FEV1/FVC ratio indicative of obstructive lung disease?
What is <0.70 or <70%?
Disease often presents with Eggshell calcification of the hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes
What is silicosis?
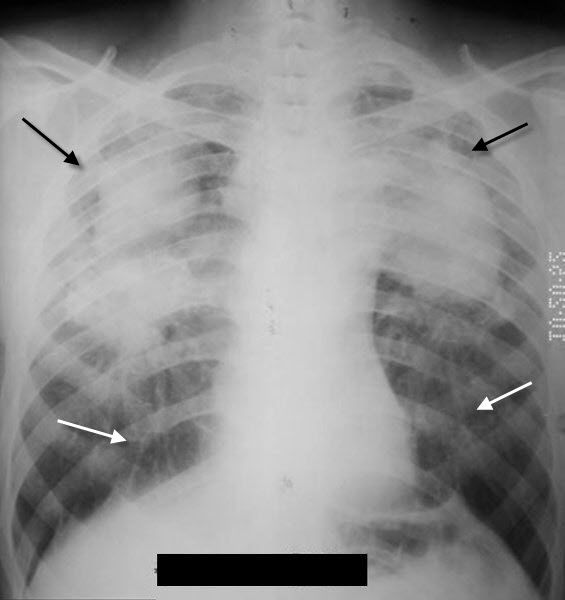
Characteristic X-ray finding laryngotracheobronchitis.
What is steeple sign?
This lab is performed to rule out a pulmonary embolism in a patient with a low-moderate likelihood for PE
What is a D-dimer?
In a background of sepsis, syndrome of dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia, refractory hypoxemia
What is Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?

Obstructive lung disease leading to right-sided heart failure with peripheral edema, hepatomegaly, inc JVP
What is Cor Pulmonale?
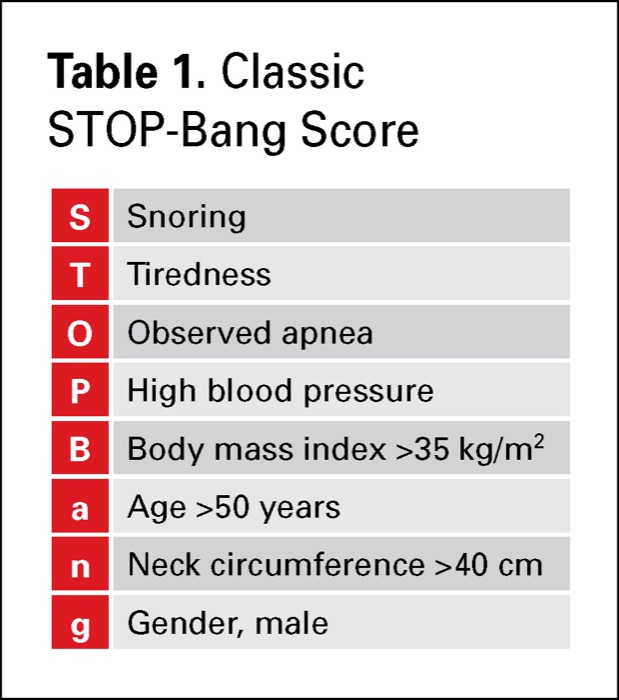
Criteria for assessment of obstructive sleep apnea
What is STOP-BANG criteria?
Inflammatory marker used to help in differentiating bacterial and viral pneumonias
What is procalcitonin?
First line treatment for hemodynamically stable patient with Pulmonary Embolism
What is anticoagulation (Lovenox/Enoxaparin)?
80 year old male patient with 40 pack-year cigarette smoking history presented with weight loss over the past few months. CXR and subsequent CT chest showed spiculated hilar mass.
What is lung cancer?
A 27-year-old woman presents to your office with a chronic cough, productive of foul smelling purulent sputum for the last year. She denies having fevers, but admits to occasional episodes of hemoptysis. She has been diagnosed and treated multiple times for pneumonia, without significant improvement. On chest x-ray you note dilated, thickened airways.
What is bronchiectasis?
In restrictive lung diseases, FEV1 and FVC are reducted to ____
What is <80% predicted?
Normal Chest X-ray following positive PPD/Quantiferon testing.
What is latent tuberculosis?
Current gold standard for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism
What is CTA chest?
Two risk factors for foreign body aspiration.
What are altered mental status (AMS) and alcoholism?
Per GOLD criteria, if FEV1 30-49% predicted
What is GOLD 3?

Patient with dyspnea, unproductive cough, fatigue & rash presents to the clinic. The X-ray shows bilateral hilar adenopathy and the histopathology shows noncaseating granulomas.
What is sarcoidosis?
Treatment for patient with positive PPD and active cavitation on chest x-ray.
What is Isoniazid + Rifampin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol for 2 months followed by Isoniazid + Rifampin for 4 months?

Per Well's criteria, a score of ___ confers high risk of pulmonary embolism
What is Well's score of >6?
Lung cancer present at apex of lung causing shoulder pain and upper arm swelling
What is pancoast tumor?

Treatment for a patient with COPD who has had >2 moderate exacerbations OR >1 exacerbation leading to hospitalization and CAT score <10
What is a LAMA? (Group C)

This lung disease can present with small upper lobe nodules and cause Caplan's syndrome when associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
What is Coal worker's pneumoconiosis (black lung disease)?
People in which pneumococcal vaccine is indicated (TWO GROUPS)
What is >65 year olds OR what is <65 year old with history of heart disease, pulmonary disease, alcoholic cirrhosis, SCD, asplenia
Pulmonary hypertension is defined as mean pulmonary arterial pressure of ______ Mm Hg at rest.
What is 20mm Hg at rest?
Top 3 clinical settings for 75% of ARDS cases.
What are sepsis, severe multitrauma, aspiration?