Physiological conditions that shift oxyhemoglobin curve to the right.
What is acute acidosis, hypercapnia, and increased temp.?
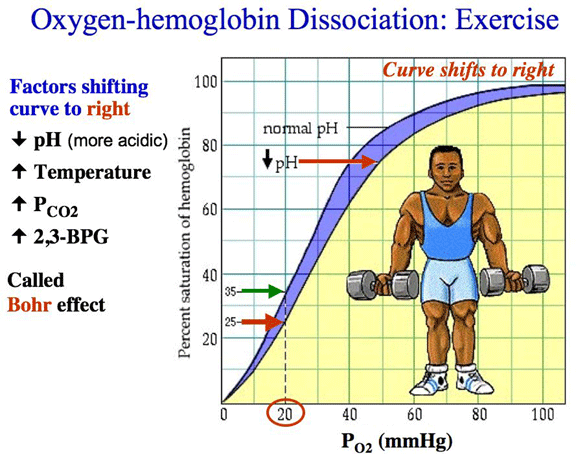
https://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Exercise%20Phys/oxygenhemoglobin.html
There are mechanical changes in the older adult's lung and chest wall, that are considered a normal part of the aging process; name those changes?
Chest wall compliance decreases (ribs become ossified (less flexible) & joints become stiffer. As a result, the chest wall loses some of its ability to expand and decreases elastic recoil of the lungs.
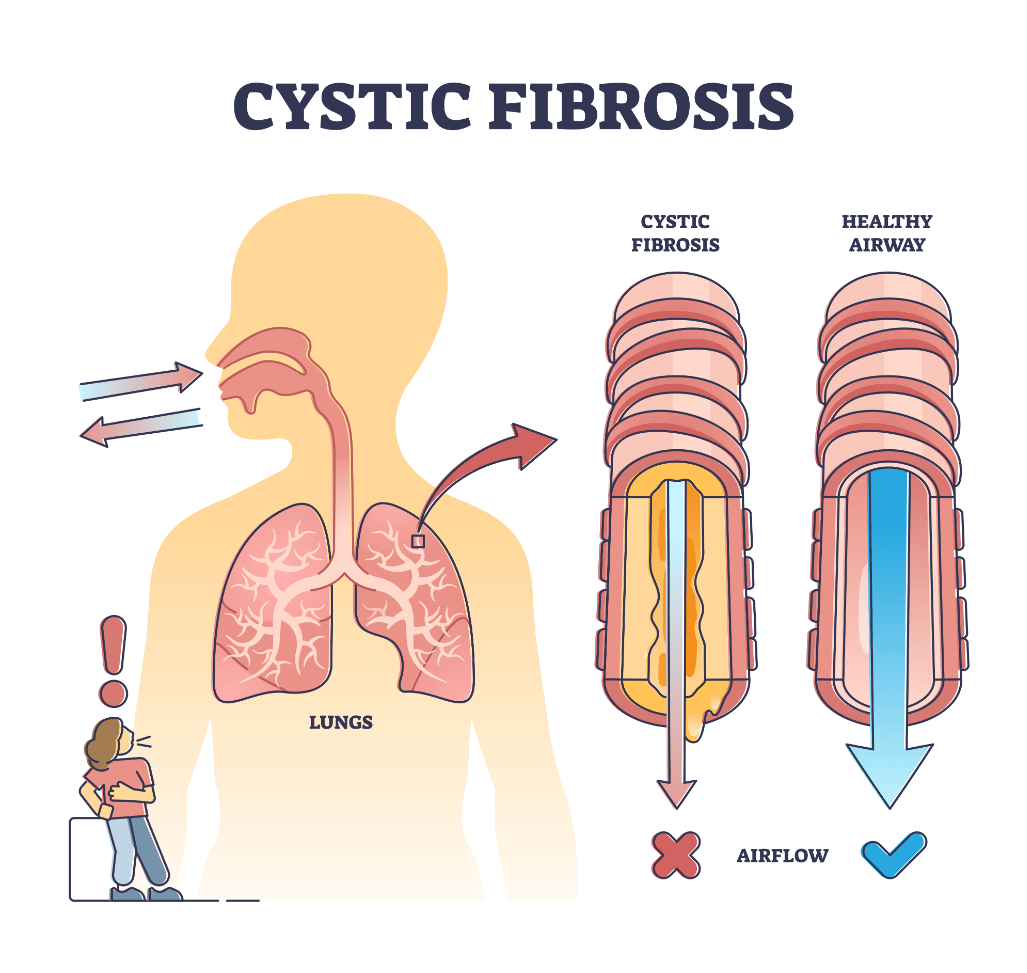
Autosomal recessive multiorgan disease that affects the lungs, causing thick, dehydrated mucus secretions. The condition causes respiratory failure and is almost always the cause of death. Name this disease.
