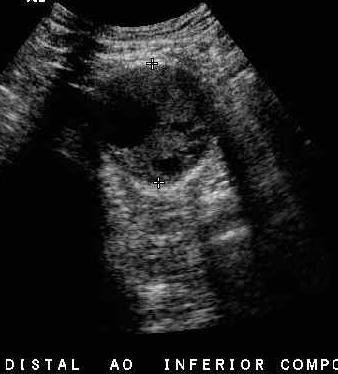
 60yo male with vague abdominal pain x4mos
60yo male with vague abdominal pain x4mos
What is AAA
Tidal volume setting in ARDS
what is 4-6mL/kg of ideal body wt.
HRCT showing basal-predominant fibrosis with traction bronchiectasis and honeycombing, but no marked inflammation, is most consistent with this pattern.
What is UIP?
This type of shock is characterized by low cardiac output and high SVR.
What is cardiogenic shock?
A patient with HIV and CD4 <200 presents with bilateral ground-glass opacities. This pathogen must be ruled out.
A patient with HIV and CD4 <200 presents with bilateral ground-glass opacities. This pathogen must be ruled out.
 What is shown here?
What is shown here?
What is collapsing IVC
The ventilator shows double triggering with two stacked breaths. This usually indicates that this set parameter is too low.
What is tidal volume, will also accept inspiratory time.
What is respiratory bronchiolitis-associated ILD (RB-ILD)?
This measurement, obtained from a pulmonary artery catheter, reflects LV preload and helps differentiate cardiogenic vs distributive shock.
What is pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)?
Patients with prolonged neutropenia are at high risk for pulmonary infections with this filamentous fungus known for “halo signs” on CT.
What is Aspergillus?

What is this pathology?
What is a large pericardial effusion with tamponade?
What does the green ventilator waveform indicate? 
What is Autopeep
This ILD presents with erythema nodosum, uveitis, arthralgias, and bilateral hilar adenopathy.
What is Lofgren syndrome (acute sarcoidosis)?
A low CVP, low wedge, and high cardiac output suggests this diagnosis.
What is septic shock?
his fungal disease, endemic to the Southwest US, can cause diffuse pulmonary nodules, meningitis, and severe disease in patients with impaired cell-mediated immunity.
What is Coccidioidomycosis?
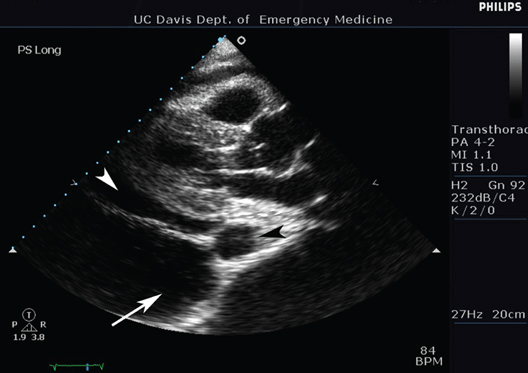
Describe what each arrow is pointing to.
White arrowhead: pericardial effusion
Black arrowhead: descending aorta
White arrow: pleural effusion
Name 2 conditions that could cause high peak pressures with a normal or low plateau pressure.
What is bronchoconstriction, tube kinking or plugging, or patient biting ETT?
This occupational ILD shows upper-lobe predominant nodules and "eggshell" calcification of the lymph nodes.
What is silicosis?
Diastolic collapse of this chamber is suggestive of tamponade?
Right ventricle

What is this fungus?
What is mucormysosi?
Non-septate branching at 90 degree angles
 The finding in this CCU patient with a new murmur on post STEMI day 3.
The finding in this CCU patient with a new murmur on post STEMI day 3.
What is ventricular wall rupture.
A sudden drop in tidal volume on pressure-control mode suggest this problem.
What is an air leak?
This connective tissue disorder causes cysts, spontaneous pneumothorax, and characteristic skin lesions called fibrofolliculomas.
What is Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome?
A patient with acute RV failure may benefit from increasing this ventilator parameter down, not up.
What is PEEP?
A patient with HIV and CD4 <100 has headache, fever, and pulmonary infiltrates. Serum cryptococcal antigen is positive.What diagnostic test should you perform next?
What is lumbar puncture?
To assess for cryptococcal meningitis