What are three of the six basic forms of communication and their definitions?
a. Intrapersonal communication: within a person’s own mind, through thinking & internal dialogue.
b. Interpersonal communication: between 2-3 people & typically concerns the creation, maintenance, or disillusion of personal relationships.
c. Group communication: among a small group of people—particularly teams—& is often focused on the completion of a task.
d. Organizational communication: within & between large in-stitutions & their members.
e. Mass communication: through media of many kinds, including television, film, & social or print media, & is transmitted to large audiences.
f. Public communication: between a speaker (or speakers) & an audience with the aim of engaging that audience on a topic of shared concern about the public interest. Public communication is always done within a public setting.
What are the five components of a good introduction?
a. Attention getter
b. Thesis statement
c. Relevance statement
d. Credibility statement
e. Preview of points.
What does it mean to generalize your experience in a speech?
a. Assume own experience in world has been same as everyone else’s.
b. When we make assumptions about audience or use phrases like, “We have all seen...” or “everyone knows...” we are generalizing our experience.
c. In doing so, we are extinguishing someone else’s experience & disinviting them from speech
What’s the difference between a toast & a eulogy?
a. Toast: a very brief speech made with a raised beverage in which the speaker celebrates an accomplishment or gathering.
b. Eulogy: a speech in celebration of the life of the deceased.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement is a single, declarative sentence in which the speaker makes the central, overarching argument of their entire speech
What’s the difference between a primary & minor goal in a speech?
a. Minor goals: small, targeted tasks to achieve over course of a speech to improve effectiveness
b. Primary goals: single, focused, overarching achievement to attain by end of speech to be successful - All speeches have primary goal to persuade
What is the primacy principle?
States that whichever point or idea in your speech is the strongest or most important should go first
What is ethnocentrism?
a. Belief that one’s own culture is superior to others
b. When a speaker denigrates another culture or people & praises their own
c. The active belief that there is only one right way to live in the world & an active intolerance of others’ differing worldviews & experiences
What makes public deliberation different from a policy or informative speech?
a. Public Deliberation focused on speaker being neutral & fairly presenting different perspectives/values/solutions
b. Policy Speech, speaker chooses a “side” & advocates for a policy solution
What are the three artistic proofs?
Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Provide two of the four specific primary goals, all of which have persuasive intent.
a. To persuade audience to learn important information about a new topic
b. To persuade audience to consider perspectives other than their own
c. To persuade audience to adopt a solution to a public problem advocated for by the speaker
d. To persuade audience to value the life & experiences of another person
List & briefly define two common ordering patterns for speeches.
a. Chronological: ordering your main points by time, step, or process
b. Spatial: ordering your main points by location, juxtaposition, or hierarchy
c. Circular: ordering your main points as proceeding through a cycle or by returning to the beginning
d. Narrative: ordering your main points as a story
Name two strategies for speaking across difference.
a. Listen to criticism, admit mistakes, and grow
b. Use inclusive language
c. Speak for yourself & invite others to speak
d. Take up less time & space
e. Be open-minded
f. Be self-reflective
g. Ask questions but do your work first
Define a wicked problem & give an example.
Problems that have no technical solutions, primarily because they involve competing underlying values & paradoxes that require either tough choices between opposing goods or innovative ideas that can transcend the inherent tensions
Name and define one type of inartistic proof.
a.. Definition-established meaning & interpretation of a term
b. Testimony-Public statements made by a witness
c. Statistics-significant sets of data
d. Laws, Contracts, Oaths-Binding agreements & documents
e. Precedent-previous occurrence to justify similar event
f. Narratives-story that exemplifies a point
What is the difference between morals & ethics?
a. Both are guidelines for determining acceptable & unacceptable conduct in life—what is “good”/“bad”
b. Morals = personal & consistent principles that individuals use to determine what is good & bad
c. Ethics = socially-defined expectation of good & bad behavior, which are almost always variable by context
What’s the difference between a preparation outline & a keyword outline?
a. Preparation: complete accounting of all info in speech, in full & complete sentences-helps speaker prepare text & practice
b. Keyword: abbreviated version of prep outline that includes key words, phrases, ideas, & evidence that can jog speaker’s mind & facilitates truly extemporaneous delivery
Define metaphor & explain how it supports clarity & eloquence.
