The process of moving air in and out of the alveoli.
What is ventilation?

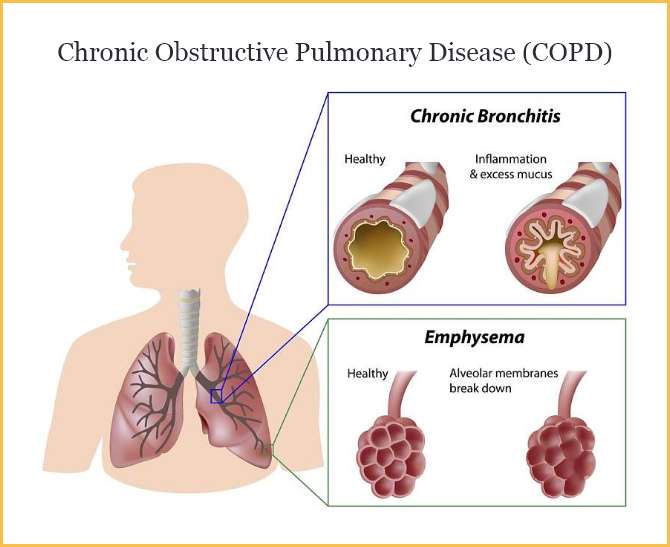
A common lung condition caused by an inflammatory reaction in the lungs, most commonly caused by cigarette smoke.
What is COPD?

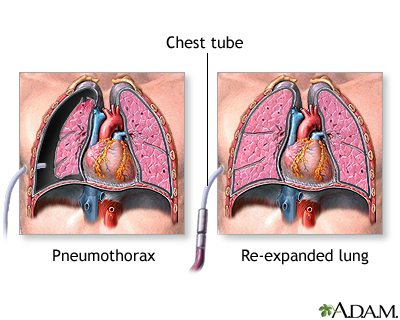
A collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity between the chest wall and the lung.
What is a pneumothorax?
A common childhood condition in which a person's airways become inflamed, narrow and swell, and produce extra mucus, making it difficult to breathe.
What is asthma?

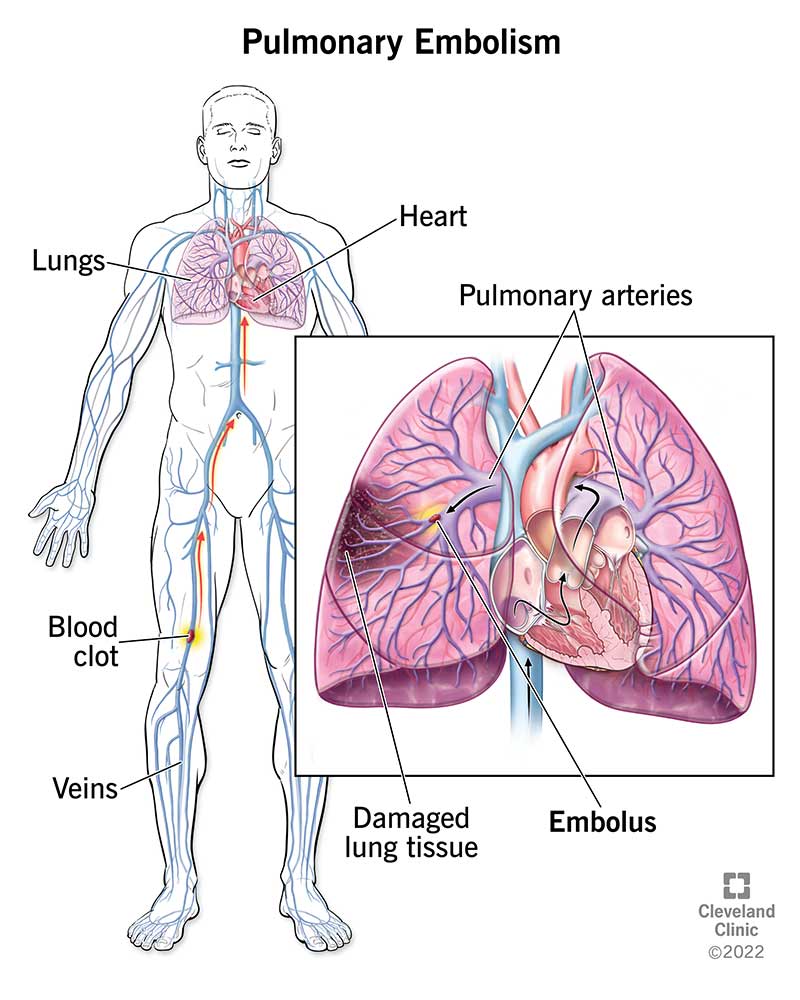
Blockage of a main artery in the lung or one of its branches by a substance that has traveled through the bloodstream.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
The delivery of blood through the pulmonary vasculature that surrounds the alveoli.
What is perfusion?

