All of the statements below regarding infections with Legionella are correct except
A. Hospitals that care for patients at risk for Legionella infections should know if their potable water systems contain Legionella.
B. Human-to-human transmission is the major mechanism of transmission of Legionella infection.
C. Legionella species can be visualized with Gram-stain if carbolfuchsin is used for the counter stain.
D. The chest radiograph of a patient who has Legionella pneumonia is indistinguishable from that of patients with pneumonia caused by other pathogens.
E. A macrolide or quinolone are the drugs of first choice for treatment of Legionella infections.
B. Human-to-human transmission is the major mechanism of transmission of Legionella infection.
A 60-year-old man has a 5-month history of progressive weakness and a weight loss of 13 kg along with intermittent fever, chills, and a chronic cough productive of yellow sputum, occasionally streaked with blood. A sputum specimen is obtained, and numerous acid-fast bacteria are seen on the smear. Culture of the sputum is positive for M. tuberculosis. Which treatment regimen is most appropriate for initial therapy?
A. Isoniazid and rifampin
B. Sulfamethoxazole–trimethoprim and streptomycin
C. Isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol
D. Isoniazid, cycloserine, and ciprofloxacin
E. Rifampin and streptomycin
C. Isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol
An adult who has never smoked or been around cigarette smoke is unlikely to have which of the following diseases?
A. Adenocarcinoma of the lung
B. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
C. Mature carcinoid tumor
D. Small cell carcinoma of the lung
E. (B) and (D)
A. Adenocarcinoma of the lung
A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of fatigue and weight loss over the past 2 months. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 33 years. She cans some of her own foods. On physical examination, she has mild ptosis of the right eyelid. The right pupil is 1 mm, and the left is 3 mm in diameter. The skin is dry. The extremity examination is significant for motor weakness in the right hand and atrophy of its muscles.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Bell palsy
B. Botulism
C. Lambert-Eaton syndrome
D. Myasthenia gravis
E. Pancoast tumor
F. Superior vena cava syndrome
E. Pancoast tumor
An 8-year-old boy, who recently arrived in the United States, develops a severe sore throat. On examination, a grayish exudate (pseudomembrane) is seen over the tonsils and pharynx. The differential diagnosis of severe pharyngitis such as this includes group A streptococcal infection, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, Neisseria gonorrhoeae pharyngitis, and diphtheria. The cause of the boy’s pharyngitis is most likely:
A. A Gram-negative bacillus
B. A single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus
C. A catalase-positive, Gram-positive coccus that grows in clusters
D. A club-shaped Gram-positive bacillus
E. A double-stranded RNA virus
D. A club-shaped Gram-positive bacillus
Humans become infected with L. pneumophila by
A. Kissing a person who is a legionella carrier
B. Breathing aerosols from environmental water sources
C. Receiving a mosquito bite
D. Consuming undercooked pork
B. Breathing aerosols from environmental water sources
A 30-year-old woman is taking over-the-counter diphenhydramine for severe hay fever. Which of the following adverse effects is she most likely to report?
A. Muscarinic increase in bladder tone
B. Nausea
C. Nervousness, anxiety
D. Sedation
E. Vertigo
D. Sedation
A 45-year-old man with a history of chronic sinusitis presents to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of hemoptysis and dyspnea on exertion. He also reports weight loss of 7 kg (15.5 lb), decreased urine output, and malaise over the past 2 months. On physical examination, the patient appears ill and has bloody nasal discharge with crusting. Crackles are heard in both lungs. Laboratory results show a serum creatinine of 2 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows hematuria and proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
B. IgA vasculitis
C. Polyarteritis nodosa
D. Small cell lung cancer
E. Thromboangiitis obliterans
A. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Oral medications are popular for the treatment of asthma in children because young children may have difficulty with the proper use of aerosol inhalers. Which of the following is an orally active inhibitor of leukotriene receptors?
A. Albuterol
B. Aminophylline
C. Ipratropium
D. Tezepelumab
E. Zafirlukast
F. Zileuton
E. Zafirlukast
Which of the following is not a recognized virulence factor of B. pertussis?
A. Heat-labile toxin
B. Filamentous hemagglutinin
C. Tracheal cytotoxin
D. Pertussis toxin
E. Dermonecrotic toxin
A. Heat-labile toxin
A 10-year-old child has a primary pulmonary M. tuberculosis infection. Which of the following features of tuberculosis is most correct?
A. In primary tuberculosis, an active exudative lesion develops and rapidly spreads to lymphatics and regional lymph nodes.
B. The exudative lesion of primary tuberculosis often heals slowly.
C. If tuberculosis develops years later, it is a result of another exposure to M. tuberculosis.
D. In primary tuberculosis, all of the infecting M. tuberculosis organisms are killed by the patient’s immune response.
E. In primary tuberculosis, the immune system is primed, but the PPD skin test result remains negative until there is a second exposure to M. tuberculosis.
