What is psychology?
The study of mental processes and behavior.
Who is the “Father of Psychology”
Wilhelm Wundt
What is a hypothesis?
A testable prediction about the relationship between two or more variables.
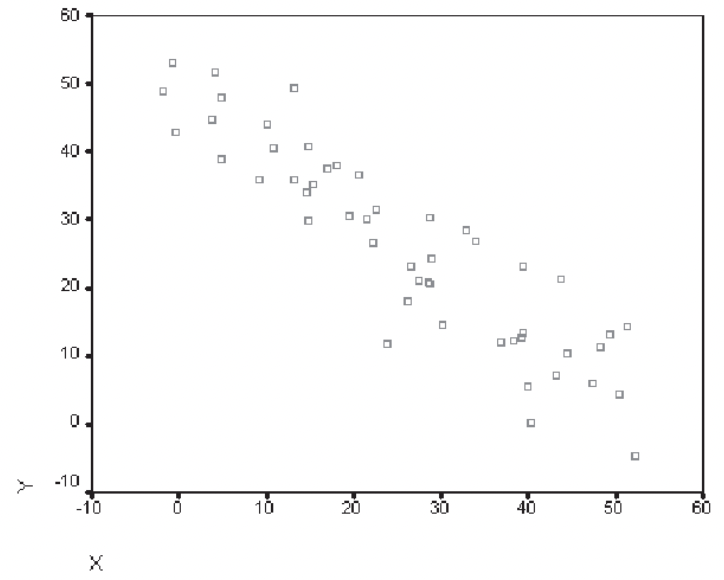 What does this scatterplot show
What does this scatterplot show
A negative correlation
Did Genie ever learn to talk?
Yes
What is Natural Selection?
Organisms that are better adapted tend to survive and produce more offspring.
What is Structuralism?
School of psychology that studied the basic units of thought (physical sensation, feelings, and memories), still used introspection - very hard to verify.
What does correlational research aim to do?
Identify and measure the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
What does a correlation coefficient (r) of
0.3 Mean?
A weak positive correlation
What helped the "wolfpack brothers" survive?
What is operant conditioning?
Rewards & punishments used to shape behavior
What is Psychodynamic Psychology?
Psychology branch that studies how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior (Freud)
What does experimental research aim to do?
Determine the cause-and-effect relationship between variables by manipulating one and measuring the outcome in another.
Why is deception important in some experiments?
So participants are not aware of the study's true purpose or altering their behavior.
If 80% of people are shorter than you:
A. You are in the 20th percentile
B. You are taller than all children below age 14
C. You are in the 80th percentile
D. You are in the 8th Order
Why do we find eyes so captivating?
Because eyes can communicate emotions and intentions, which is important for survival.
What did Pavlov test his theories on?
Dogs (bells & food)
What are strengths and weaknesses of case studies?
They provide detailed information but cannot be easily replicated or generalized.
Why can we not decide that one variable causes another when there is a correlation between the two?
Because we do not know which variable causes the other.
Because a third variable might be causing both observed variables to change together.
How would you identify the data in this chart AND give an example of how you might get this data:
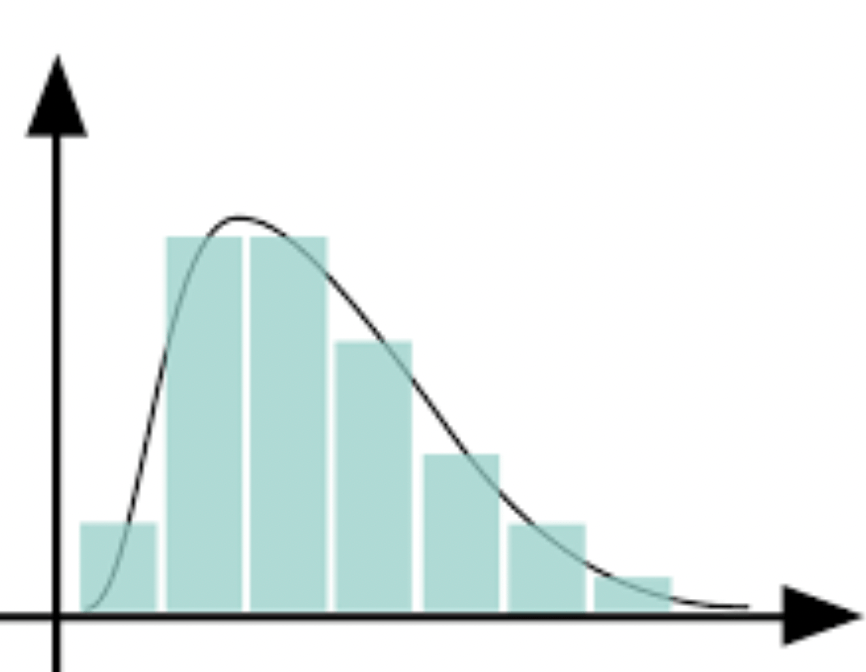
Positively skewed
Ex: one VERY unordinarily tall person in a survey about height
What is the first (lowest) step in humanistic psychology?
Physiological needs, like food, water, and shelter necessary for survival.
What happened to baby Albert?
No one knows, he was taken out of the experiment.
How do you make sure that your survey renders accurate data about a population?
Use a large sample size that accurately represents the population and ensure the questions are clear and unbiased.
To find the “center” (most common responses or measurements of a variable) from skewed data, what measure of central tendency should be used?
Median
Explain the purpose of a double blind experiment, defining demand characteristics & experimenter bias and how they play a role in experiments.
Double blind: neither the experimenter or the subjects know what group the are in.
This lowers the chance of demand characteristics (tester implying expectations to subject) or tester bias (tester analyzing data with a certain desire to see results).