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
________ is excess fluid in the lung which develops when these protective mechanisms are disrupted. Predisposing factors for this condition include heart disease, lung capillary injury, and processes that block the lymphatic vessels. Name this condition.
What is Pulmonary edema?
Type II cells secret _______ which reduce surface tension in the alveoli, preventing them from collapsing during exhalation.
What is Surfactant?
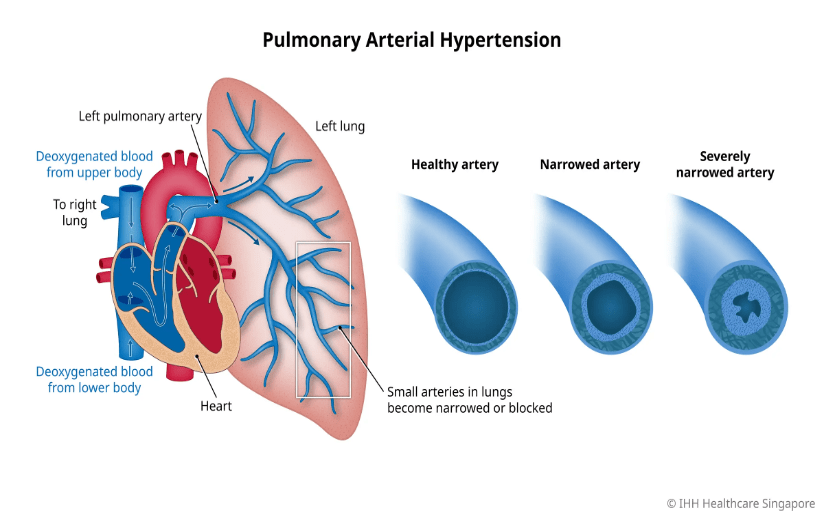
Endothelial dysfunction and overproduction of vasoconstrictors. Inflammation leads to fibrosis and vascular remodeling (changes in the layers of the blood vessel). What is this called?
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Characterized by endothelial dysfunction with overproduction of vasoconstrictors, decreased production of vasodilators and inflammation and can be associated with right ventricular hypertrophy and left heart disease.
What is Pulmonary Hypertension?
With aging, ___________ receptors become less sensitive to gas partial pressures.
What are Chemoreceptors?
Upper respiratory infection with subglottic inflammation (edema) in the larynx causing inspiratory stridor and a harsh, seal-like barky cough.
Other S/S: rhinorrhea, sore throat, low grade fever.
What is Croup?
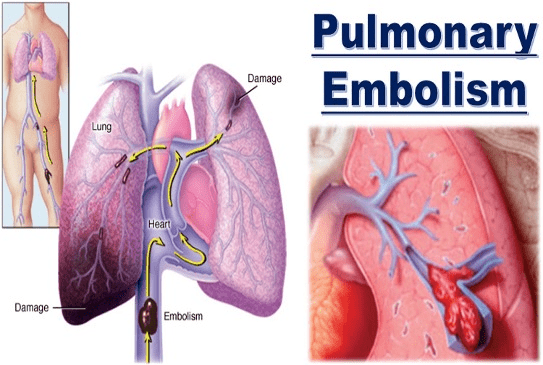
Patients who present with dyspnea and unilateral leg swelling may have this type of pulmonary disorder.
What is Pulmonary Emboli?
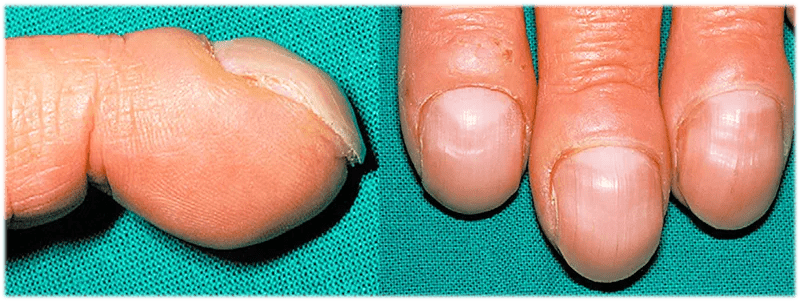
The exact cause of __________ is unknown.