A. In primary tuberculosis, an active exudative lesion develops and rapidly spreads to lymphatics and regional lymph nodes.
A 60-year-old man has a 5-month history of progressive weakness and a weight loss of 13 kg along with intermittent fever, chills, and a chronic cough productive of yellow sputum, occasionally streaked with blood. A sputum specimen is obtained, and numerous acid-fast bacteria are seen on the smear. Culture of the sputum is positive for M. tuberculosis.
If the patient’s M. tuberculosis isolate proves to be resistant to isoniazid, the likely mechanism for resistance is
A. β-Lactamase
B. Mutations in the catalase-peroxidase gene
C. Alterations in the β subunit of RNA polymerase
D. Mutations in the DNA gyrase gene
E. Mutations in the genes encoding the S12 protein and 16S rRNA
B. Mutations in the catalase-peroxidase gene
A 55-year-old man is hospitalized because of increasing bilateral leg weakness over the past 3 weeks. He reports difficulty getting in and out of chairs and that walking up a flight of stairs is especially difficult. After he walks for a short period, the strength seems to return to his legs. More recently, he notices a dry mouth and that he chokes when trying to drink a glass of water quickly. His past medical history is unremarkable except for a 30-year history of smoking 2 packs of cigarettes/day. On examination, he has mild proximal muscle weakness in the legs. Reflexes are 1+. After being asked to walk up and down the hallway several times, the muscle strength is improved, and the reflexes are 2 to 3+.
Which of the following diseases is associated with this patient’s most likely diagnosis?
A. Pituitary adenoma
B. Renal cell carcinoma
C. Small cell lung carcinoma
D. Squamous cell lung carcinoma
E. Thymoma
C. Small cell lung carcinoma
A 76-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of high fever, shortness of breath, cough, diarrhea, and malaise. He has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes per day for the past 40 years. Temperature is 40°C (104°F) and respirations are 28/min. The sputum Gram stain is negative. A silver-stain micrograph from the patient’s sputum is shown.

Image courtesy of CDC/Dr. William Cherry
Which of the following organisms is the most likely causal agent?
A. Coccidioides immitis
B. Haemophilus influenzae type B
C. Legionella pneumophila
D. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
E. Streptococcus pneumoniae
C. Legionella pneumophila
A 37-year-old man with AIDS, currently living in Indianapolis, Indiana, presented with osteomyelitis of the left hip. A needle biopsy of the bone marrow was obtained, and the calcofluor white smear revealed a variety of myelogenous cells, monocytes, and macrophages containing numerous intracellular yeast cells that were elliptical and approximately 2 × 4 µm. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Blastomycosis
B. Candidiasis
C. Cryptococcosis
D. Histoplasmosis
E. No diagnostic significance
D. Histoplasmosis
An 8-year-old boy, who recently arrived in the United States, develops a severe sore throat. On examination, a grayish exudate (pseudomembrane) is seen over the tonsils and pharynx. The differential diagnosis of severe pharyngitis such as this includes group A streptococcal infection, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, Neisseria gonorrhoeaepharyngitis, and diphtheria.
The primary mechanism in the pathogenesis of the boy’s disease is
A. A net increase in intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate
B. Action of pyrogenic exotoxin (a superantigen)
C. Inactivation of acetylcholine esterase
D. Action of enterotoxin A
E. Inactivation of elongation factor 2
E. Inactivation of elongation factor 2
A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after suffering seizures resulting from an overdose of a drug he has been taking. His friends state that he took the drug orally and sometimes had insomnia after taking it. Which of the following is a direct bronchodilator that is most often used in asthma by the oral route and is capable of causing insomnia and seizures?
A. Cromolyn
B. Epinephrine
C. Ipratropium
D. Metaproterenol
E. Metoprolol
F. Prednisone
G. Salmeterol
H. Theophylline
I. Zileuton
H. Theophylline
A 55-year-old man comes to his primary care physician because of a 2-month history of cough, left shoulder pain, and hoarseness. On ocular examination, the right pupil is larger than the left, (as shown in the photograph). The patient has no smoking history. A CT scan of the chest reveals a 3-cm nodule in one lung.
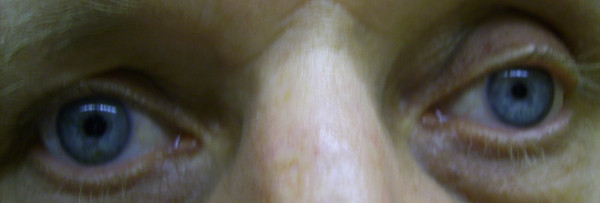
Which of the following is the most likely type and location of this patient’s tumor?
A. Adenocarcinoma in the apex of the right lung
B. Adenocarcinoma located in the apex of the left lung
C. Small cell carcinoma located in the apex of the right lung
D. Small cell carcinoma located in the hilum of the left lung
E. Squamous cell carcinoma located in the apex of the right lung
F. Squamous cell carcinoma located in the hilum of the left lung
B. Adenocarcinoma located in the apex of the left lung
A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of 1 month of left flank pain that radiates to the groin and intermittent productive cough for 4 months. He has smoked cigarettes since age 20. Urinalysis shows hematuria. X-ray of the chest is shown. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level is normal.