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is an umbrella term used to refer to these two diseases.
What is emphysema and chronic bronchitis?
Spontaneous rupture of a congenital bleb, bullous emphysema, chest trauma, or a complication of a medical treatment (such as insertion of a central IV line, ventilation, CPR).
What are the causes of a tension pneumothorax?

The increased tendency for the airway to have bronchospasms is usually in response to an allergen or irritant.
What are "triggers"?
![]()
This condition is usually caused by blood clots, but can also be caused by these.
What are air, fat, or amniotic fluid?

Inhaled oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
What is the work of a healthy lung?

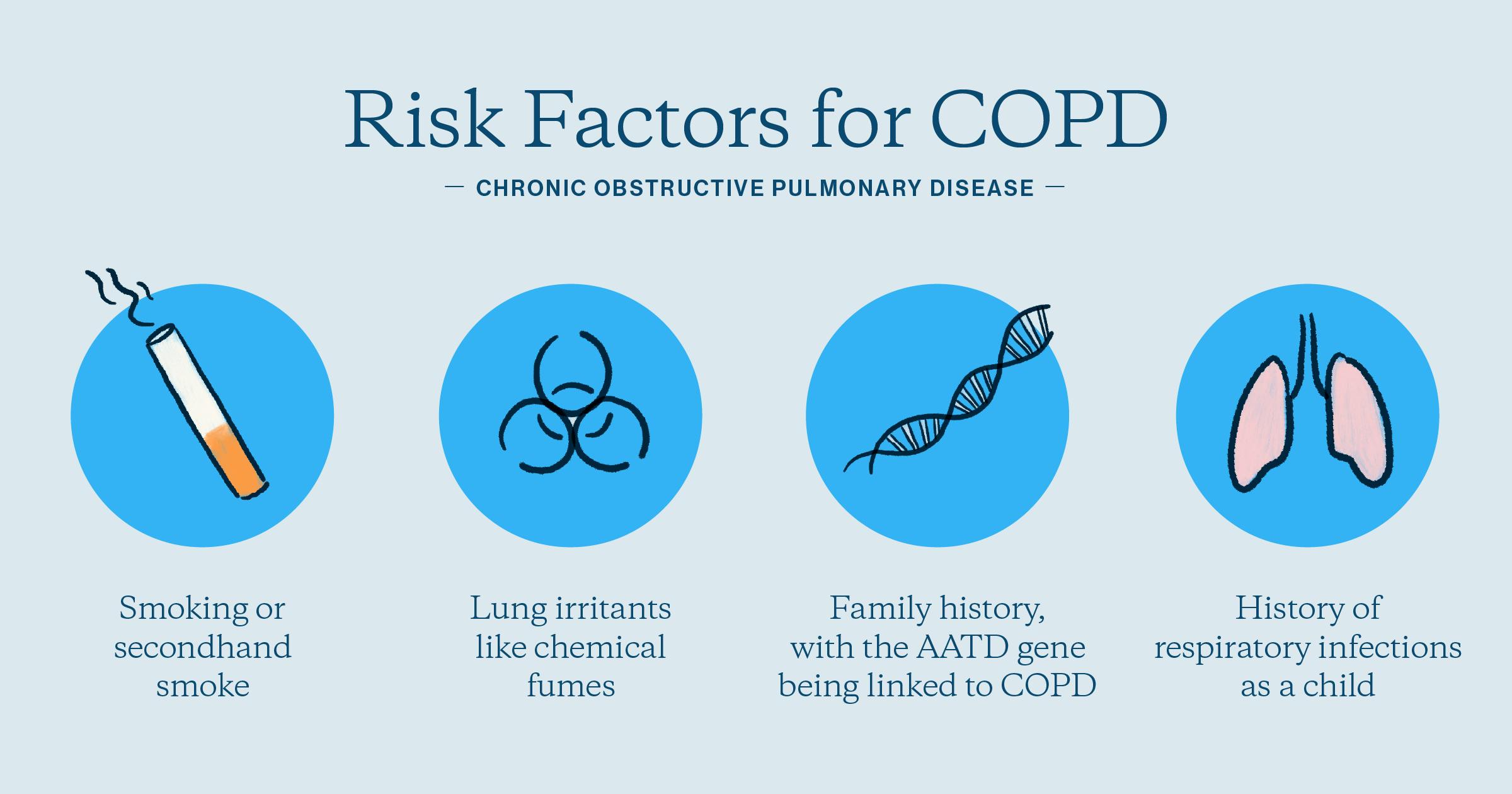
Risk factors for COPD.
What are cigarette smoking, age, genetic factors, air pollution, occupational exposures, respiratory infections, and asthma?
The accumulation of infected fluid in the pleural cavity.
What is empyema?