a. A comparison between two things with similar qualities to explain or simplify one of those things
b. B/c often used to explain something complex, can be key to clarity & eloquence i. when used numerous times in speech or form foundation to speech, more likely for eloquence rather than clarity
What is the purpose of a commencement address?
longer speeches that celebrate the educational attainment of a group of students
Name and define a logical fallacy
a. Ad Hominem - attacks a person instead of challenging the person’s argument
b. Bandwagon - something should be done just because it is popular
c. Slippery Slope - a small & reasonable step will inevitably lead to the most severe & outlandish outcome
d. What-about-ism - attempts to avoid criticism by suggesting the critic is actually just as guilty or wrong as the speaker…
e. False Dilemma - present two options to the audience as their only possible choices when, in reality, there are many actual choices the audience could make
f. False Cause - perverting the reasoning of cause-effect relationships - claims that just because one event happened prior to another event, the first event must have directly caused the second event
g. Hasty Generalization - pervert the logic of induction to advance an unethical claim - make sweeping claims based on one or too few examples
h. Red Herring - introduces information or ideas into an argument to confuse or distract from the information that actually matters
i. Strawman - intentionally mischaracterizes the position of their opponent & then attacks their opponent for that position
What is a demagogue?
A speaker who appeals to popular prejudices rather than reason & argument… excel at using public speaking to whip a crowd into a frenzy, fueling people’s worst instincts & using their rage, anger, & resentment to achieve their own political or personal ends
Name and define one of the four types of plagiarism. How can you avoid plagiarism?
a. Global: taking a complete work
b. Incremental: taking short line/small amount from a work w/o appropriately citing
c. Patchwork: taking statements/ideas from many different works & combining them w/o citing
d. Self: unauthorized reuse of own work
*AVOID BY USING QUOTE/PARAPHRASE INDICATORS & CITING
What are two stylistic choices associated with speaking for inclusion & affirmation?
a. Avoid Offensive Terms, Names, & Phrases
b. Avoid Social Justice Elitism- packing speech with selective, complex, & unexplained terms about social justice
c. Use Gender-Neutral Language
d. Use Ability-Inclusive Language- avoid ableist language
e. Use Community-Preferred Terminology
f. Use Preferred Names & Pronouns
What are the five characteristics of a public deliberation speech?
a. Choose a controversial problem
b. Be audience-focused
c. Be the honest broker
d. Use multiple perspective ordering patterns
e. Use appropriate language
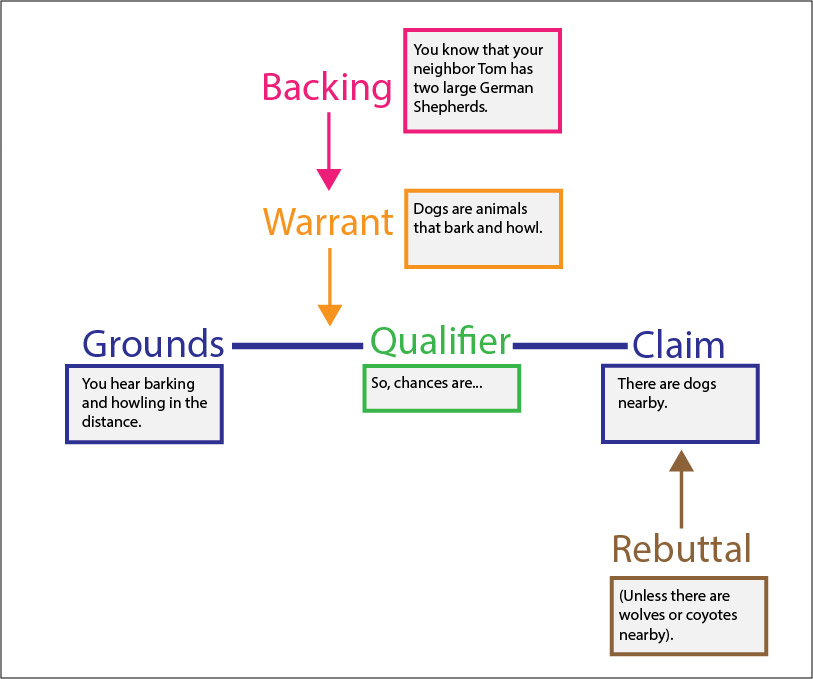
Name the primary & secondary components of the Toulmin Model (6 parts)