Where are the 3 common locations for Peripheral IV lines?
Hand, Elbow, Foot
This is a symptom related to the intensity of work of breathing
Dyspnea
In this type of heart failure, the left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally and is unable to pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation
Systolic HF or HFrEF
What medications are used for HF management?
ACE inhibitors, Diuretics, Inotropes
This device consists of a tube connected to the vena cava that allows for blood to flow out into an oxygenator/artificial lung to add O2 and remove CO2 from the blood
ECMO
Which type of Respiratory Failure results in hypoxemia due to alveolar flooding and shunting?
Type 1 Respiratory Failure
What is the main use for an Arterial Line?
Invasive BP monitoring (provides a continuous measurement of systolic, diastolic, and MAP)
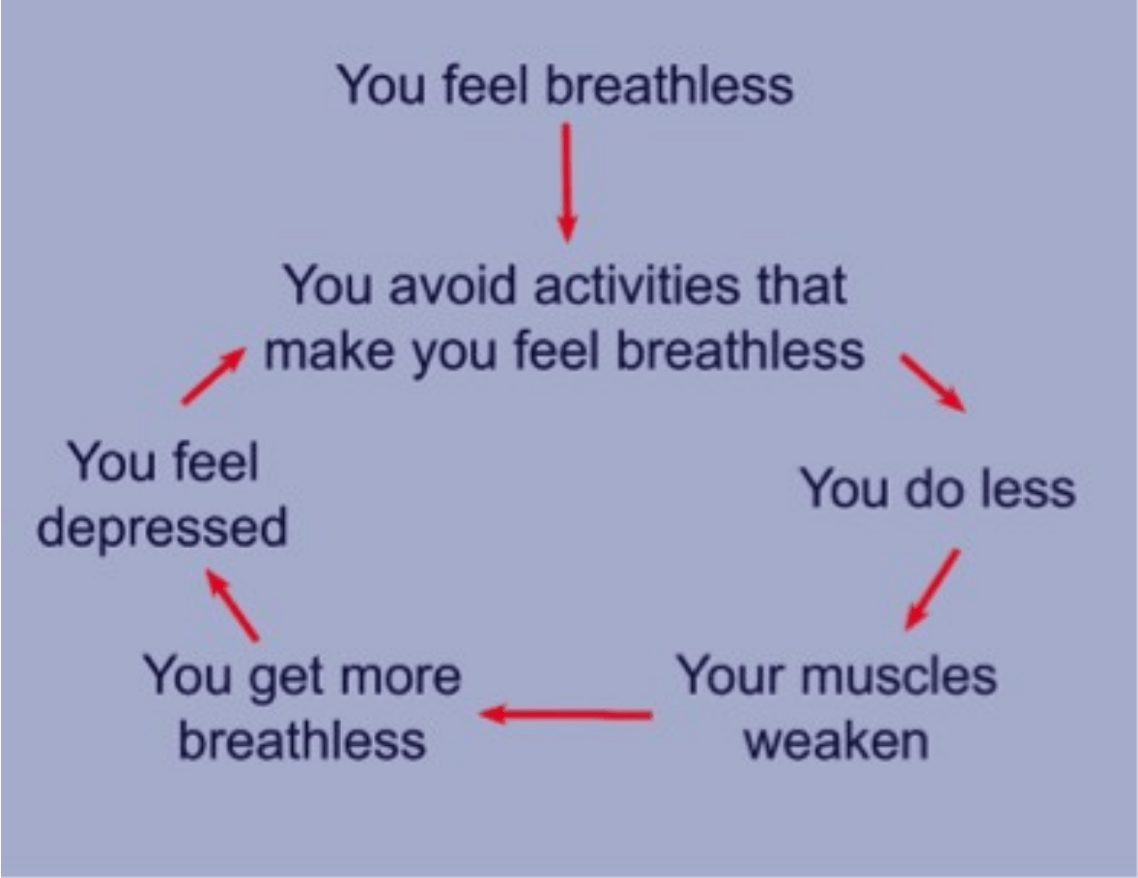
What is this called?
Dyspnea Spiral
In this type of heart failure, the left ventricle loses its ability to relax normally due to muscle stiffness and the heart can't properly fill with blood during the resting period between each beat
Diastolic HF or HFpEF
Inotropes
This device consists of a battery operated pump that is surgically implanted i the upper part of the abdomen and provides circulatory support by pulling blood from the left ventricle and pumping it into the aorta
LVAD
Acute or Chronic Respiratory Failure:
characterized by SOB, air hunger, rapid RR, confusion/sleepiness, LOC, cyanosis
Acute Respiratory Failure
This type of line allows direct continuous monitoring of Central Venous Pressure or Right Arterial Pressure in order to assess cardiac function and intravascular fluid status
Central Line
This condition refers to a sudden event characterized by sustained worsening of any patient's respiratory symptoms
Acute Exacerbation
What are the effects of HF on the MSK system?
Decreased muscle mass, increased muscle atrophy, myopathy
Partial Credit Available:
Which oxygen delivery systems are low flow? Which are high flow?