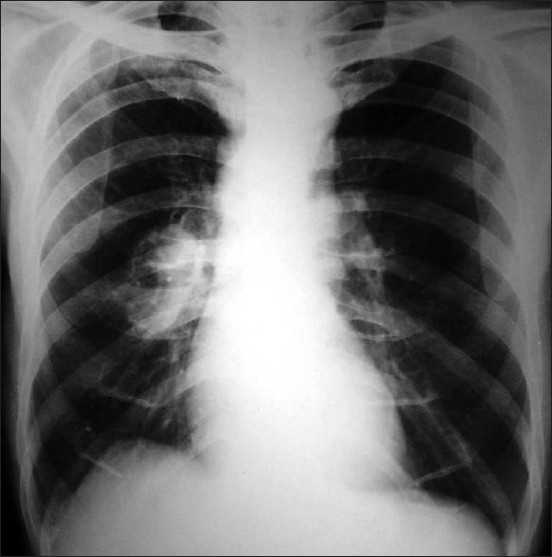
Copyright © Lung India
Which of the following abnormalities most likely led to this patient’s hematuria?
A. High vitamin D levels
B. Hypercalciuria
C. Metastatic cancer to the kidney
D. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
E. Multiple endocrine neoplasia
B. Hypercalciuria
Which statement about blastomycosis is correct?
A. Similar to other endemic mycoses, this infection occurs equally in men and women.
B. Infection starts in the skin, and the organisms commonly disseminate to the lungs, bone, genitourinary tract, or other sites.
C. The disease is endemic to certain areas of South America.
D. In tissue, one finds large, thick-walled, single budding yeast cells with broad connections between the parent yeast and bud.
E. All cases require treatment with amphotericin B.
D. In tissue, one finds large, thick-walled, single budding yeast cells with broad connections between the parent yeast and bud.
Three months ago, a 53-year-old woman had surgery and chemotherapy for breast cancer. Four weeks ago, she developed a cough occasionally productive of purulent sputum. About 2 weeks ago, she noted a slight but progressive weakness of her left arm and leg. On chest examination, rales were heard over the left upper back when the patient breathed deeply. Neurologic examination confirmed weakness of the left arm and leg. Chest radiography showed a left upper lobe infiltrate. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography showed two lesions in the right hemisphere. Gram-stain of a purulent sputum specimen showed branching Gram-positive rods that were partially acid fast.
The drug of choice to treat this patient’s infection is
A. Penicillin G
B. Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole
C. Gentamicin
D. Amphotericin B
E. A third-generation cephalosporin
B. Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole
Which of the following in its parenteral form is lifesaving in severe status asthmaticus and acts, in part, by inhibiting phospholipase A2?
A. Aminophylline
B. Cromolyn
C. Epinephrine
D. Ipratropium
E. Metaproterenol
F. Metoprolol
G. Prednisone
H. Salmeterol
I. Zafirlukast
J. Zileuton
G. Prednisone
A 74-year-old man comes to his primary care physician because of a 2-month history of right shoulder pain that travels down the middle of his forearm and into his fourth and fifth fingers. He also reports an unintentional 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss. He has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and a 50-pack-year history of smoking. The examination shows dullness to percussion and decreased breath sounds at the right lung apex. There is atrophy of the intrinsic muscles of the right hand, decreased grip strength, and diminished triceps reflex. There is a narrowed right palpebral fissure. X-ray of the chest shows a right apical opacity.
Which of the following additional physical examination findings would most likely be present in this patient?
A. Asymmetric pupils
B. Facial droop
C. Inability to adduct the right eye when abducting the left
D. Polyuria and polydipsia
A. Asymmetric pupils
A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with fever, chills, body aches, and coughing. She reports feeling ill for the past 20 hours and that her symptoms have been worsening. Past medical history is unremarkable, but she notes that several of her officemates have been sick with similar symptoms. She is found to have a fever of 101.5°F and diffuse rhonchi throughout her lungs. A rapid influenza test comes back positive for influenza A.
Which oral drug is most likely to be prescribed at this time?
A. Amantadine
B. Oseltamivir
C. Peramivir
D. Ritonavir
E. Zanamivir
B. Oseltamivir
Explanation: Zanamivir (intranasal) and peramivir (IV) would be effective but are not orally administered. Amantadine is effective but resistance is high. The answer is B.
A 2-month-old infant developed a respiratory illness that the pediatrician diagnosed as bronchiolitis. The most likely cause of the disease is
A. Parainfluenza virus type 4
B. Respiratory syncytial virus
C. Influenza virus
D. Coronovirus
E. Bordetella Purtussis
B. Respiratory syncytial virus