In individuals with chronic hypoxemia, some suggest that decreased oxygen causes the release of vascular endothelial growth factor, which promotes proliferation of the connective tissue between the nail matrix and the distal phalanx. What is this condition?
What is clubbing?
Occlusion of the pulmonary vasculature causing vasoconstriction that impairs blood flow. What is this called?
Pulmonary Embolism
As air is inhaled into the lungs, the process of gasses with a higher concentration, moving into an area of lower concentration gradient is called what?
"Diffusion"
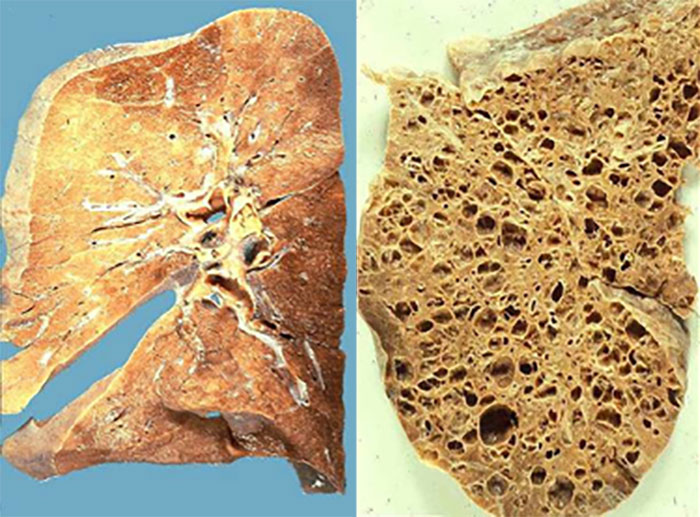
This condition is usually found in older adults, it causes destruction of elastin and loss of passive elastic recoil, leading to obstruction of gas flow during expiration and air trapping. What is this condition?
"Emphysema"
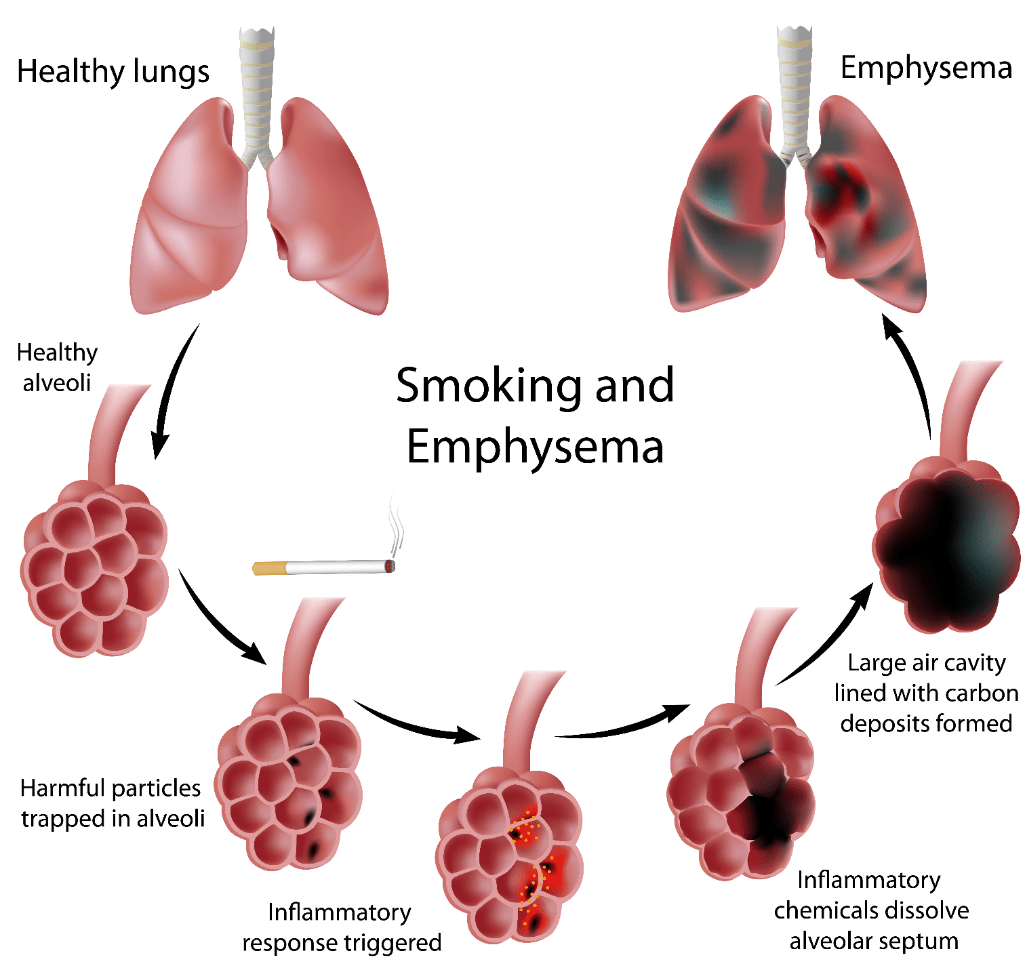
The pathologic changes of ____ occur in large central airways, small peripheral airways, and the lung parenchyma.
