What must happen to the particles in the middle beaker for the substance to change into the state shown in the beaker on the left?

The water is beginning to boil in an iron pot on the stovetop. Compare the particle motion of the water particles to the motion of the iron particles?
As the temperature increases, the water particles slide past each other faster, and the iron particles vibrate in place faster.
Elements form in a fixed ratio. What does that mean?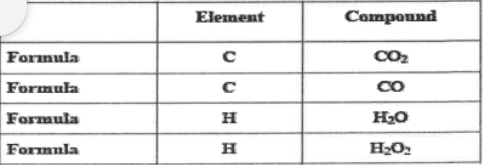
The number of elements and the formation of elements in a compound.
Milk of magnesia is a liquid people drink when they have an upset stomach. What occurs when you drink the milk of magnesia?
It raises the pH in your stomach.
How would you describe the air in our atmosphere? Is it a mixture or a compound? Support your answer with a rationale (explanation).
Mixture (rationales may vary)
What happens to the distance of the particles of a liquid when heat energy is removed from them?
They decrease (get closer together)
Which of these choices is a physical property?
reactivity
flammability
melting point
corrosiveness
melting point
Each of the following is a compound except which one. Explain your answer.
Cl
NaCl
H20
Cl
Which one of these is not a pure substance and give an example.
Mixture
Element
Molecule
Compound
Mixture
Salt and Water (NaCl and H20)
Which image(s) are pure substance(s)?
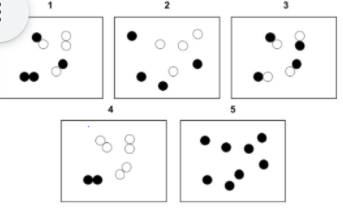
3 and 5
How does the behavior of particles in a solid prevent it from moving from place to place?
They are closely packed together and have little empty space between them allowing them only to vibrate.
Which of these physical properties would be most helpful for Sal to determine the identity of a liquid?
the color
the boiling point
the volume
the mass
Its boiling point.
The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas is its...
Boiling point
Why is oxygen classified as a pure substance and air is classified as a mixture?
Oxygen contains only one substance, but air contains several gasses (Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, etc.).
What are the major differences between mixtures and compounds?
Mixtures are physically combined and compounds are chemically combined. A mixture can be physically separated, but a compound cannot.
How would you describe the shape and level of energy in the empty B part of the Venn Diagram?
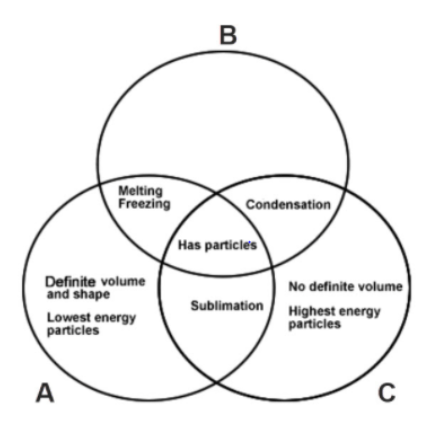
Liquid: No definite shape and medium energy particles
Why is the state of matter considered a physical property?
The chemical nature of the substance does not change. Liquid H20 becomes Solid Ice H20
An unknown solution has a pH of less than 7. Is this substance an acid or a base?
It is an acid.
What is the difference between a heterogeneous mixture and a homogeneous mixture?
A homogeneous mixture is uniform throughout the substance, making it difficult to separate. A heterogeneous mixture has layers making it easy to separate.
What might be a limitation of a scientific model?
Models are not able to correctly represent a system in all respects.
In what states of matter are particles constantly moving?
All three states (solid, liquid and gas).
Looking at the illustrations from left to right, label the models?
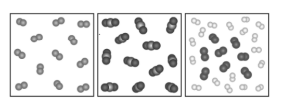
Elements, compounds, and mixtures.
Salt dissolves, but pepper does not. Why is this?
Salt has solubility in water.
Give an example of a mixture that is a solution, and a mixture that is not? Which one is heterogeneous, and which one is homogeneous?
Answers may vary.
Why should a scientist perform repeated trials of their experiment?
To reduce the effect of errors and thus increase the reliability of the results of an experiment.