Unprotected exposure to the sun’s rays is a factor in the development of skin cancer. Which of the following is an example of empirical evidence that supports this hypothesis? (7.N.1.6)
A) a sunscreen advertisement B) data about skin cancer C) a skin cancer survivor’s memory about a bad sunburn as a child D) a model of a skin cell showing where DNA is in the cell
B
A scientist wants to know why the honeybee population is declining. Which step would the scientist most likely to do first? (7.N.1.7)
A) Research to see if there is already a widely accepted explanation.
B) Observe the problem and make a hypothesis about what is causing it.
C) Communicate the question to as many other scientists as possible so that they can discuss it.
D) Conduct an experiment to see if increased pollution is causing a decrease in the honeybee population.
A
Which portion of visible light (ROYgBiV) has the longest wavelength? (7.P.10.1)
Red
Light travels more slowly through glass than it does through air. What happens when light passes through glass into the air? (7.P.10.2)
the light will be refracted
Would a sound wave travel fastest through a sponge, a beaker of water, the air in the room, or a wooden desk? (7.P.10.3)
wooden desk
Why is statement B an inference? (7.N.1.5)
A) The plant’s leaves are green and appear wilted.
B) The plant's leaves are wilted due to lack of water.
Claire decided to find out which wildflowers are most abundant near roadsides in her community. Which of the following would best help Claire with her investigation? (7.N.1.3)
A) observation B) making a physical model C) using a computer model D) conducting a controlled experiment
A
When Hector was at the beach, he forgot to put on sunscreen. What type of radiation from the Sun caused Hector to get sunburned? (7.P.10.1)
ultraviolet radiation
You may see something under water and reach into the water to pick it up. However, the object is not where you thought it would be. What property of light is responsible for this? (7.P.10.2)
Refraction
Would light travel fastest through air, plastic, or water? (7.P.10.3)
Air
If a scientist makes a new discovery, other scientists review and ______________ the results before the discovery can be published.
What is replicate?
According to the Rate of Carrot Growth with Growfast Fertilizer graph below, what is the BEST amount of fertilizer to use to grow carrots the fastest?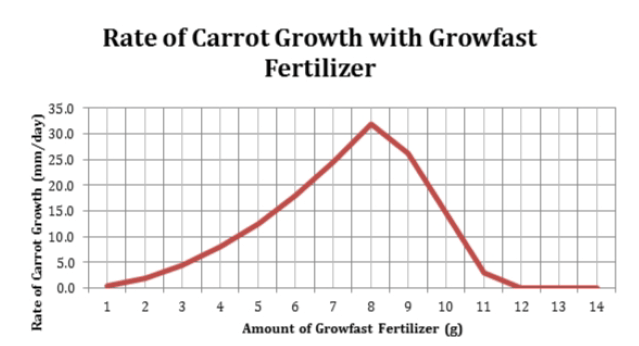
8 grams
Arrange the types of energy listed below from longest to shortest wavelength. (7.P.10.1)
infrared, visible light, ultraviolet
infrared, visible light, ultraviolet
Label the features #1, 2, and 3 of the wave in the illustration below. (7.P.10.1)
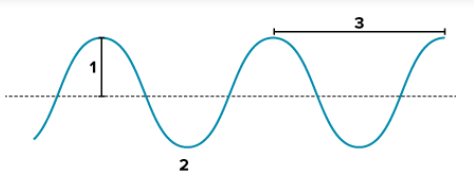
1. amplitude 2. trough 3. wavelength
The speed of _____ is slower in water than in air because _____. (7.P.10.3)
The speed of light is slower in water than in air because the molecules are closer together.
A scientist conducted an experiment to determine how the amount of salt in a body of water affects the number of aquatic plants that can live in the water. What is the outcome (dependent) variable?
Number of plants
Kodak Black wants to create a new sound for his music. He is testing new sound equipment to produce the music. His testing is informal, flexible, and does not need to follow a specific scientific method. Yet he still learns from his experience. Is this an example of an experiment or an investigation?
investigation
How is ultraviolet light different from the light emitted by a flashlight? (7.P.10.1)
Answers may vary. Accept all reasonable answers related to ultraviolet light being invisible to the human eye, ultraviolet light having a shorter wavelength/higher frequency than visible light, or ultraviolet light not being part of visible light.
When white light passes through a prism, it is separated into different colors. What is the name of this process and how does it happen? (7.P.10.1)
Refraction. The colors of light each travel at different speeds through the prism, causing them to bend and separate into the colors of the rainbow
In the desert air, sound travels at 358 meters per second (m/s). In the polar air, sound travels at 330 meters per second (m/s). What can you conclude about the relationship between the speed of sound and temperature from this information? (7.P.10.3)
as the temperature of the medium decreases, the speed of sound decreases
Jason states the following prediction: “As the air temperature increases, the air in a balloon will expand, increasing the circumference of the balloon.” What is the test variable (independent variable) AND the outcome variable (dependent variable) in Jason’s prediction?
Independent: temperature.
Dependent: balloon size.
Consider the following hypothesis: “The time it takes for sugar to dissolve in water depends on the temperature of the water.” What is the test (independent) variable for this experiment? (7.N.1.4)
the temperature of the water in which the sugar was placed
What happens to the frequency of the waves as wavelength increases across the EM spectrum (7.P.10.1)
frequency decreases
Use the terms absorb, reflect, and/or refract to explain why a green frog appears green. (7.P.10.3)
It reflects green light and absorbs all other colors. Refraction is not involved.
The graph below shows the speed of sound waves in air and water. What can you conclude from the data in this graph? (7.P.10.3)
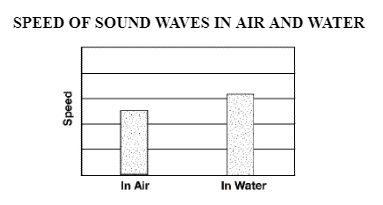
The speed of sound waves depends on the medium through which they travel.