What is COPD?
Any disorder that involves reduced diaphragm movement can lead to what CO2 problem?
What is Hypercapnea ?
If the diaphragm is not functioning, carbon dioxide (CO2) builds up.
Summary causes of Hypercapnia (Decreased minute ventilation)
CNS
- Drugs affecting respiratory drive, eg. opiates
- Brainstem or cortical lesion affecting consciousness
- Central sleep apnea
- Spinal cord injury
Neuromuscular
- Neuropathy, eg. Guillain-Barre
- NMJ disorder, eg. Myasthenia gravis
- Myopathy
Respiratory
- Decreased lung compliance, eg. pulmonary edema
- Decreased chest wall compliance, eg. kyphosis or obesity
- Increased airway resistance, eg. COPD or asthma
Pink skin, pursed lip breathing, accessory muscle use, tachypnea, cachexia. Name this condition.
What is emphysema?

The work it takes to expand the lungs. What do we all this?
Compliance
(Poor/decreased lung compliance increases the work of breathing and affects the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood)
This is an abnormal structural finding with the alveolus that causes the blood to be poorly oxygenated, what is this called?
"Shunt"

Vital capacity decreases, and residual volume increases with age; however, ___________ remains unchanged.
What is: Total lung capacity?
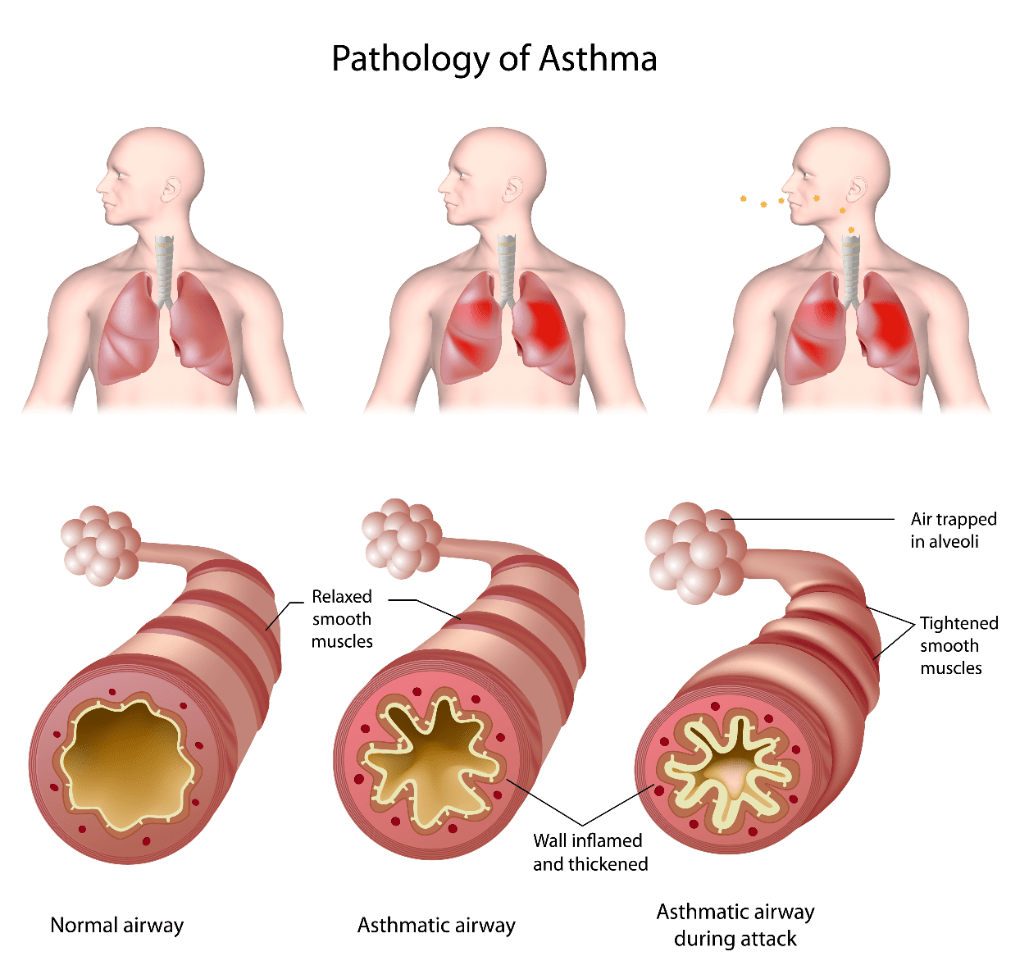
_______ is a heterogenous disease, usually characterized by chronic airway inflammation. It is defined by the history of respiratory symptoms, such as wheeze, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and cough that vary over time and in intensity, together with variable expiratory airflow limitation. Name this disease.
What is Asthma?
Young children are susceptible to an inflammatory infection called Bronchiolitis caused by a virus, what is the name of this virus?
What is Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
