
Wernicke's area controls the ability to understand the meaning of words, Broca's area, in conjunction with the motor cortex, controls the ability to speak those words.
Then, both are located in the left hemisphere to facilitate language processing.
Name and Describe the following reflexes in Newborns:
Palmar Grasp Reflex, Babinski Reflex, Moro Reflex
Moro Reflex —A response to unexpected loud noise or when the infant feels like it is falling, the newborns fling out their arms then bring them together
Palmar Grasp Reflex—when something touches their palms, their hands grip tightly.
Babinski Reflex — when you stroke the side of a newborn’s foot, their toes fan outward
What is some of the medical equipment used to measure brain function?
EEG (Electroencephalogram), CT (Computed Tomography) Scan, MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Imaging), PET Scan (Positron Emission
Tomography).
Explain Structuralism and Functionalism.
Structuralism: Breaking consciousness into its basic sensation.
Functionalism: Focuses on how an object or phenomenon is used.
What is correlational research? And what type of Correlation would these following be: -0.80, 0.01, 0.50.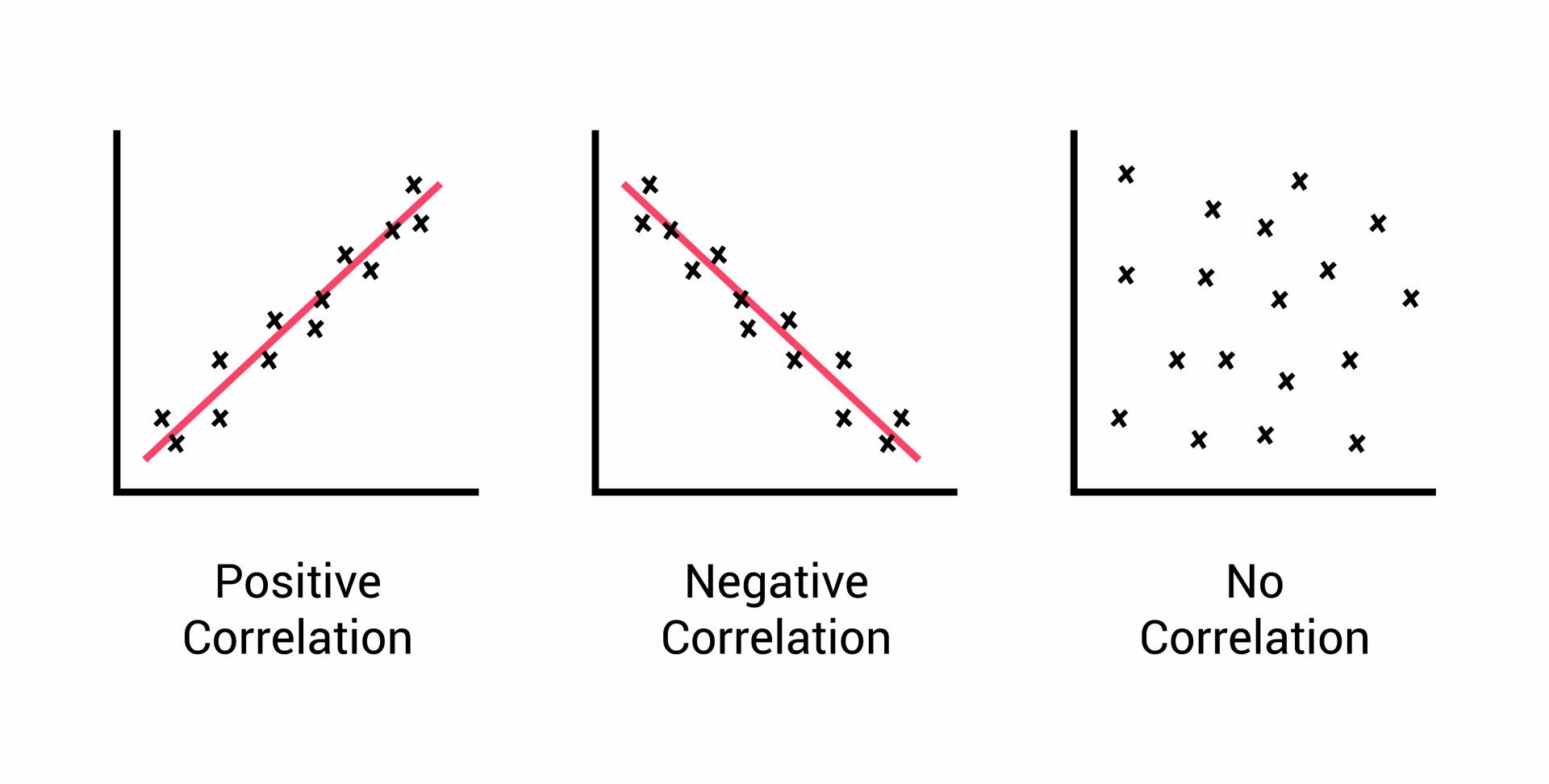
A relationship (association) between two variables. (Makes predictions of future behaviors).
Label the Neuron Apropriately.
Refer to powerpoint.
What is Adolescent Thinking? What are three psychological states associated with it?
Def: Characteristic of adolescent thinking that leads young people to focus on themselves to the exclusion of others
The Personal Fable: Young person might believe his or her thoughts, feelings, and experiences are unique
The Invincibility Fable: Adolescent’s egocentric conviction he or she cannot be harmed by anything that might defeat a normal mortal
Imaginary Audience: Belief that other people are watching, and taking note of, his or her appearance, ideas, and behavior
After a neuron fires, it becomes
hyperpolarized for a brief period of time,
this state is known as the
Refractory Period
What are the 7 perspectives of psychology and could you briefly explain them?
Psychodynamic, Behavioral, Humanistic, Biological, Evolutionary, Cognitive, and sociocultural.
Distinguish the Independent variable and Dependent variable in this example:
A study is conducted to determine how varying levels of caffeine intake affect students' test scores. In this case, what is the independent variable, and what is the dependent variable?
Dependent Variable: Student Test scores
Independent Variable: Caffeine Intake
Right Hemisphere: Sensory from left of body, controls motor movement of left, emotional + creative impulses, appreciation of art, whole picture analysis ( Facial recognition).
Left Hemisphere: Sensory from right of body, controls motor movement of right, language, logical reasoning, detailed analysis.
Write out Jean Piaget's Four Stages of Development.
Refer to Powerpoint.
Label and explain each part of a neuron.
Dendrites—Receive information from other neurons
Cell body (Soma)—Receives information from dendrites
Nucleus—Contains genetic material (DNA)
Axon Hillock—measures stimulation of neuron; if sufficiently excited, neuron fires
Myelin Sheath: Speeds up the firing of the neuron.
Terminal Endings: neurotransmitter is released into synapse.