The basic functional units of all living organisms.
Cells
What is the function of the skeletal system?
support and structure
Where does digestion begin?
The Mouth
What is the main function of the respiratory system?
To exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide)
What organ pumps blood through your body?
Heart
What organ in your skin helps you get rid of waste through sweat
Skin
Your heart is made up of different types of tissues working together. What level of organization is the heart?
Organ
Are bones living tissue?
YES!
In the digestive system, what organ is primarily responsible for absorbing nutrients from food?
Small Intestine
What gas is removed from the body by the lungs?
Carbon dioxide
What color is our blood when it's inside of our bodies?
Dark red (not blue).
What liquid waste do your kidneys produce?
Urine
What type of muscle is responsible for pumping blood through your body?
Cardiac muscle
What type of joint allows your arm to swing in a circle?
Ball-and-socket joint
What is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius?
1 calorie
What is the name of the plant tissue that carries water upward
Xylem
What is the function of a Nephron?and where do you find nephrons in the human body
To filter blood, Kidneys
What is the main function of the nervous system?
To control and coordinate bodily functions.
Which level of organization is more complex: tissues or organs?
Organs
Which of the body systems is responsible for contracting and allowing movement in the body.
Muscular System
What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion
Mechanical digestion is physical breakdown (chewing,chuning), chemical digestion is breakdown by enzymes/acids.
What parts of the respiratory system make up the throat?
Pharynx, Larynx, and Trachea (upper portion)
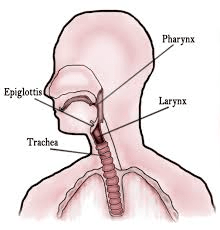
What does your heart rate tell you about your body?
How quickly your heart is pumping blood, beats per minutes
What are the basic building blocks of the nervous system
Neurons
A group of organs that work together to perform major bodily functions.
Organ System
Which type of muscle do you consciously control to move your arms and legs?
Skeletal muscle
What is the purpose of villi in the small intestine?
To increase the surface area for nutrient absorption into the bloodstream
Write a definition for Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What are the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart called?
Arteries
Name three major organ systems contribute to the overall process of excretion in the human body?
Urinary system, respiratory system, digestive and integumentary (skin) system.
What type of tissue is found in your stomach walls?
Smooth Muscle
What type of joint is located at the base of your thumb?
Saddle Joint
What organ produces bile?
Liver
What are vascular tissues?
Tissues in plants that transport water and nutrients (xylem and phloem).
How fast is blood circulated around the body?
About 20 seconds
What is the main function of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
To connect the Central Nervous System (CNS) to the rest of the body.
When a scientist studies a group of cells under a microscope that all perform the same function, what level of organization are they observing?
Tissue
If you hold a weight in your hand, what type of muscle are you using, and is it voluntary or involuntary? How do you know?
Skeletal muscle, which is voluntary. You know because you are consciously controlling the movement.
What is the difference between a macronutrient and a micronutrient?Give examples of both
Macronutrients are needed in large amounts (carbs, proteins, fats), micronutrients are needed in small amounts (vitamins, minerals).
What process moves oxygen from your lungs to your blood?
Diffusion
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
Atria
Explain the difference between sensory neurons and motor neurons
Sensory neurons carry signals to the CNS
Motor neurons carry signals from the CNS to muscles or glands
Name an example of an organ system in the human body and list two organs that are part of it
Examples: Digestive System - stomach, intestines; Respiratory System - lungs, trachea; Circulatory System - heart, blood vessels
Imagine you are a doctor looking at an X-ray of someone's spine. What type of joints would you see between the vertebrae, and what is their main function?
Gliding joints; their main function is to allow limited sliding movement and provide flexibility.
When you swallow food, 1.what type of muscle helps move it down your esophagus, and is this 2.voluntary or involuntary? 3.What is this motion called?
Smooth muscle; involuntary. Peristalsis
Describe the functions of the Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) occurs between the air and the blood.
Write a definition for Capillaries
Tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins, where gas and nutrient exchange occurs.
How does your brain remember things?
By making connections between nerves stronger.