The primary function of the pulmonary system is the exchange of gases between the environmental air and the blood. The three steps in this process are: ___________
What are:
(1) ventilation, the movement of air into and out of the lungs
(2) diffusion, the movement of gases between air spaces in the lungs and the bloodstream
(3) perfusion, the movement of blood into the capillary beds of the lungs and out to body organs and tissues.
The first two functions are carried out by the pulmonary system, and the third by the cardiovascular system.
Increased rate and rhythm, hypocapnia, respiratory alkalosis. What do we call this?
Hyperventilation
A patient that is lethargic with RR of 8, has ABG lab values: pH-7.3, HCO3-27 mEq/L, CO2 - 58 mm Hg. What would this patient's ABG diagnosis be?
"Respiratory acidosis"
This condition is typically found in older adults. The lung becomes stiff and difficult to ventilate, and the diffusing capacity of the alveolocapillary membrane may decrease, causing hypoxia. What is this condition?
"Pulmonary Fibrosis"
Pathophysiological changes that can occur in endothelium layer of the Pulmonary Artery, due to disease processes like Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension is called what?
"Vascular remodeling"
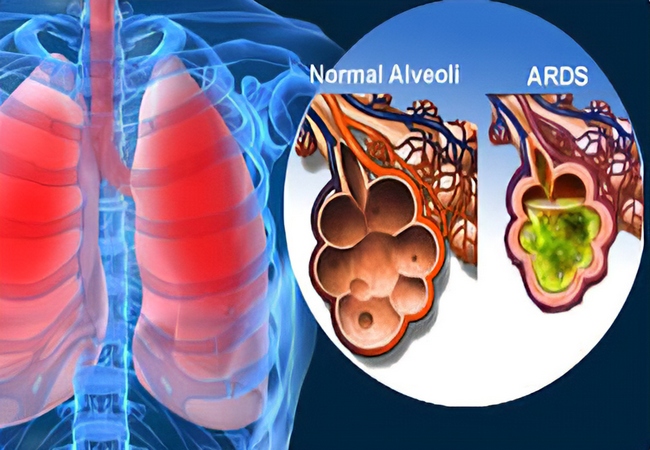
A serious condition that causes inflammation, diffused alveolocapillary injury, fluid build up inside of the alveoli, and prevents gas exchange. What is this called?
"Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome" (ARDS)
Important part of being able to determine a patient's respiratory condition is by evaluating their ABG lab results. This requires that you know 3 specific lab results and their normal ranges. What are these labs and what is their normal range?
Ph: 7.35 to 7.45
PCo2: 35 to 45 mm Hg
HCO3-: 22 to 26 mEqL
This is a type of pulmonary disease that requires more force to expire volume of air, what type is this?
"Obstructive"