Although mainly caused by environmental and genetic factors that are not completely understood, a few risk factors stand out.
What is history of atopic disease, obesity, GERD, maternal tobacco use during pregnancy and after delivery, and poor air quality.
BHR: Bronchial hyper responsiveness
BPD: Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
ACOS: Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome

Risk factors for this condition.
What are COPD, CHF, Hypercoagulable states, Hypertension, Heavy cigarette smoking, Age, Race (black), Surgery, Major medical illness, immobility, air travel, cancer and some cancer treatments, central lines, pregnancy, oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, and obesity?

A by-product of cellular metabolism.
What is carbon dioxide?

Hand-held screening tool for COPD.
What is spirometry?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/200531_color1-5bbe0d94c9e77c00510969af.png)
This condition is commonly caused by bacterial infection or pneumonia, but may also be caused by this.
What is trauma or surgery in the chest area?

Medications that are used to treat asthma.
What are short acting beta agonist (Albuterol, Levalbuterol); Anticholinergics (Atrovent, Spiriva); Inhaled Corticosteroids (Pulmacort, Flovent); Combination inhalers (Advair, Symbicort); Theophylline; and Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist (Singulair, Accolate)?

Risk during air travel can be reduced be these things.
What is adequate hydration, seated leg exercises, wear compression socks, and walking as much as possible during the flight?

Most diseases of the lung affect one or the other, producing a mis-match.
What is ventilation and perfusion?

Measurements that can be used as a screening, and to stage COPD,
What is FVC, FEV1, and FEV percentage?

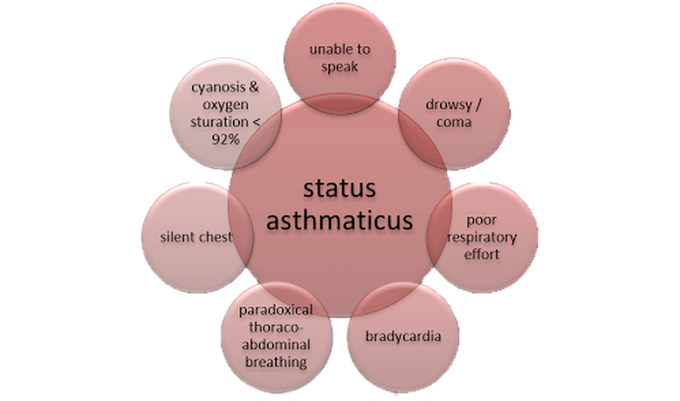
An acute asthma attack that does not respond to the usual therapy of bronchodilators and steroids. Without emergency intervention, this condition can lead to respiratory and cardiac arrest.
What is status asthmaticus?