Your patient weighs 220lb, what is the poundage setting you should use to treat lumbar facet dysfunction for their 3rd treatment with traction?
Answer: 110lb (50%)
Resource: Physio-u
Your patient presents with knee swelling status post meniscus repair, what type of kinesio tape technique would you use?
Answer: Fan technique
Resource: Physio-u
Upon assessment of your patient prior to e-stim use you notice that they are slightly confused, relating to their medical history of dementia. Why is e-stim a precaution for this patient?
Answer: They may not understand the level of intensity required if motor responses are desired, which could result in agitation
Resource: Beherns pg 479
Name an indication for use of a high gain setting with biofeedback.
Answer: turning muscles “off” that are hyperactive, keep muscles “off” that are compensating during movements
Resource: Physio-u
Which medication with a negative polarity will most likely be prescribed with iontophoresis for management of lateral epicondylitis symptoms?
Answer: Dexamethasone, Salicylate
What adverse effect could happen if we increase the poundage in traction beyond the recommended settings?
Answer: Muscle guarding
Resource: Beherns pg 174
The treatment plan indicates to use kinesio taping to inhibit an overactive gastrocnemius. How would the PTA apply the tape, considering tape direction and stretch?
Answer: Insertion to origin with 10% stretch; dorsiflexion and knee extension during application
Resource: Physio-u
Name the pulse frequency, pulse duration, and sensation needed to activate the endogenous opiate system with TENS.
Answer: 200-300 us, 1-10 pps, muscle twitch
Resource: Beherns pg 400
Name an indication for use of a low gain setting with biofeedback.
Answer: Desired muscle activation
Resource: Physio-u
Which electrode should be placed at the site of injury when the patient has swelling, and why?
Answer: Negative electrode since it will repel the negatively charged plasma
Resource: A&R video
Your patient weighs 250lb, what is the initial poundage used in treating lumbar muscle spasm?
Answer: 30-45 lb
Resource: Physio-u
The treatment plan indicates use of kinesio taping to facilitate dorsiflexion during gait training. How would the PTA apply the tape, considering tape direction and stretch?
Answer: Origin to insertion with 25-50% stretch, foot in plantarflexion during application
Resource: Physio-u
Which type of e-stim will provide the BEST and longest lasting pain relief for a meniscus injury?
Answer: Low-rate Interferential current
Resource: Beherns pg 433
The treatment plan indicates neuromuscular electrical stimulation for swelling management status post R femoral ORIF 2 weeks ago. MD orders indicate WBAT. What setting would be most appropriate?
Answer: 35-80 pps, 200-300 µs, 1:1 duty cycle, for 20 minutes
Resource: Resource: Beherns pg 344
Daily double: (1) Which modalities are contraindicated with a patient that has Raynaud’s? (2) What modalities can be used in its substitution?
Answer: (1) Cryotherapy (2) Depends… what pathology and symptom are we treating?
Resource: Beherns pg 466
You are performing cross friction massage to your patient’s healed achilles tendon repair surgery scar. What are the specifics of the technique that need to be considered and why?
Answer: Dorsiflexion (stretched tissue), medial-lateral (perpendicular) strokes, 2-3 strokes/second, 5-20 minutes. Why - improper technique will not address the adhesions and tissues will remain tight
Resource: Beherns pg 238
Daily double: (1) What type of current is seen in the photo? (2) Which types of e-stim use this type of current?
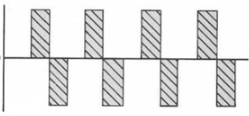
Answer: (1) pulsed biphasic (symmetrical/balanced) current (2) TENS & NMES (FES)
Resource: Beherns pg 278
Why is obesity a precaution for electrical stimulation?
Answer: May not be tolerated well; increased levels of intensity are required because adipose is a poor conductor.
Resource: Beherns pg 481
Why is biofeedback contraindicated with a recent fracture in the area?
Answer: Contraction of muscles could disrupt the healing process
Resource: Physio-u
Which modalities can be used to increase passive range of motion?
Answer: STM, Thermotherapy, continuous ultrasound, (TENS/IFC if limited by pain and not tissue elasticity)
Resource: The entire book
Why is a hiatal hernia a contraindication for lumbar traction?
Answer: Pressure from the harness increases abdominal pressure.
Resource: Beherns pg 473
In what order are nerves stimulated as amplitude increases with e-stim?
Answer: A-beta, motor, A-delta, C-fibers, Denervated muscles
Resource: Beherns pg 282
Explain the type of current used in IFC, including the current felt by the patient.
Answer: 2 medium frequency currents interfere with each other and result in a beat frequency, which is felt by the patient
Resource: Beherns pg 433
Why is an electrical implant contraindicated with use of neuromuscular electrical stimulation?
Answer: Current may interfere with the function of implanted devices.
Resource: Beherns pg 481
Which modalities can be used to decrease pain?
Answer: Basically all of them, some depending on how you use them. Biofeedback? STM?
Resource: The entire book