Low: Nasal Cannula/Catheter, Transtracheal Catheters
High: Venturi, HFNC
When looking at flow rate, at what point should you terminate exercise in an LVAD patient for centrifugal and pulsatile?
Centrifugal flow rate < 4L/min
Pulsatile flow rate < 3L/min
With this type of ventilator setting, the patient is heavily sedated and not allowed to initiate a breath
Controlled Mandatory Ventilation (CMV)
This type of line helps to monitor the heart's function, blood flow, and pressure in/around the heart; it consists of placing a catheter into the right side of the heart and arteries the lead to the lungs
Swan-Ganz Catheter
Increasing volume of exhaled air
Reducing dynamic hyperinflation
Increasing tidal volume
Decreasing respiratory rate
Decreasing airway collapseWhat lab result is most indicative of HF and is released in response to increased stretch resulting?
Elevated BNP
What is the SpO2 and PaO2 value for mild hypoxemia?
91 - 94%
70 - 79 mmHg
7 - 10 days
This type of respiratory support system is used in conjunction with other modes in order to prevent airway collapse; a complication associated with this system is barotrauma
PEEP (positive end expiratory pressure)
What are the types of feeding tubes?
Dobhoff, G Tube (aka J Tube), NG Tube
What are the Dyspnea Relieving Positions?
(demonstration!)
What are the three medical management options for HF?
Decrease fluid overload, Improve cardiac contractility, Correct electrical activity
What is a side effect of bronchodilators? >:(
Tachycardia
When working with a HF patient who has had an ICD implanted; what is an important HR parameter to keep in mind?
This type of system provides a preset pressure to patient's airways for the duration of spontaneous breaths; it is typically used with SIMV mode
PSV (pressure support ventilation -- increases spontaneous tidal volume and decreases work of breathing)
Name 2 possible complications of a chest tube
Pain, Failure to enter pleural space, infection, penetration/laceration to lungs or peritoneal space, hemorrhage, blocked drains, pleural sepsis, subcutaneous emphysema
Name the five steps of Energy Conservation
1. Plan the Day
2. Organize Time to Conserve Energy
3. Modify/Change Activities
4. Eliminate Unnecessary Steps
5. Analyze Methods
This device is capable of correcting life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias in HF patients
ICD (performs cardioversion, defibrillation, and pacing of the heart)
What are the FiO2 that correspond to the oxygen delivery systems? (partial credit available -> 6 possible oxygen delivery systems)
Low flow: 40%
Simple reservoir mask: 35 - 55%
Partial rebreather mask: 40 - 60%
Non-rebreathing: 80%
Venturi: 60%
HFNC: 100%
What are the acceptable limits for BP in both centrifugal (MAP) and pulsatile (SBP & DBP) LVAD?
Centrifugal: keep MAP between 70 - 90 mmHg
Pulsatile: SBP < 200 mmHg and DBP < 115 mmHg
What are the two types of NIV?
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP -- positive pressure applied to a spontaneously breathing patient)
Bi Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP -- allows for IPAP and EPAP, provides positive pressure breaths and improves hypoxemia and hypercapnia as well as improves oxygenation by increasing FRC and enhancing alveolar recruitment)
Out of both artificial airways, which tracheal airway is more mobile and therefore more conducive for movement?
Tracheostomy
In stable patients, what is the SpO2 cut off for activity?
85%
The one you've been waiting for!
What is the FITTOP for compensated HF patients?
Partial credit for Aerobic, Resistance, and IMT
Aerobic:
- F: 2 - 5 days/week
- I: 65 - 85% of max HR
- T: 5 - 10 mins (progress to 30 mins)
- T: continuous or interval
Resistance
- F: 2 days/week
- I: 40 - 70% 1 RM (1 - 2 sets/day of 10 - 15 reps)
- T: 12 - 20 minutes
IMT
- F: 3 times/day
- I: 20% of MIP
- T: 5 - 15 minutes
What are the oxygen flow rates corresponding to the oxygen delivery systems? (partial credit available -> 6 possible oxygen delivery systems)
Low Flow: < 8 L/min
Simple Reservoir Mask: 10 L/min
Partial Rebreather: 10 L/min
Non-rebreathing: 15 L/min
Venturi: 15 L/min
HFNC: 60 L/min
What is the FITTOP for LVAD patients?
Aerobic
- F: 3 - 5 days/week
- I: 60 - 80% HRR (if a-fib = RPE 11 - 14)
- T: 30 - 60 mins/day
- T: early mobilization to treadmill/cycling
Resistance
- F: 1 - 2 days/week (nonconsecutive)
- I: 40 - 50% 1 RM (progress to 70%)
2 sets of 10 - 15 reps
IMT
- F: 3 times/day
- I: 20% of MIP- T: 5 - 15 mins
What are two ventilator settings that indicate severe hypoxemia at rest and are considered critical values?
FiO2 > 60% and PEEP > 10 cmH2O (both are CONTRAINDICATIONS for moving the patient)